Many internet users take their routers for granted. Once set up, no one really thinks about the router until something goes wrong. You shouldn’t treat your router like that because it’s the most important part of your Wi-Fi network. Your network will not run if your router is not working.
A router is not just a device that routes your internet signal. You’d be surprised how many controls and features are present around this device. Port forwarding and port triggering are part of the said features. This article explains the difference between the two procedures, how they work, and how to set them up.
Briefly, port forwarding is a technique of forwarding intended data from a node’s port to another node. In contrast, port triggering, as the name suggests, dynamically triggers a port when needed. Let’s take a closer look at each technique.
CONTENTS
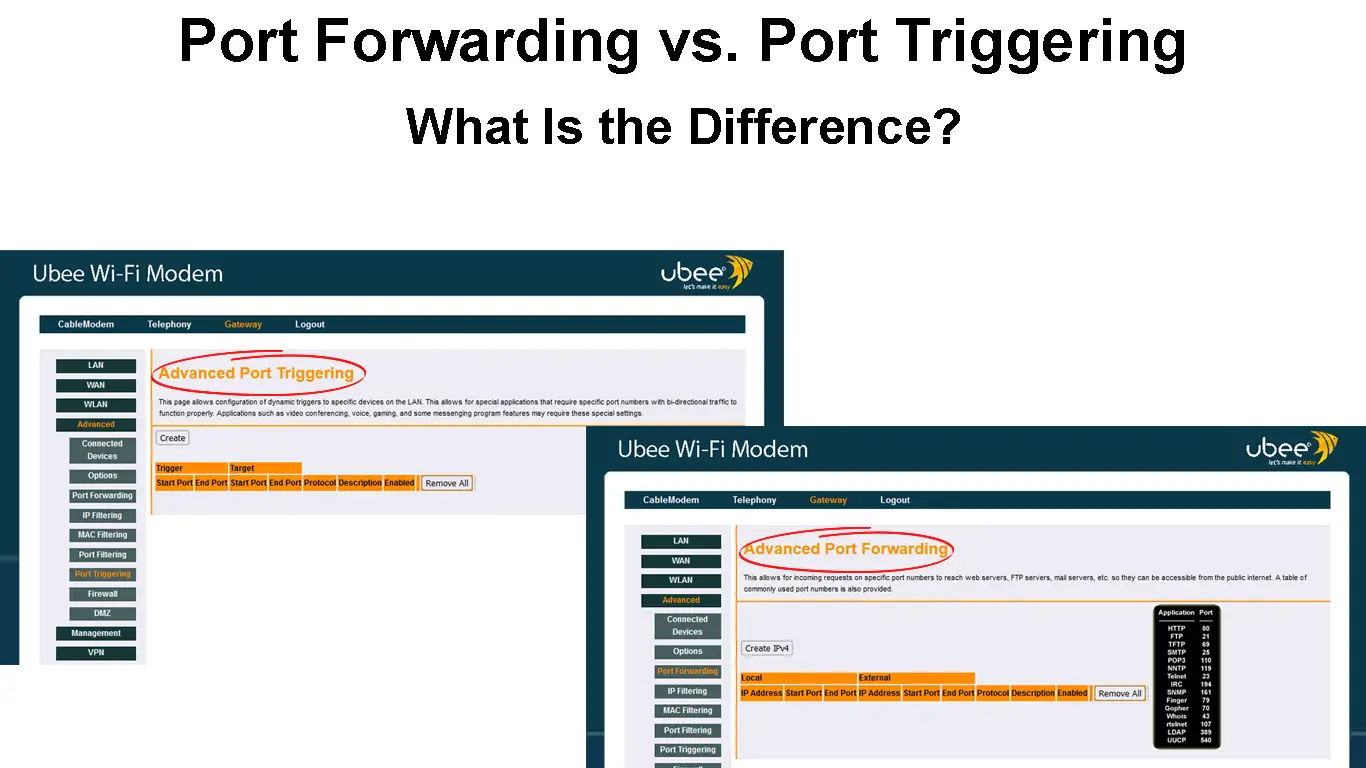
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding, also known as port mapping, is a technique used in forwarding data from one computer to another, where data is intercepted from its regular path to a directed path. Typically, a remote user will use this port forwarding technique to access a computer/device on a local area network.
Port forwarding appears in several different forms. Here are a few major forms:
- Localized Port Forwarding – transmits data within a local system while avoiding firewalls.
- Distant Port Forwarding – provides applications for access from remote devices.
- Dynamic Port Forwarding – dynamically forward data past firewalls through loopholes.
Port Forwarding Data Transmissions
To understand how port forwarding works, we must first take a look at how data is generally transmitted in a network. When data is transmitted from one point to another, it breaks down into packets for easy transmission (TCP/IP model). The packets hold detailed information, including its final travel destination. Your Wi-Fi router acts as a routing device that guides the data packet to its intended final destination. It does it by reading the particulars and instructions inside the data packet.
Port forwarding comes into the picture by intercepting the packet route and taking over the router’s function. It will rewrite the instructions and other details on the data packet and forward it to a different destination based on the revised instructions.
