Many procedures happen in the background so your devices can connect to the internet via Wi-Fi. For instance, IP addresses act as postal addresses that help the network infrastructure direct data to the intended devices. The router issues these IP addresses and regulates how long a device can have a particular IP address. That means the router leases out IP addresses to devices on the network so that they stay connected. However, more happens than just issuing IP addresses, as we shall see in this article.
Keep reading as we look into what ‘renew lease’ means on your devices and why it is important.
CONTENTS
- What Is an IP Address?
- The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- What Is a Wi-Fi Lease?
- What Is a Wi-Fi Lease Renewal?
- Should I Renew the Wi-Fi Lease on My Devices?
- How to Renew Lease on iPhone?
- How to Renew the Wi-Fi Lease on Windows
- How to Renew Wi-Fi Lease on Mac
- How to Renew the Lease on Other Devices?
- Does Renewing the Lease Change My Device’s IP Address?
- Conclusion
What Is an IP Address?
To adequately understand what renewing the lease on Wi-Fi means, we start with the fundamentals of internet connectivity through your router/modem.
An Internet Protocol address is a string of characters issued to devices that use the internet protocol. The internet protocol entails guidelines that govern data transfer and routing over the internet or local networks.
An IP address identifies devices on the network so that information is directed to the correct device once it gets to your router or gateway from the internet.
Your home router works with two sets of IP addresses: public IP addresses and private IP addresses.

The public IP address is a bridge that connects all the devices on your local network to the internet. In other words, the public IP address identifies your home network on the internet. Often the IP address is issued to the router by the internet service provider.
A private IP address identifies individual devices in your home network. Therefore, all the devices in your home, like the phone, PC, printer, Play Station, and Smart TV, have a private IP address, and the router has a public IP address (along with its private IP address called default IP address).
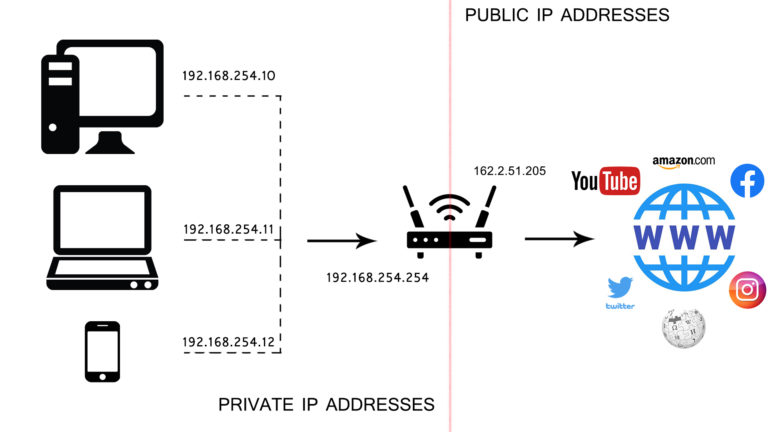
The router uses private IP addresses to route data to the right devices, and it uses its public IP address to identify itself on the internet.
Since the router can only issue a specific range of IP addresses within a local network, the addresses must be efficiently managed to ensure swift data transfer.
And that is where the dynamic host control protocol comes in.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
As we have established, the router or gateway issues IP addresses to devices on your local network.
DHCP refers to guidelines governing how the router issues IP addresses and other configuration parameters to devices on the network. The router uses a DHCP server to automate issuing IP addresses to devices on your local network.
For the router’s DHCP server to assign an IP address, your device (client) first requests an IP address.
