Wi-Fi technology has become a significant part of daily life. You can seamlessly connect your wireless devices, such as smartphones, cameras, laptops, and smart TVs, to your router without running cables around the home or office.
Wi-Fi networks operate using frequency bands. These bands are radio waves used to transmit data from your router to your devices. Two standard frequency bands apply in Wi-Fi technology, including 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The former is renowned for its expansive network coverage, while the latter is for faster internet speeds.
As the reliance on Wi-Fi continues to grow, the demand for fast internet increases equally. This is where 5 GHz Wi-Fi comes into play.
This post explains everything you need to know about 5 GHz and why it could be ideal for your internet needs. Please keep reading to find out more.

CONTENTS
What Exactly Is 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
5 GHz Wi-Fi is a wireless networking system that operates on the 5-gigahertz frequency band.
As you know, Wi-Fi technology primarily uses two standard frequency bands, including 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 5 GHz band is an upgrade to the 2.4 GHz band. It offers more channels for compatible devices to connect, reducing overcrowding and facilitating faster speeds.
Not many devices support the 5 GHz frequency band, which explains why it is less prone to interference and congestion.
Even though 5 GHz Wi-Fi is renowned for its fast data transmission, the band provides less network coverage. It has a shorter range since it cannot penetrate through solid objects such as walls, doors, and floors.

Previously, networking equipment and wireless devices were only compatible with the 2.4 GHz frequency band. The emergence of the Wi-Fi 4 standard in 2009 changed everything, and the 5 GHz band became mainstream. Modern home routers and wireless network cards now support the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands.
2.4 GHz VS 5 GHz
History of 5 GHz Wi-Fi
The 5 GHz Wi-Fi frequency has been around since 1999, but it was only after the emergence of the 802.11n standard (Wi-Fi 4) in 2009 that the band became common in the consumer market.
Most wireless devices, including microwaves, Bluetooth gadgets, baby monitors, cordless phones, garage door openers, and smartphones, support the 2.4 GHz band. However, this always leads to overcrowding. The 5 GHz band came about to mitigate the issue of interference and congestion.
The 5 GHz band has higher frequencies, and it offers over 23 channels for devices to use, leading to faster speeds and less congestion. Available channels depend on the regulations in your region since some 5 GHz routers and cards provide 45 Wi-Fi channels.
About 68 percent of wireless devices produced after 2015 use the 5 GHz Wi-Fi frequency band. Experts project the percentage of gadgets supporting 5 GHz to be over 96% in the next few years.
The only shortcoming of the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network is its shorter range. The frequencies cannot penetrate solid objects such as thick walls, doors, slabs, and floors. You must move closer to the router or access point to experience fast internet speeds.
How to Check if You Have 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
The 5 GHz Wi-Fi network is renowned for its incredible speeds and seamless connections. You do not have to struggle for bandwidth with other wireless devices. Moreover, the 5 GHz network is less prone to interference, making it the most preferred choice for most end-users.
Unfortunately, not all devices support the 5 GHz connection band. To make the most out of your Wi-Fi, you need to check if your device is compatible with this frequency.
Whether you want to decongest your network or experience faster speeds, switching to the 5 GHz Wi-Fi connection is logical.
