Wi-Fi is not anything new as it has become synonymous with internet connectivity. This wireless networking technology allows you to connect your computers, smartphones, tablets, and wearables to the internet.
It uses radio-wave frequencies to send internet signals from a modem or Wi-Fi router to your connected wireless devices.
Presently, six major Wi-Fi standards, ranging from Wi-Fi 1 to Wi-Fi 6, provide the specifications for wireless internet connectivity.
These Wi-Fi versions use either or both of the two radio-wave frequency bands, including 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, to transmit data between the connected wireless devices on your network.
This post focuses on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, dissecting how it works and why you should use it for your wireless connections.

CONTENTS
- What Exactly is 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?
- The Working Principle of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
- How Far Can 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi Reach?
- Differences Between Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz?
- How to Tell If You Have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on your Router?
- How to Tell If You Have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on your Phone?
- How to Tell If You Have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on your PC?
- How to Set Up 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on Your Phone?
- How to Switch to 2.4 GHz on Windows PC?
- How to Switch to 2.4 GHz on Your Router?
- Pros of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
- Cons of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
- Is 2.4 GHz Good for Wi-Fi?
- Should I Use 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?
What Exactly is 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi is a wireless data transmission technology that uses the old yet highly effective 2.4 GHz radio band to transfer signals between a Wi-Fi router and connected devices.
Wi-Fi technology uses radio-wave frequencies to transmit signals between a router or modem and the connected wireless devices on a network to facilitate internet access.
The two prominent radio-wave frequencies used to transfer data from your router to your wireless devices include the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz frequency bands.
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi is the first radio band to come out, and most Wi-Fi routers support this frequency band for data transmission between connected devices.
The 2.4 GHz frequency band is renowned for its broad network coverage and ability to penetrate thick walls, floors, and solid obstacles.
The frequency band has longer waves, meaning it can cover more distance. The broad network range makes the 2.4 GHz band suitable for larger homes and commercial spaces.
Recommended reading: What is Dual-Band Wi-Fi? (Dual-Band Wi-Fi Explained)
One noticeable downside with 2.4 GHz connections is that they are painstakingly slow due to the low radio-wave frequency. For this reason, the 2.4 GHz frequency is not suitable for high-bandwidth activities like online gaming and video streaming.
Since most devices like microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors use the 2.4 GHz frequency, the band is highly prone to interference, increasing the likelihood of network congestion when connecting multiple gadgets.
The Working Principle of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi works by slowly transmitting wireless signals over long distances to connected devices. It uses longer radio waves to cover more ground, effectively eliminating dead zones from your premises and ensuring better network coverage.
The 2.4 GHz band has 11 wireless channels that send and receive data within your Wi-Fi network.
Each channel on the 2.4 GHz band is 20 MHz wide with a wavelength of 0.125 meters (12.5cm), allowing the frequency to penetrate significant depths seamlessly.
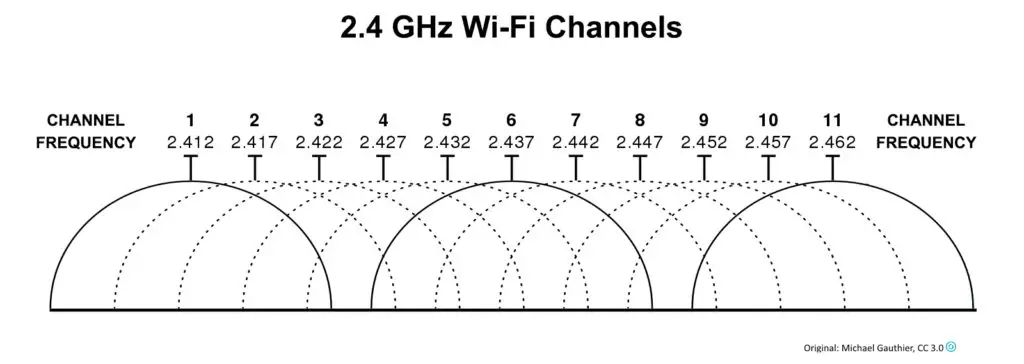
The channel width determines data throughput and link rates between the Wi-Fi router and connected devices within the network.
