Does your switch, range extender, or router have this address assigned to it as a default gateway? Wondering what kind of address this is? Don’t know how to use it? The following article will help you learn all you need to know about 192.168.0.2. We’ll quickly go through the basics of IP addressing, give you some general info about this IP address, discuss its purpose, and explain how to solve the most common issues related to this address.
CONTENTS
Is 192.168.0.2 Public or Private IP Address?
Like all the addresses from the 192.168.x.x block of addresses, 192.168.0.2 is a private IP address. As it is a private address, it can only be used on local area networks (or LANs) and can’t be routed over the internet.
This address can be assigned to your router or some other networking device (switch, repeater, extender), or it can be assigned to any device that you use to surf the internet and that is connected to your home network (PC, laptop, smartphone, tablet, etc.).
All the devices connected to your home network use private addresses to communicate with each other. Every device connected to your home network will have a unique IP address. The rule is – one IP address per one device. So, there can be only one device in your home using 192.168.0.2 as its address.
Your router is the device that assigns IP addresses to all the other devices. In the router’s settings, there’s something called the DHCP pool, which is a predefined pool (or scope) of available addresses – every device gets one address from this pool. The router can assign this address automatically to every device that connects to the network (dynamic IP) or you can go to your router’s settings and assign a specific address to some or all devices manually (static IP).
Similar Articles:
Your router also has a private IP address, but the router doesn’t assign this address to itself. The address is pre-assigned to the router by the manufacturer. The IP address of your router is often called the default gateway or default IP address.
Private IP address has to be unique within a single local area network, but they can be used on other LANs, too. There can be an unlimited number of devices using 192.168.0.2 (or any other private IP address) as their IP address. They just have to be on different LANs.
Private addresses are not used to access the internet. When you want to visit a website on your laptop, you send the request to the router (which is a hub of your LAN). Your laptop and your router communicate using their unique private IP addresses. When the router receives the request, it connects to the DNS server using a public address. This public address is assigned to your router by your ISP. When it gets feedback from the DNS server (through its public IP address), your router then forwards all the data to your laptop (using a private address).
Can 192.168.0.2 Be My Default Gateway?
192.168.0.2 could be your default gateway. It can be, just like any private address, assigned to any router, switch, range extender, etc. To check if this address is assigned to your router, you can check the label on your router or go through the user manual. If there’s no label and you can’t find the manual, you can easily find your default gateway on any device (Windows, Linux, macOS, Android, iOS). Here’s how:
Windows: In the Command Prompt, type in the following command: ipconfig and press enter. Look for the default gateway.
Linux: In the Terminal, type in the following command: route -n.
macOS: In the Terminal, type in the following command: netstat -nr
iOS: In the wi-fi settings, tap the letter ‘’i” and scroll down to IPv4 addresses. Your default gateway is the address standing next to ”Router”.
Android: In the wi-fi settings, tap on your wi-fi network (long tap), select Modify, and then Advanced options. Scroll down to DHCP settings, tap it, select Static, and scroll down till you find Gateway.
What Devices Use 192.168.0.2 as a Default Gateway?
As you may know, 192.168.0.1 is probably the most popular default gateway. 192.168.0.2 is much less popular. We have found just a few older devices (mostly switches and access points) using this address. The most notable brands using it are Actiontec and Belkin. Here’s the list of devices using this address as a default gateway:
Comtrend: WAP-5883, WAP-5835n (wireless access points)
Luxul: XMS-1024 (24-port smart switch)
Actiontec: HPAP108T (range extender)
Belkin: F5D8231au4 (wireless router)
How to Access Device’s Settings if the Device’s Default Gateway is 192.168.0.2?
When you know your default gateway, accessing your device’s user interface (settings dashboard) is pretty easy. Just open your browser and type in your default gateway in the address bar. Here’s how to access the settings for Luxul XMS-1024 smart switch.
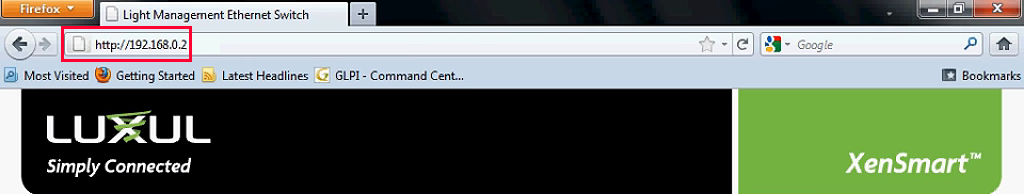
Enter the default gateway
Once you enter the address and press Enter, the login page will appear, and you’ll have to enter your credentials (username and password). The default username and password for XMS-1024 are admin/admin.
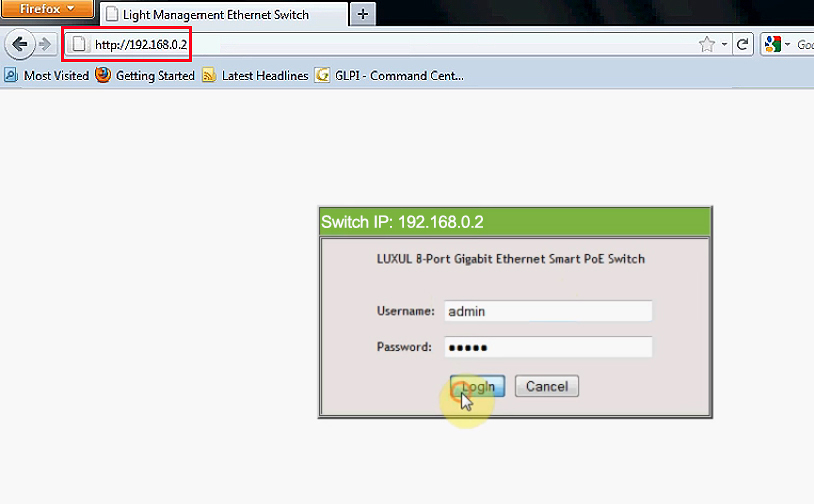
Login page – Enter your username and password
If you have changed the credentials at some point in the past, but can’t remember them now, you can only try to reset your device to factory settings. After your reset it, you can use the default username and password again.