Here are the steps to check if your device supports the 5 GHz network band:
- Type cmd in the search bar of your PC to launch Command Prompt
- Select Run Command Prompt as an Administrator
- Type: netsh wlan show drivers in the Command Prompt
- Press the return key (Enter)
- Navigate to the “Radio types supported” section
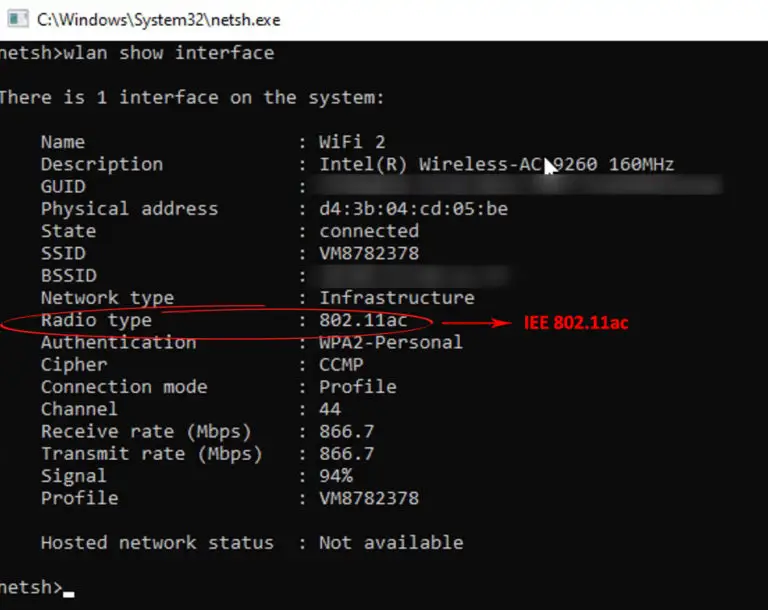
Note: If the network adapter supports 802.11ac, it is dual compatible and supports both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. If the adapter supports 802.11n, you have to test your PC to see if you can establish a 5 GHz connection. In most cases, it won’t support 5 GHz.
Alternatively, you can check if you have a 5 GHz Wi-Fi network using these steps:
- Connect your PC to the Wi-Fi network
- Click the Wi-Fi icon on the taskbar to open your network’s control panel
- Click on Properties
- From the new window, navigate to Properties
- Click Network band to see your connected frequency band
How to Enable 5 GHz on Your Wireless Router?
Since most devices, particularly the older models, support 2.4 GHz, you will likely experience slow speeds and heavy interference from nearby wireless gadgets, such as baby monitors, microwaves, and cordless phones.
The connected devices will likely overcrowd available channels, leading to congestion. Fortunately, enabling the 5 GHz band on your wireless router can help solve this problem.
The router will automatically switch 5GHz-compatible gadgets to the new band and lockout the 2.4 GHz devices, preventing interference from other wireless devices.
Follow these steps to enable 5 GHz on your router:
- Connect to the Wi-Fi network
- Launch your favorite browser on your PC
- Type 192.168.0.1 on the address bar to access your router’s admin page. But first, find your default IP – yours may not be 192.168.0.1. It could be 192.168.1.1, 10.0.0.1, or something else.
- Enter your username and password to log in
- Select Wireless from the menu
- Choose 5 GHz from the band selection field and enable it
- Click Apply to set and save changes
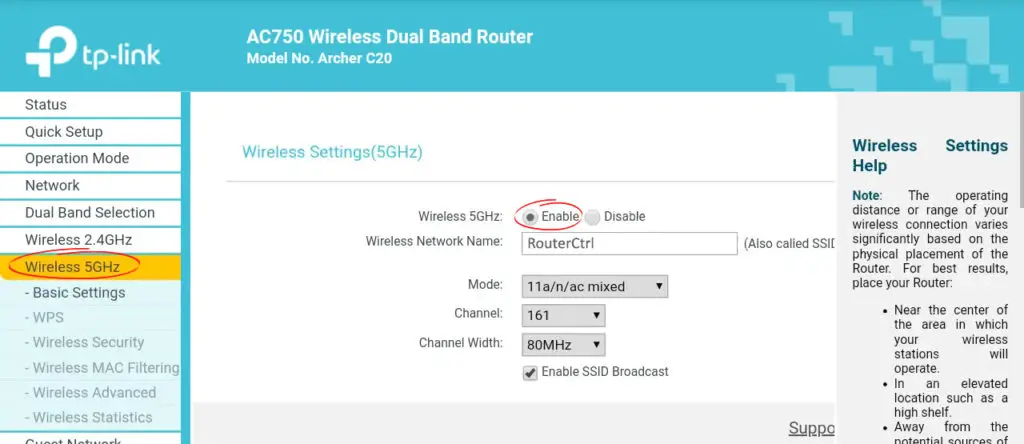
Note: Ensure you set the channels to 100 and 140, and your wireless devices support 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
How to Enable 5 GHz on Your Android Phone
5 GHz Wi-Fi is undoubtedly faster and more interference-free than the 2.4 GHz band. For this reason, it is not uncommon for most end-users to prefer the 5 GHz network over the 2.4 GHz band.