All the 11 wireless channels except 3 overlap each other, with channels 1, 6, and 11 the only non-overlapping channels on the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
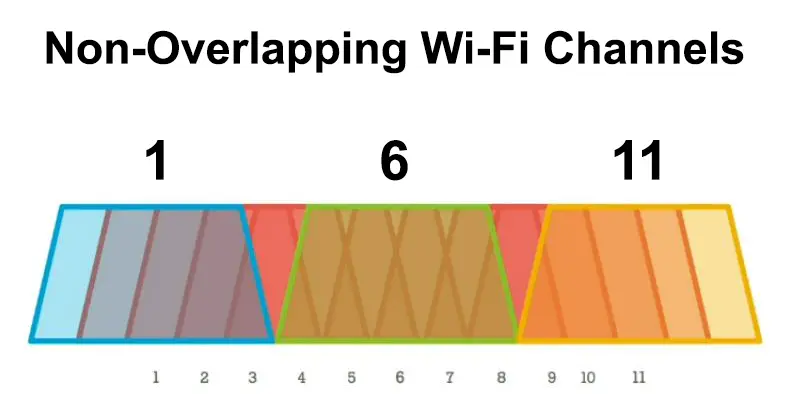
Overlapping channels are prone to network interference, so it is only logical to select the non-overlapping channels when setting up your network for better Wi-Fi performance.
Depending on the model, your router should ideally be able to select a suitable channel for your wireless devices automatically to reduce network interference.
How Far Can 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi Reach?
The 2.4 Wi-Fi band is renowned for its extensive network coverage, reaching 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors.
Even though 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi has fewer wireless channels, each channel is broader and longer than other channels on other frequency bands, meaning it has a more extended range.
The longer wavelengths allow the transmitted signals to penetrate through thick walls, floors, doors, metal frames, and other physical obstructions, effectively extending your network to far-flung corners of your space.
Recommended reading: What is VZW Wi-Fi? (Do I Want VZW Wi-Fi Calling ON or OFF?)
The antenna orientation and router model also determine how far your 2.4 GHz connection can reach. Some 2.4 GHz routers can transmit signals as far as 400 feet in open spaces.
The only critical issue with 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi is that it is prone to interference. You can connect to your wireless router from the farthest corner of the room but won’t have a pleasant Wi-Fi experience due to radio signal interference from other consumer gadgets.
Wi-Fi Interference
Differences Between Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz?
The two licensed frequency bands include 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Even though these radio bands perform the same function, they slightly differ in how they operate.
Here are the differences between Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz:
- Wi-Fi Range
The 2.4 GHz band has a more extended network range than the 5 GHz band. 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi covers 150 feet indoors and 300-400 feet in open spaces. The longer wavelengths penetrate through physical obstacles while covering more distances than 5 GHz Wi-Fi, effectively eliminating dead zones in your premises.
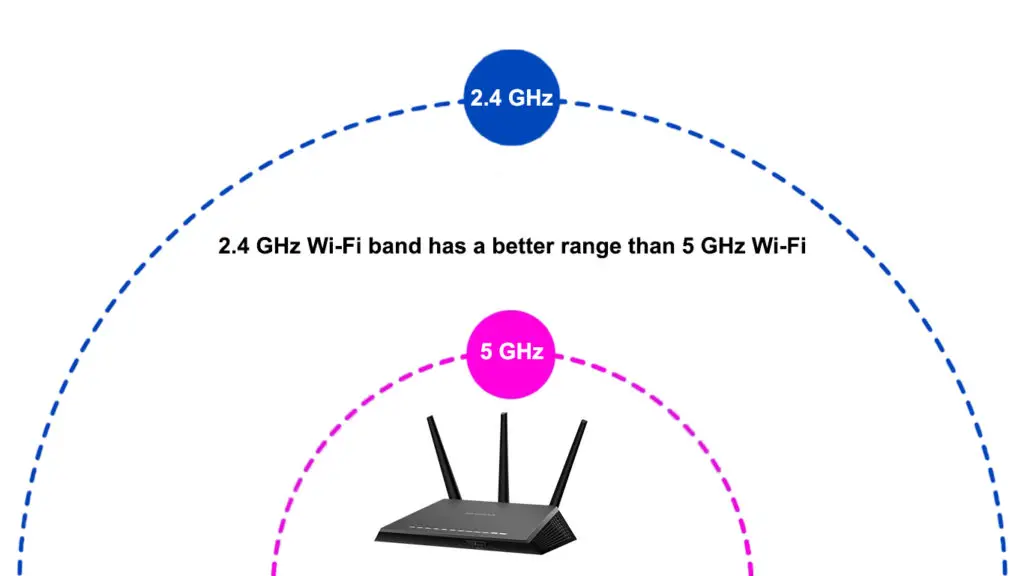
- Wi-Fi Speeds
Even though 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi has a broader network range, it is comparatively slower than 5 GHz Wi-Fi. Usable network speeds depend on the Wi-Fi standard, but they do not exceed 400 Mbps in real-world scenarios. 5 GHz Wi-Fi can surpass maximum link rates of 1,300 Mbps but over shorter distances.