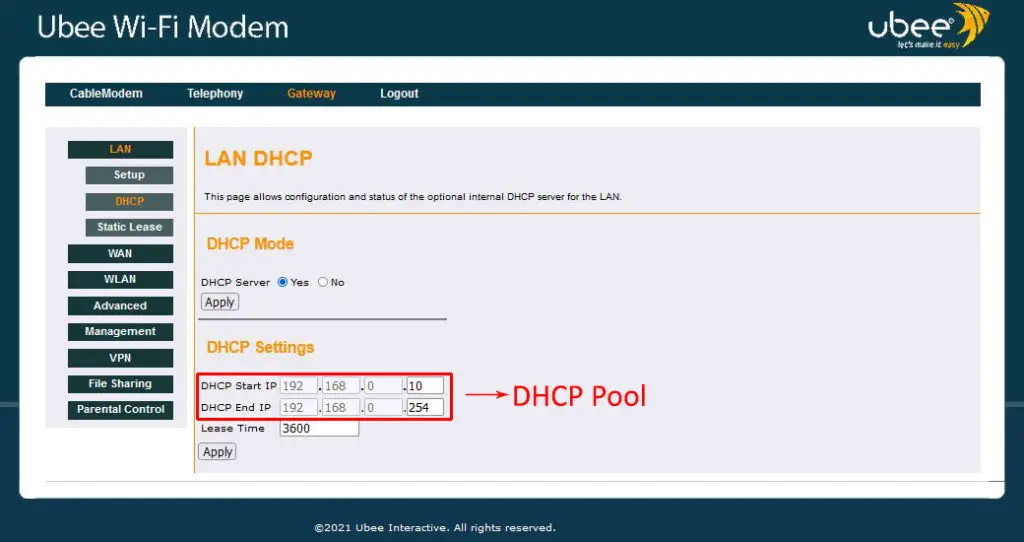
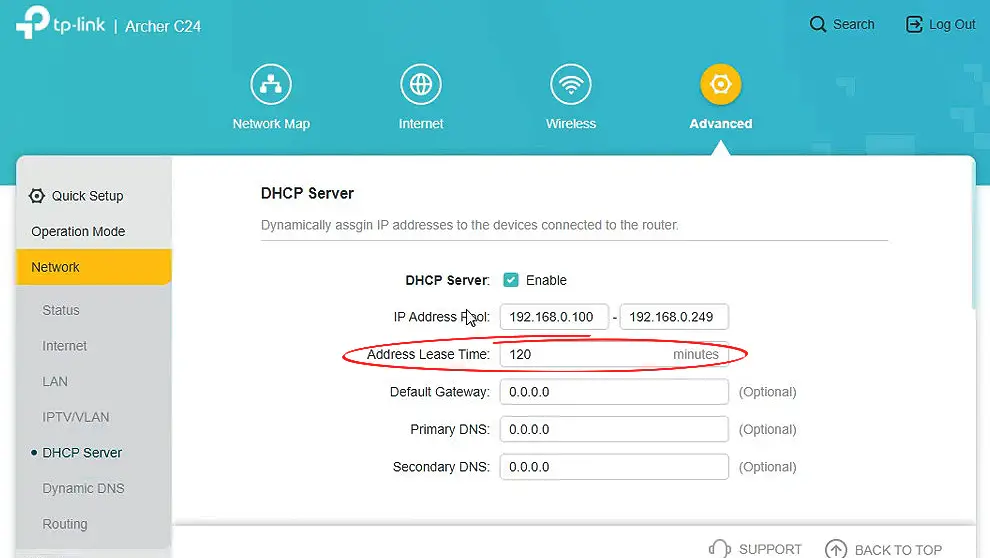
Once the router receives the request, it responds with a message that contains an IP address with the necessary configuration information, like the client’s MAC address, subnet mask, DNS address, and the address lease time. The address comes from the server’s DHCP pool, i.e., a combination of all the available IP addresses for clients.
The client will then request the DHCP server to use the offered IP address. This is necessary since the client might have received multiple IP offers from other DHCP servers on the network. By sending a request to use the offered IP, the client device ensures it connects to the intended server, i.e., your router’s DHCP server. The rest of the servers that might have offered IP addresses withdraw their offers and wait for the next IP request.
The router’s DHCP server then acknowledges that it has leased the client an IP address and thus completes the DHCP handshake.
Note the above procedure refers to when the router is set to use dynamic IP addresses. You can also set it to use static IP addresses, i.e., the router reserves particular addresses for specific devices on the network.
DHCP Explained
What Is a Wi-Fi Lease?
When the router offers wireless clients IP addresses, it does so on leasing terms. That means the wireless client can use the address for a certain duration then it is re-assigned once that duration lapses. Therefore, as long as the lease has stayed active, the assigned IP will remain reserved for a wireless client.