To make the most of 5 GHz Wi-Fi on your Android phone, you need to know whether it supports it in the first place.
Here are the steps:
- Open the Settings app on your phone
- Tap on Wi-Fi & Network
- Tap the three-dot icon
- Select Advanced
- Choose Frequency Band to see available options (5 GHz will appear if your phone supports it)
- Select 5 GHz to connect to the band
How to Enable 5 GHz on Your Windows PC
If you notice your Windows PC is sluggish and experiencing slow Wi-Fi speeds, perhaps it’s stuck on the 2.4 GHz band. Switching to the 5 GHz band can help improve data transmission rates and enhance your browsing experience.
Tri-band routers automatically and intelligently shift connected devices to the 5 GHz network without your intervention. With a dual-band router, you may have to manually switch your laptop’s Wi-Fi connection to the 5 GHz band since the process is not automatic.
Here’s how to enable 5 GHz Wi-Fi on your Windows PC:
- Press the Windows Key and R simultaneous to open the Run dialogue box
- Type “devmgmt.msc” to open Device Manager
- Navigate to Network adapters and expand the menu
- Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter and select properties
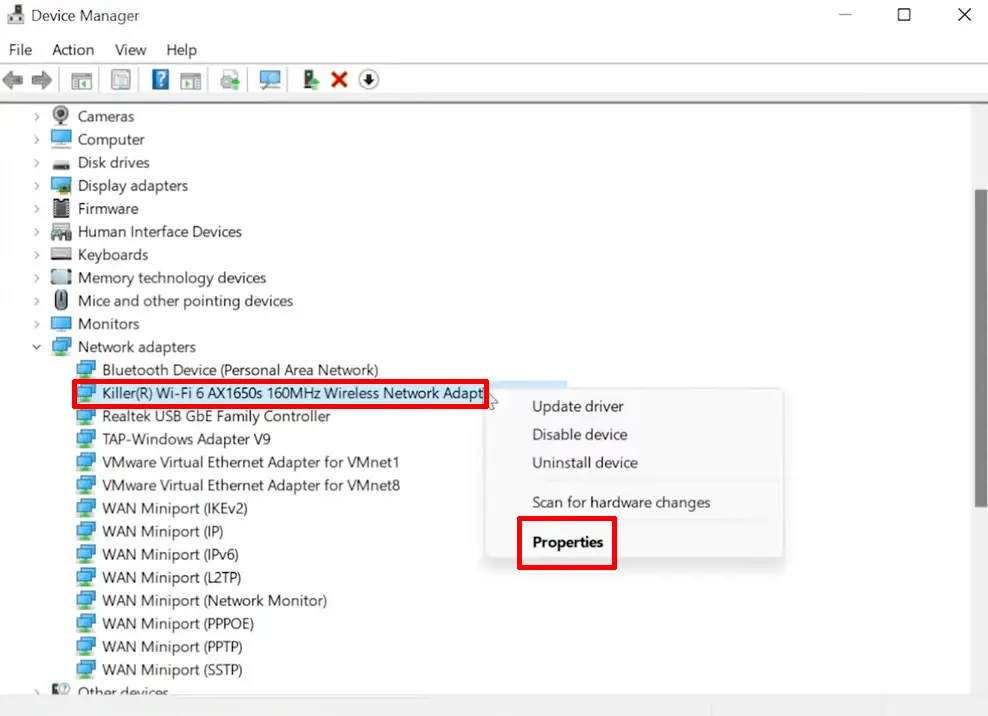
- Click the Advanced tab
- Select Wireless Mode under Property
- Under Value, choose Auto (or dual-band) and click OK.
