Wi-Fi has transformed how people access the web and has become a fundamental part of everyday life.
It allows you to connect to the internet wirelessly through your phone, laptop, or other compatible devices.
From airports to restaurants to coffee shops, you can find a Wi-Fi hotspot in private and public spaces, ensuring you stay connected wherever you go.
However, few people understand the working principles that define how Wi-Fi signals get to their devices.
If you are wondering how your router broadcasts Wi-Fi signals to your device, this post is for you.

CONTENTS
- First Things First: What is Wi-Fi?
- How Does Wi-Fi Work?
- So, What is Wi-Fi Signal Broadcasting?
- How Does a Router Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals?
- How Do Connected Devices Receive Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals?
- How to Know If Your Wi-Fi Router is Broadcasting?
- How Far Can a Router Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals?
- Configuring a Router to Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals Effectively
- Conclusion
First Things First: What is Wi-Fi?
To understand how Wi-Fi signals are broadcast, you must know what Wi-Fi is in the first place.
Wi-Fi is a form of electromagnetic radiation that transmits data through radio waves from a sending device such as a router to connected devices like smartphones and laptops.
The router receives signals from your ISP via an Ethernet cable plugged into your modem before transmitting the same signals to connected devices.
The process by which the router transmits signals to connected devices is called broadcasting.
How Does Wi-Fi Work?
Wi-Fi technology carries data using radio-wave frequencies to facilitate communication between the connected devices.
The most common bands used for data transmission are 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These bands further comprise multiple Wi-Fi channels that determine data throughput and link rates.
The 2.4 GHz band is slower but has an extended Wi-Fi range and can penetrate thick walls and obstacles, while the 5 GHz is super-fast but has a poor range and can’t go through physical objects.

So, What is Wi-Fi Signal Broadcasting?
Broadcasting in Wi-Fi technology is a method of transmitting data over radio waves from a router to all connected devices within a network simultaneously.
The router casts Wi-Fi signals in all directions, with all connected devices receiving the transmission simultaneously instead of one at a time.
All devices within a Wi-Fi network share a broadcast address, which makes it possible for the router to transmit data to multiple endpoints associated with the address.
How Does Wi-Fi Work?
How Does a Router Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals?
A router is an integral component of any networking environment as it is responsible for broadcasting Wi-Fi signals to the connected devices within the network.
It is the intermediary or the main access point between the modem and your devices, allowing them to communicate and ensure a stable internet connection.
Routers systematically broadcast Wi-Fi signals to devices within a network with zero chance of error unless the router is faulty or aged.
Your Wi-Fi router receives internet signals from a modem and converts them into data packets before broadcasting them to your devices through its built-in antennas.
It has a routing table embedded in its memory that lists all known network routes and determines where broadcast data packets will go.
Each data packet that passes through the router has a network address associated with a specific device.
The router reads the info on the packet header to establish the correct destination address.
The router also uses artificial intelligence to control incoming and outgoing traffic and determine the best path the data will go through to reach the destination address.
How Does a Wi-Fi Router Work?
How Do Connected Devices Receive Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals?
The function of a router is to receive internet signals from the modem and decode them into data packets before broadcasting them wirelessly to connected devices.
The entire process is similar to a radio broadcast since Wi-Fi uses radio frequencies to carry and distribute signals to your devices.
However, not all devices will receive the broadcast signals. Your device must join the network before receiving Wi-Fi signals from the router.
For this to be possible, the router will broadcast the SSID (Service Set Identifier) or simply the Wi-Fi network name and make your wireless network visible to surrounding devices within range.
When searching for available Wi-Fi networks on your device, the broadcast SSID will appear on the list.
You can join the network by entering the set password, effectively setting up your device to receive broadcast Wi-Fi signals from the router.
How to Know If Your Wi-Fi Router is Broadcasting?
The quickest way to know if your router is broadcasting Wi-Fi signals is to check the connection status.
Follow these steps:
- Connect to your Wi-Fi network
- Launch your preferred web browser
- Enter your router’s default gateway address into the address bar to access the router’s admin site
- Enter your login credentials (username and password) and click OK
- Click Status to see your internet connection status
- If it says connected, your router is receiving internet signals from the modem.
How Far Can a Router Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals?
The distance a router can broadcast Wi-Fi signals depends on the router type and supported frequency bands.
Wi-Fi signals travel best in open spaces since they are less prone to interference in such environments.
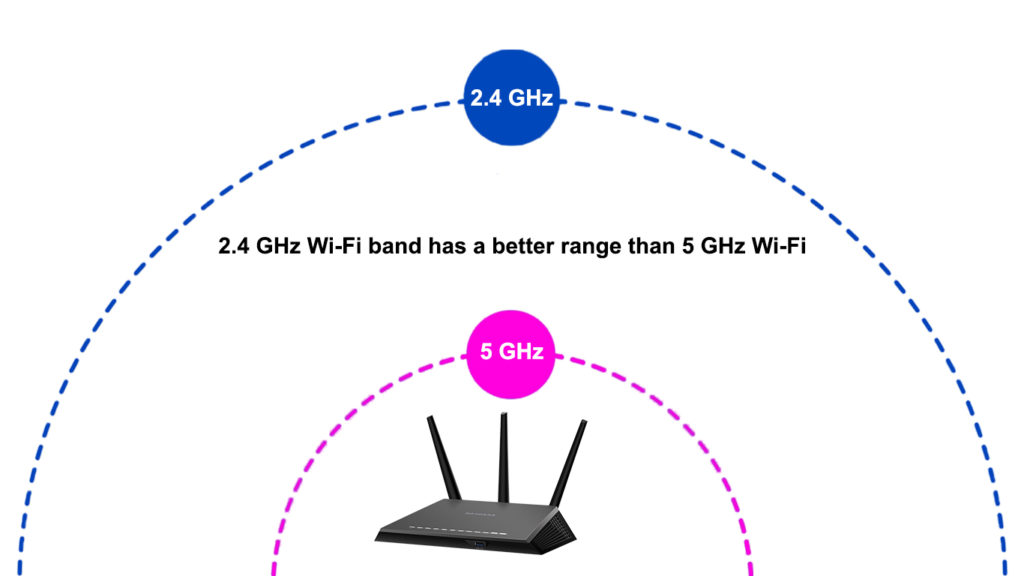
The 2.4 GHz band has the broadest network coverage reaching 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors, while the 5 GHz band can only get to 45 feet indoors and 100 feet outdoors.
The router type also determines how far it can broadcast Wi-Fi signals.
Routers with more antennas have better signal directionality and enhanced range, making them ideal for eliminating dead spots in your space.
You can also choose between single, dual, and tri-band routers, with the latter two options offering better connection and network coverage features.
Configuring a Router to Broadcast Wi-Fi Signals Effectively
How you configure and set up your router will determine its overall performance in broadcasting Wi-Fi signals to your devices.
Fortunately, optimizing a router to broadcast Wi-Fi signals effectively is not complex.
Here are a few tips:
- Position your router centrally, away from physical obstacles and obstructions
- Switch off wireless gadgets such as Bluetooth speakers, baby monitors, and cordless phones when not using them
- Enable radio mode in your router’s control panel
- Utilize auto-configuration tools to manage IP addresses, connected devices, and control data traffic
Conclusion
Understanding how Wi-Fi signals are broadcast can help you make the most of your internet connection.
You will know when to change the default frequency band or channel and troubleshoot any network issues appropriately for uninterrupted signal broadcasts.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