Once you log in, the Configuration Window will open and you can start changing all kinds of settings.
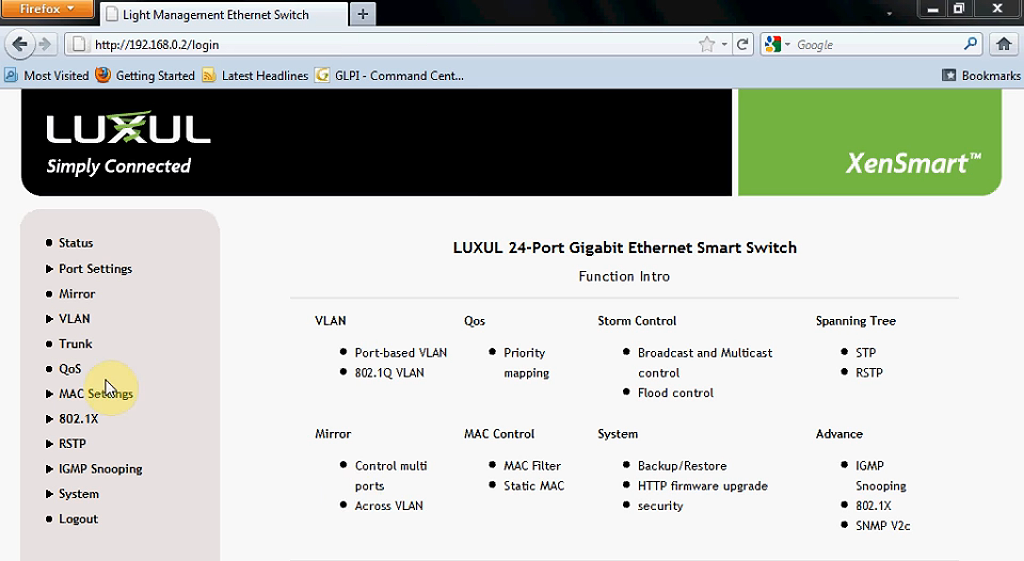
Luxul XMS-1024 configuration window
Depending on the device you’re using, this page may look different, and you will have different options to choose from.
192.168.0.2 as a Host IP Address
This address can be one of the addresses assigned to your PC, laptop, or some other device that you’re using to surf the internet (it can be a host IP address). In fact, 192.168.0.2 is far more often a host IP address than a default gateway.
As discussed in one of the previous sections, 192.168.0.1 is the most popular and most commonly used default gateway. If your router, for example, uses 192.168.0.1 as a default IP, there’s a good chance that its DHCP pool starts with 192.168.0.2.
192.168.0.2 as a Dynamic IP
As you remember, the DHCP pool is one segment of your router’s settings. It’s a scope of addresses that your router assigns to other devices. Your router will assign an IP address to every device connected to your wi-fi network automatically. If the address is assigned automatically, it is considered a dynamic IP address.
The term dynamic means that the address is assigned automatically and that your device doesn’t get to keep it forever. The router actually just leases the address to your device. When the lease time expires (you can set the duration of the lease in the settings), the router will check if the device is still connected. If it’s not connected, it will take the address back, and the address will, once again, become available. The router can now assign this address to some other device. When you connect your old device to the network, it will get some other IP address.
192.168.0.2 as a Static IP
Any of your devices can also have a static IP, but if you want your device to have a static IP, you have to assign it manually. So, you have to access the settings of your router, go to DHCP settings, and make a reservation (assign a specific IP address to your device). Depending on the router, the settings may look different, but the basic procedure is always the same.
One thing you should do before you assign some IP address to your device manually is to exclude that address from the DHCP pool. You have to shrink your DHCP pool.
For example, if your DHCP pool starts with 192.168.0.2, and you want to assign this address to your printer, you have to set 192.168.0.3 as a starting address first. If you don’t do this, you may experience some connection issues. This brings us to the last section of our article…
Troubleshooting 192.168.0.2
Problem 1 – IP Conflict
One of the most common issues is the so-called IP conflict. IP conflict is a phenomenon when two devices connected to the same LAN have the same IP address. As we have already said, every device connected to a single LAN must have a unique IP address.
So, how is this possible? How can two devices have the same IP? Well, this is usually a problem with the DHCP pool settings. If, for example, the DHCP pool starts with 192.168.0.2 and you assign this address manually to your PC (as a static IP) but don’t exclude it from the DHCP pool, the router may assign the same address to the second device connected to your network (it shouldn’t but it may). When an IP conflict happens, devices using the same IP address will not be able to access the internet or communicate with other devices on the same LAN.
To solve the issue, you have to release the IP address on both devices, go to the router’s settings, and make proper adjustments (shrink your DHCP pool to exclude the address that you want to make static).
Problem 2 – I can’t open the login page
If 192.168.0.2 is your default gateway, but you can’t access the login page, you can do two things. Check if you have entered the right address. IP addresses can be confusing – they all look very similar. One typing mistake, and you won’t be able to open the login page. If there’re no typing mistakes, then check your default gateway again using your PC. 192.168.0.2 may not be your default gateway.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.
