Following technological advancements, you can now access the internet directly from your phone or tablet via cellular data or Wi-Fi.
Cellular data requires you to purchase a data plan from your mobile carrier, while Wi-Fi is available from your internet service provider and requires a wireless router to connect.
Even though you can simultaneously activate cellular data and Wi-Fi on your device, your cell phone will always connect to Wi-Fi as the default internet gateway.
Your cell phone may only use cellular data when you are not within range of your Wi-Fi network.
After all, Wi-Fi has limited coverage not exceeding 150 feet (approx. 46m) indoors and 300 feet (approx. 96m) outdoors
Please keep reading to learn the differences between Wi-Fi and cellular data and the instances where your phone might use data when connected to Wi-Fi.

CONTENTS
What is the Difference Between Wi-Fi Data and Cellular Data?
Wi-Fi and cellular data are strikingly similar since they all act as the wireless gateway to your internet connectivity.
Wi-Fi Vs. Cellular Data – What’s the Difference?
Even though these data options seem similar, they have several notable differences, including:
1. Network Coverage/Range
Wi-Fi usually works within a limited range, not exceeding 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors, depending on the frequency band.
The 2.4 GHz frequency band has the longest range, while the 5 GHz band has the shortest range, confining Wi-Fi data to residential and commercial properties.

Cellular data has wide network coverage spanning several miles, allowing users to access the internet anywhere.
Cellular providers have invested heavily in network towers throughout the globe, meaning you only need a data plan to access the web.
2. Connectivity Equipment
Wi-Fi requires a wireless router to broadcast signals to connected devices within a network.
In contrast, cellular data relies on cell towers and macrocells strategically located in various parts of a geographical area.
Your device must connect to the wireless router to use Wi-Fi, while cellular data only requires you to have a data plan and be within a coverage area.
3. Data Transmission
Both cellular data and Wi-Fi use radio frequencies to transmit signals to connected devices.
However, cellular data relies on wireless technologies such as 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G, while Wi-Fi uses the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands for data transmission.
4. Compatible Devices
Some devices are for Wi-Fi use only, while others support cellular data and Wi-Fi connectivity.
Most devices that support cellular data are mobile phones, while the latest laptops, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, soundbars, gaming consoles, Blu-Ray players, and even smart appliances are Wi-Fi enabled.
You may have to use a broadband modem or cellular router to connect your TV or laptop to cellular data.
Why is My Phone Using Data When Connected to Wi-Fi?
As mentioned at the outset, when cellular data and Wi-Fi are simultaneously active on your phone, your device will select Wi-Fi as the default internet connection.
However, your phone may continue using data even when connected to Wi-Fi for several reasons.
Here are the top reasons:
1. Range Issues
Wi-Fi works within a limited range, not exceeding 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors, depending on the frequency band.
If you are out of the Wi-Fi coverage area, your cell phone will automatically switch to cellular data to guarantee strong signals and better speeds.
Ensure you are within the coverage area to continue using your Wi-Fi data.
2. Inactive Wi-Fi Connection
Your wireless router might be ON, but your connection may not be active because of an expired subscription, service outage, or network issues.
For these reasons, your cell phone may resort to using cellular data even if it indicates it has an active Wi-Fi connection.
Check with your ISP for any service outages and confirm your subscription bills are up to date to continue enjoying your Wi-Fi connection.
3. Black-Listing
Sometimes the network admin may limit or list your connection if they suspect your device is untrustworthy.
Limiting or blacklisting your device will automatically force your cell phone to switch to using cellular data.
You can approach the admin to ask and ensure your device is not on the blacklist.
4. Wi-Fi Network Lags
Some cell phones support Wi-Fi+ (aka Wi-Fi Assist or Adaptive Wi-Fi), a feature that allows your phone to simultaneously connect to Wi-Fi and mobile networks and switch to cellular data if your Wi-Fi has slowdowns.
In essence, Wi-Fi+ forces your phone to switch to the most stable internet connection between the two.