Leasing the IP addresses is important to ensure the addresses are re-usable once a device is no longer connected to the wireless network.
However, the address is only sometimes re-assigned. The client can request a lease renewal if it is still connected to the router.
DHCP Lease Explained
What Is a Wi-Fi Lease Renewal?
Since the router’s DHCP server often leases out IP addresses for certain durations, there is a need to renew the lease whenever a wireless client is still using an IP address and the lease time is about to expire.
To renew the lease, the client will send a lease renewal request to the router halfway into the lease period. If the lease duration was 24 hours (as it usually is for most routers), the client sends a lease renewal request after 12 hours, i.e., after 50% of the lease duration. If it does not receive a response, it will send another request after 87.5% of the lease duration expires and will eventually ask for a new IP address should all the requests go unanswered.
Notably, some devices like iPhones provide the option to request a Wi-Fi lease renewal manually. You can also set different lease durations for IP addresses issued by your router through the router’s administration page.
In summary, a Wi-Fi lease renewal request is a way for your wireless device to tell the router, “I need this IP for a bit longer, so increase my lease duration.”
If the router cannot extend the lease time, it will notify the client, and the client will initiate a new IP address request.
Should I Renew the Wi-Fi Lease on My Devices?
There is no need to manually renew the Wi-Fi lease if the devices on your network work as they should. However, if you have connection issues on a client device, you can renew its lease as a troubleshooting measure.
If a device asks you to renew the Wi-Fi lease when you reconnect to a router, it means there is a configuration issue, or the initially provided IP address has expired. However, this rarely happens as the lease renewal process happens automatically.
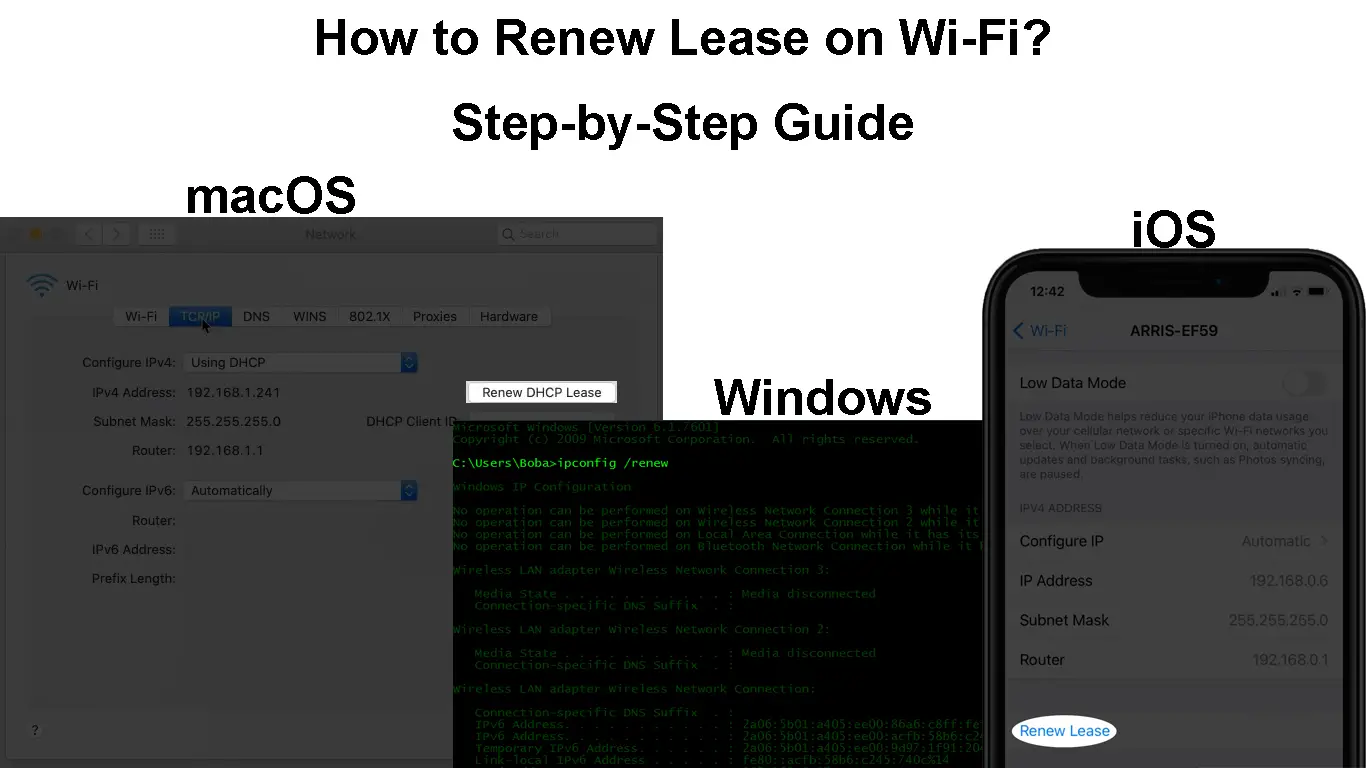
How to Renew Lease on iPhone?