- Wi-Fi Channels
The 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands use multiple Wi-Fi channels to send and receive data signals within a wireless network. The 2.4 GHz frequency band has 11 Wi-Fi channels (8 overlapping and 3 non-overlapping), while the 5 GHz band has 45 Wi-Fi channels (21 overlapping and 24 non-overlapping).
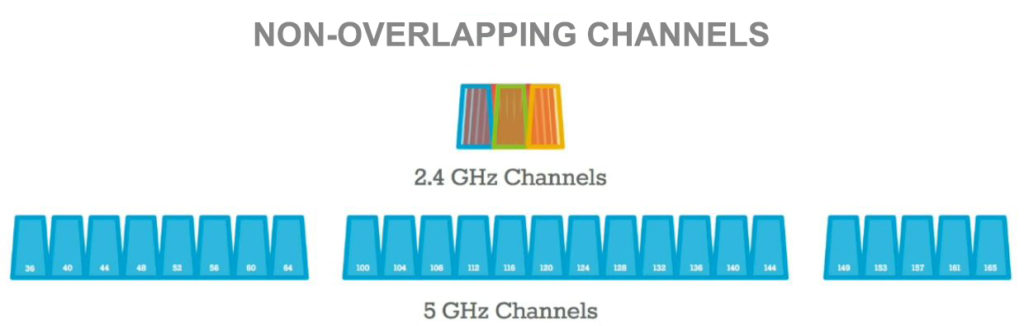
- Channel Width
The width of each channel varies depending on the frequency band. Each wireless channel on the 2.4 GHz band is 20 MHz wide with a wavelength of 0.125 meters. In contrast, the channel width on the 5 GHz varies between 20 MHz, 40 MHz, and 80 MHz. Wider channels support more devices with less congestion.
- Interference and Network Congestion
The 2.4 GHz frequency band is more prone to interference and network congestion than the 5 GHz band. After all, most wireless devices and consumer gadgets such as baby monitors, microwaves, and cordless phones operate on the 2.4 GHz band. The 5 GHz experiences less interference and cuts through network clutter for maximum Wi-Fi performance.
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi VS 5 GHZ Wi-Fi
How to Tell If You Have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on your Router?
Previous router models were single-band, working using the 2.4 GHz band only. Most Wi-Fi routers we use today are dual-band, meaning they operate on the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Recommended reading: What is EVDO? (Guide to EVDO Telecommunications Standard)
These modern routers automatically switch between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi bands, depending on the connected wireless devices.
You can check if your router supports 2.4 GHz from the router’s control panel on your PC or phone. Here are the steps:
- Connect your PC to your router’s Wi-Fi
- Launch your favorite browser
- Enter the default IP address (most common are 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.1.1) on the address bar
- Log in to your router’s web management page
- Go to Wireless Settings or Manage Device and check if your router supports the 2.4 GHz band
How to Tell If You Have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on your Phone?
Most smartphones and Wi-Fi-capable mobile devices support the 2.4 GHz band. Newer models work with both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
Your phone cannot connect to both frequency bands at the same time. It can only operate on one frequency band at a time.