What Is Port Forwarding
Setting Up Port Forwarding
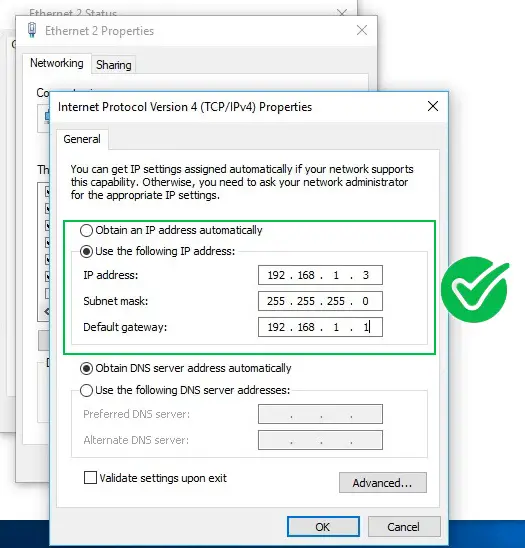
How do you set up port forwarding? Firstly, you need to set up a device that utilizes a static IP address. From your computer or router, you will need to configure the IP address.
Follow these steps to assign a static IP address to your PC:
- Start the Windows Control Panel and then go to Network Connections – either wired or wireless connections.
- Right-click on your network connection and then choose Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then select Properties.
- On the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, select Use the following IP address.
- Enter a specific IP address in the IP address space.
- Still, in the Internet Properties dialog box, enter the Subnet mask field as indicated in the router setup.
- In the Default Gateway space, key in your router’s local IP Address, and don’t forget to click OK.
If you want to set up a static IP for some other device (like a gaming console), the procedure will be different. The easiest way to assign static IP to any device is through your router’s settings. Most modern routers have Static IP Lease or Address Reservation, which is the option that allows you to assign static IP to any device. You will have to enter your device’s MAC address, type in the desired IP address for that device, and save the settings.
Once your device receives a static IP address, you can enable port forwarding. Here are the steps to forward a port:
- Key in the router’s IP address in the address bar of your internet browser.
- Log on to the router admin page using your admin username and password.
- Look for the Applications and Gaming section and find the port range forwarding page.
- Type in the desired port you intend to forward (or the port range).
- Key in the IP address of your device (that static IP that you have just set).
- Lastly, don’t forget to click Save for all the changes you made.
Setting Up Port Forwarding Rules (TP-Link Router)
Port Triggering
Port triggering is similar to port forwarding. However, while the port forwarding is static, port triggering is dynamic – ports remain open when in use and close when not in use. It’s useful when you need to forward the data packet to various local computers.
Port Triggering Data Transmissions
Your router will monitor the network’s traffic while using port triggering. When a user identifies a trigger port sending a data packet, the router logs the computer’s IP address which sends the data to that port. Next, the router assigns a port and forwards the data to that particular port.
Port triggering is secure since the ports are closed when not in use. That way, it closes possible points of entry that would have been vulnerable to malicious hackers and unwanted intruders.
What Are the Differences?
You can observe the main differences between port forwarding and port triggering as summarized in the following table:
| Port Forwarding | Port Triggering |
| Static IP | Dynamic IP |
| Need to specify IP addresses | Automatically identify IP addresses |
| Ports are always available | Ports only open when triggered |
| Not secure – open ports are vulnerable to intruders | Secure – close ports lure intruders away |
The major difference between port forwarding and port triggering is the use of open and closed ports, respectively. Port forwarding keeps the router’s port open for quick and easy reception of data packets. In contrast, port triggering opens a port while using it and then closes it when the data packet forwarding is completed. Thus, port triggering is dynamic compared to port forwarding.
For the same reason, port triggering is more secure since it keeps the ports closed and it locks up the network from possible malicious intruders. Port forwarding, in contrast, keeps the ports open when not in use, and that leaves the network vulnerable to such malicious cyber-attacks.
Port Forwarding vs. Port Triggering
Port Forwarding and Port Triggering – FAQs
Question: Is DMZ the same as port forwarding?
Answer: No, a DMZ or “demilitarized zone” is a sub-network that the public can access. However, it also has a firewall and DDoS protection that act as the primary network’s first line of defense. While port forwarding deals with NAT (network address translation) for use over the internet.
Question: Is port forwarding useful?
Answer: Although port forwarding weakens network defense, businesses find implementing port forwarding useful in certain situations, especially when they need multiple incoming connections.
Question: Do you have to restart the router after implementing port forwarding?
Answer: No. The router will implement the port forwarding commands right after saving the changes. Restarting the router could reset or clear the changes made.
Conclusions
Port forwarding and port triggering are two useful techniques to control data packet traffic on your network. These terms sound pretty technical, but they are fairly easy to understand and apply.
Both techniques are designed to provide the fastest path for the incoming data sent to a specific device. Your router will pick up such data and forward it to the applicable computer based on the specific instructions. While port forwarding uses static IP, port triggering uses dynamic IP and automatically selects an IP address.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.