iPhones have a renew lease option that initiates a renewal lease request from the phone to the router. You can access it by following the steps below:
- Ensure the device is connected to your preferred Wi-Fi network.
- Navigate Settings > Wi-Fi.
- Tap the information icon (i) next to the connected Wi-Fi network.
- Scroll to the bottom for the ‘Renew Lease’ option and press it.
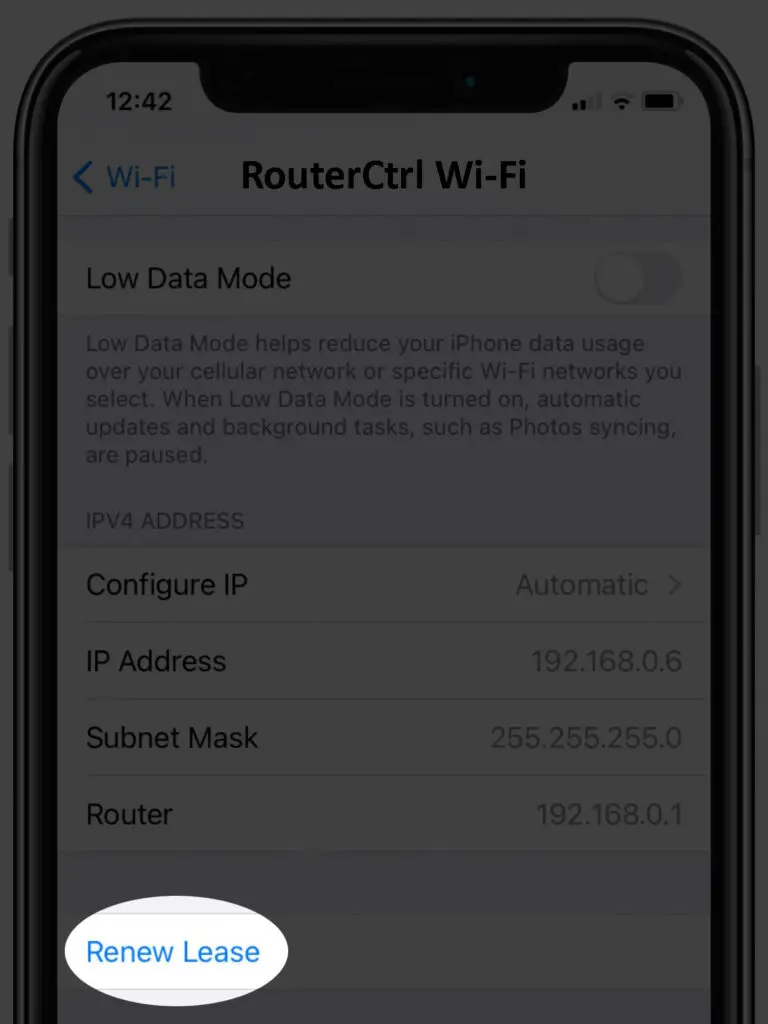
- Finally, tap ‘Renew Lease’ to confirm the action, and you are done.