Wi-Fi Assist (Wi-Fi+) Explained
And if you want to continue using Wi-Fi instead of mobile data, you must disable the Wi-Fi+ feature. Simply:
- Go to the Settings app
- Go to Internet & Network
- Go to Wi-Fi and then Wi-Fi+ (or Wi-Fi Assist or Adaptive Wi-Fi)
- Tap the slider next to Wi-Fi+ to disable it
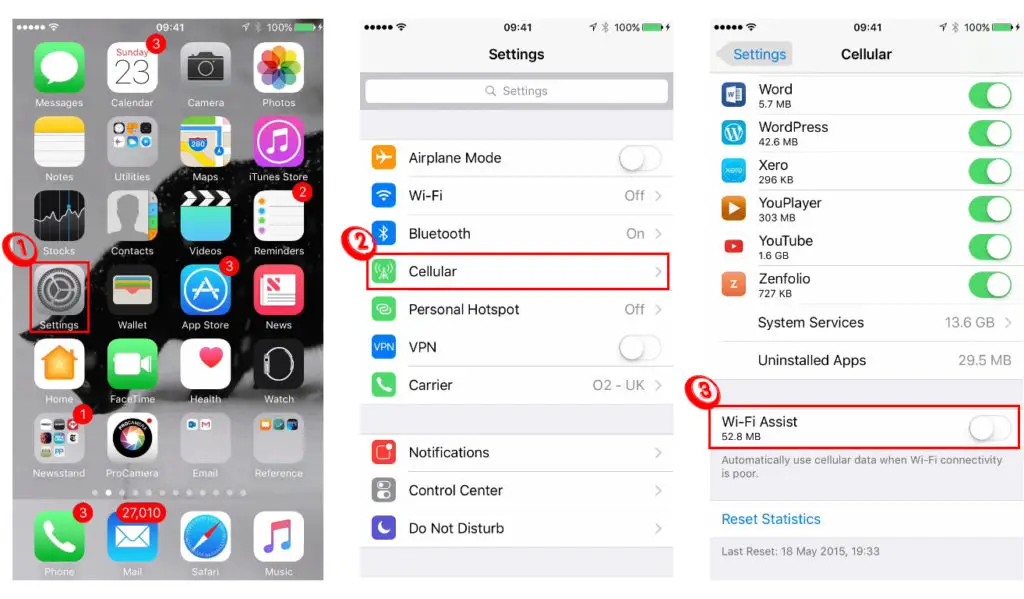
Disabling Wi-Fi Assist on an iPhone
5. Third-Party Apps
Some mobile applications, particularly banking apps, consume mobile data even if your Wi-Fi connection is active.
These third-party apps require your cellular data to verify your identity and gadget status to safeguard your sensitive information.
The good news is that they do not require much data, so you don’t have to worry about increasing charges.
How to Tell If Your Phone is Using Cellular Data or Wi-Fi?
You can tell your cell phone is using cellular data or Wi-Fi by checking the icons on the notification bar.
When using cellular data, your phone will indicate a 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G icon with upstream and downstream arrows.
Recommended reading:
- Why Does My Wi-Fi Turn on Automatically in The Morning? (Best Ways to Prevent Wi-Fi from Turning on Automatically)
- Are Wired and Wi-Fi Considered One Network? (Wired & Wi-Fi Networks Compared)
- How Do You Log in to a Wi-Fi Extender Network? (Step-by-Step Instructions)
If your phone is actively using Wi-Fi, you will see a colored wireless icon that looks like a fan with uplink and downlink arrows.
Ways to Stop Your Cell Phone from Using Data When Connected to Wi-Fi
You can stop your cell phone from using cellular data when connected to Wi-Fi using these tips:
- Turn off mobile data – You can manually turn off mobile data by tapping the appropriate icon on the notification bar and leaving Wi-Fi ON
- Stay within range – Ensure you are within range to stop your cell phone from using data. You can install a Wi-Fi extender to enhance coverage
- Disable third-party apps – Consider disabling third-party apps that might want to use mobile data instead of Wi-Fi
Conclusion
Even though you can simultaneously activate cellular data and Wi-Fi on your device, your cell phone will always connect to Wi-Fi as the default internet gateway.
If you notice any issues and want to stop your phone from using data, you can use our tips explained in this post.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