Follow these steps to check if your phone is on the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network:
- Connect your phone to your Wi-Fi network
- Go to the Settings app
- Tap Network & Internet
- Go to Wi-Fi
- Tap the connected Wi-Fi network
- Read the connected frequency band
You can also tell if your phone has 2.4 GHz by tapping the three-dotted menu in the upper right corner on the Wi-Fi settings page. Your phone will display available radio bands supported.
How to Tell If You Have 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on your PC?
The latest PCs come with built-in wireless adapters for Wi-Fi connectivity. If your laptop or desktop cannot connect to Wi-Fi, you should consider purchasing a USB Wi-Fi adapter.
You can check if your PC has 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi using several methods depending on your tech-savvy skills.
Here’s how to go about it:
- Press the Windows Key + R to open the run dialog box
- Type cmd to open Command Prompt
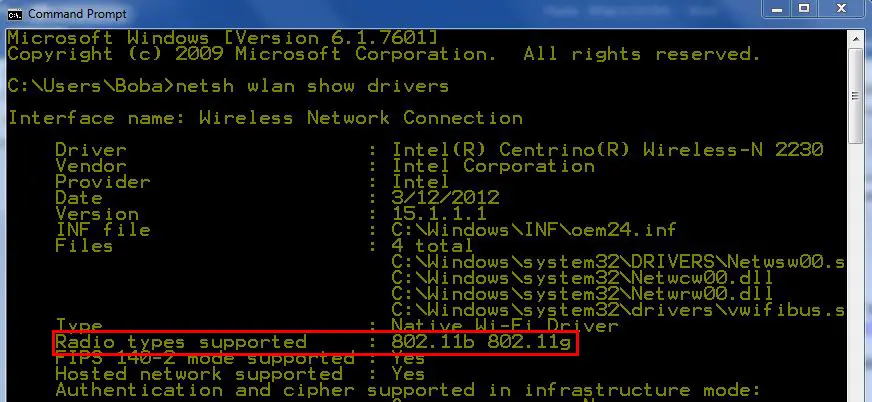
- Type the following command: netsh wlan show drivers
- Press the Enter key
- Locate “Radio types supported” from the results
- If you see 802.11g and 802.11n, your PC supports 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi (only 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi). If you see 802.11ac or 802.11ax, your PC supports both bands
How to Set Up 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on Your Phone?
If you experience constant slowdowns and weak signal strength, you are probably out of range and should consider switching to the 2.4 GHz network.
The 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi band is renowned for its broad network coverage, even in large spaces. It can reach 150 feet indoors and 300-400 feet outdoors, so it is only logical to set it up on your phone for better connectivity.
Follow these steps to set up 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi on your phone or tablet:
- Connect your phone to your Wi-Fi network
- Go to the Settings app
- Tap Network & Internet
- Go to Wi-Fi
- Tap the three dots in the upper right corner
- Select Advanced Settings
- Choose the 2.4 GHz frequency band
Note: If your phone only supports the 2.4 GHz band, you won’t have an option to switch between different frequency bands
How to Switch to 2.4 GHz on Windows PC?
Setting 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi as your preferred network band on your PC is equally easy. You don’t have to be tech-savvy to adjust these settings.