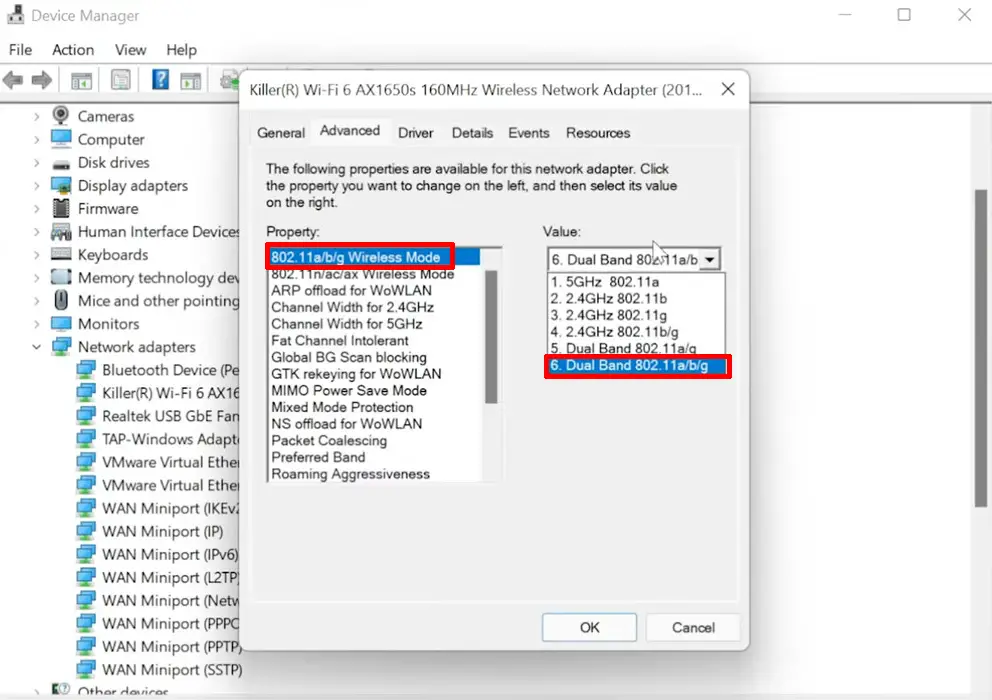
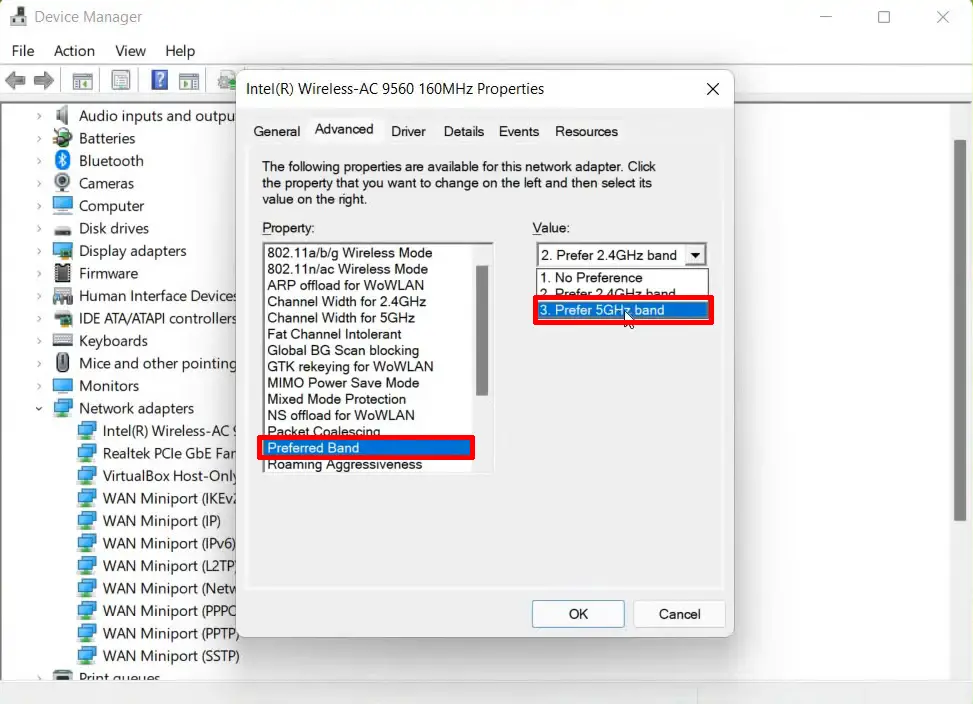
- Go to the Advanced tab again and select Preferred Band
- Select 5 GHz under the value option
- Click OK to apply and save changes
How to Enable 5 GHz Wi-Fi on macOS?