Here are the steps:
- Press the Windows Key + X
- Click Device Manager
- Go to Network Adapters
- Expand the Network Adapters menu to locate your wireless adapter
- Right-click your wireless adapter and select Properties
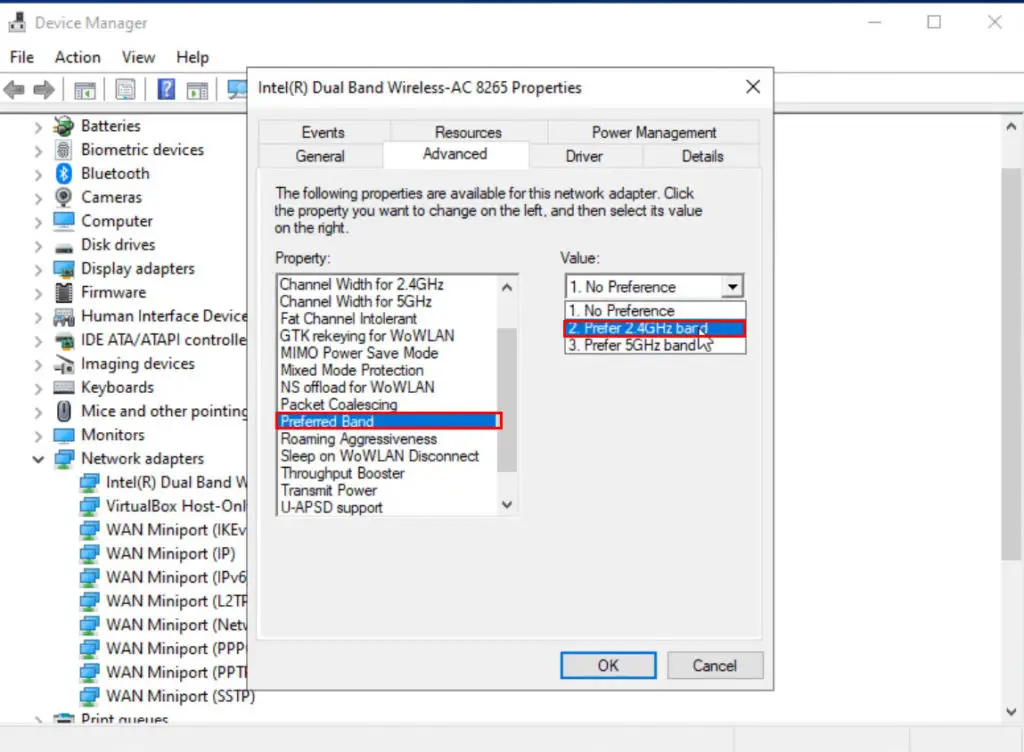
- Go to the Advanced tab
- Select Band
- Click the Value drop-down list
- Select 2.4 GHz only
- Click OK to apply changes
How to Switch to 2.4 GHz on Your Router?
If you have a dual-band or tri-band router, it will automatically switch between Wi-Fi network bands depending on the connected devices.
If your tablet or smartphone works best on the 5 GHz network, the router will switch it to that band to reduce congestion on the 2.4 GHz.
Older routers might have issues with automatic switching, meaning you have to do it manually. Here are the steps:
- Connect to your Wi-Fi router with your PC
- Launch your preferred web browser
- Enter the default IP address to access your router’s control panel
- Enter your login credentials when prompted
- Open Wireless Settings
- Under the Advanced tab, click 2.4 GHz
- Click Apply or Save to save the changes
Pros of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
- Broader network range (150 feet indoors and 300-400 feet outdoors)
- Can penetrate through solid obstacles and thick walls
- Provides stable Wi-Fi connectivity
- Supports most wireless devices
Cons of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
- Slow Wi-Fi speeds
- Prone to interference
- Vulnerable to network congestion
- Not suitable for heavy video streaming and online gaming

Is 2.4 GHz Good for Wi-Fi?
Yes. The 2.4 GHz frequency band has a more extended range, effectively eliminating dead zones in your premises and improving network coverage in your entire space.
Recommended reading: What is Panoramic Wi-Fi? (Introduction to Cox Panoramic Wi-Fi)
Since the 2.4 GHz radio band has longer wavelengths, it can penetrate through thick, solid obstacles without issues.
The only concern is that 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi is slower than 5 GHz Wi-Fi, but this cannot inhibit you from regular browsing and light streaming.
Should I Use 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?
If you live in a large house with many rooms and want adequate Wi-Fi coverage without buying a repeater or range extender, consider sticking to the 2.4 GHz network.
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi has a broad range covering up to 150 feet indoors and 300-400 feet in open spaces. Moreover, it facilitates Wi-Fi signals to penetrate the thickest walls and floors without compromising your internet connection.
You only have to contend with slower speeds. However, this is not an issue since the latest 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi routers support data transfer rates of 400 Mbps, which is adequate for typical online activities.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