Before enabling the 5 GHz Wi-Fi on your Mac, you need to check if your machine supports it in the first place. Fortunately, the process is fast and straightforward. Here are the steps:
- Hold down the Alt Key on your keyboard and click the Wi-Fi icon on the menu bar
- From the drop-down menu, locate your network name and scroll down to Channel
- You’ll see the channel number and the frequency band enclosed inside the parenthesis
You also need to set up 5 GHz on your router to switch your Mac to the 5 GHz network as covered in the previous section above. If you have a dual-band or tri-band router, it certainly supports 5 GHz, so setting it up to this network won’t be an issue.
Follow these steps to enable 5 GHz on your Mac computer:
- Launch System Settings
- Select Network Option
- Click the Advanced option in the lower right corner
- Check the list of the preferred networks
- Choose your preferred network and drag it to the top of the list
- Your Mac will automatically connect to 5 GHz Wi-Fi as long as your router is on the 5 GHz network
Pros of 5 GHz Wi-Fi
5 GHz has numerous advantages, which explains why it is the most preferred network band. It is fast and seamless, with minimal interference, allowing smooth data transmission.
Here are the top benefits of 5 GHz Wi-Fi:
- Fast Data Transmission
The main advantage of 5 GHz Wi-Fi is fast data transfer speeds. Under ideal conditions, 5 GHz networks support data transmission rates of 1,300 Mbps, guaranteeing an enjoyable browsing experience. Nevertheless, the maximum speed of your wireless network might depend on other factors such as your router’s Wi-Fi specification and the number of connected devices.
- Less Congestion
Older frequency bands, particularly the 2.4 GHz band, are prone to overcrowding since most wireless devices are on this network. The 5 GHz band offers relief by ensuring there is less congestion. After all, only modern gadgets support this frequency band. Besides, it has multiple channels, allowing more devices to connect to the network.
- Minimal Interference
Another significant advantage of the 5 GHz frequency band is that it is less prone to interference. It has no overlapping channels that are usually the cause of interference in wireless networks. Moreover, gadgets and appliances like baby monitors, cordless phones, garage door openers, and microwaves, which interfere with wireless networks, do not support the 5 GHz frequency.
- Improved Uptime
Since the 5 GHz network has minimal interference and less congestion, you will likely experience improved uptime and continuous Wi-Fi connections. Fewer devices operate on 5 GHz, meaning you will benefit from clearer signals and better speeds. It also runs on a broader spectrum for efficient data transmission.
- Extended Battery Life
With a stronger signal and faster data throughput, your devices do not have to use too much power to connect to your wireless network. This feature remarkably benefits your devices by saving battery power and extending their lifespan. You do not need to worry about replacing your battery regularly.
- Future Proof
Even though the 6 GHz is already here with us, the 5 GHz is future-proof and will last for a long time without being outdated anytime soon. Besides, the production of devices that support the 5 GHz is rising, with the latest gadgets running exclusively on this network.
Cons of 5GHz Wi-Fi
The 5 GHz band might be fast and seamless, but it also has several downsides. Some of the cons associated with this frequency band include:
- Smaller Coverage Area
Even though 5 GHz offers faster data rates, it has a shorter range than the 2.4 GHz network. It cannot penetrate through solid objects like thick walls, doors, floors, and even furniture. You may have to purchase a Wi-Fi booster or extender to extend the range of your wireless network throughout the entire home.
- Limited Support by Devices
Not all devices run on the 5 GHz network. Most wireless technologies revolve around the 2.4 GHz frequency band, meaning older networking equipment might not be compatible with 5 GHz Wi-Fi. Fortunately, the production of compatible devices is increasing, with the latest gadgets capable of supporting newer Wi-Fi standards.
- More Costly
5 GHz Wi-Fi is relatively more expensive than its predecessor, 2.4 GHz. However, the prices of dual-band and tri-band routers that support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz are dropping drastically.
Conclusion
5 GHz Wi-Fi technology is no longer a pipe dream but a reality. This frequency band is fast, seamless, and with negligible interference, making it the ideal choice for an enjoyable internet experience.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