How to Renew Wi-Fi Lease on an iPhone
How to Renew the Wi-Fi Lease on Windows
You can use the command prompt to renew your Windows IP address as long as it is connected to a computer network through Ethernet or Wi-Fi.
The process is as follows;
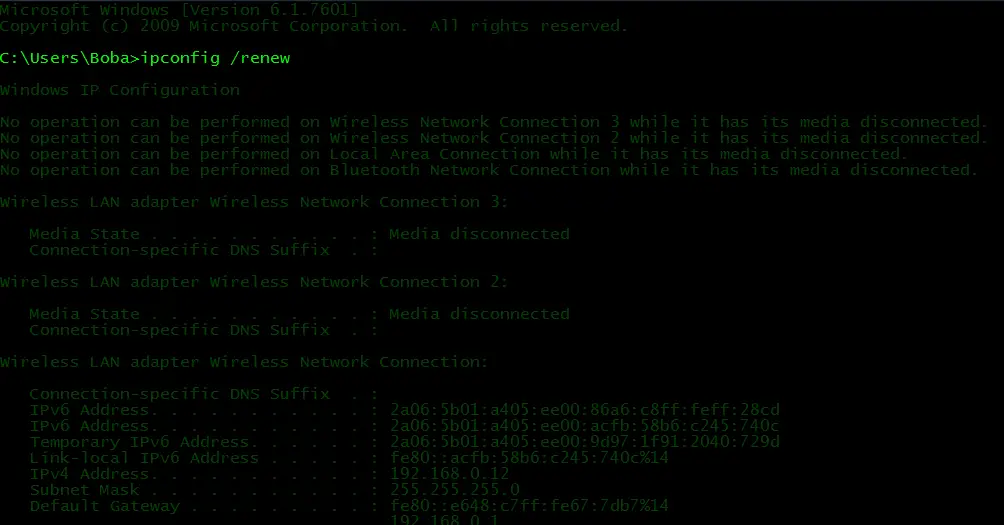
- Press the Windows + R buttons.
- Enter into CMD the RUN dialogue box that pops up and press Enter.
- Enter the command ipconfig /release, then press Enter.
- Then enter the command ipconfig /renew to renew the IP lease.
How to Renew Wi-Fi Lease on Mac
You can also use the procedure below to renew the lease of the various mac operating systems.
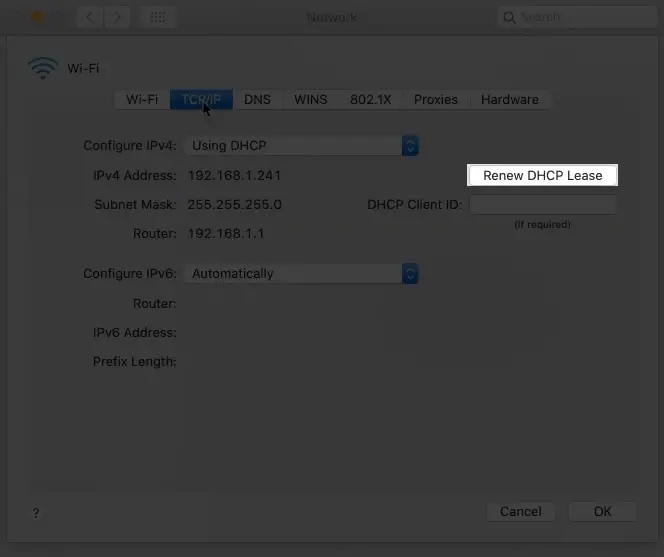
- Ensure the device is connected to a Wi-Fi network, then launch the Apple menu by clicking on the Apple icon.
- Next, go to System preferences > Network.
- Click on the current connection type from the network connection services list on the right, in our case, Wi-Fi.
- Next, navigate Advanced > TCP/IP > Renew DHCP Lease and complete the process by clicking OK.
How to Renew Lease on a Mac
How to Renew the Lease on Other Devices?
If a device does not have a renew Wi-Fi lease option in its settings, e.g., an Android, you can initiate the process by forgetting the Wi-Fi SSID and reconnecting the device to the same network.
Doing this refreshes the connection and forces the client and DHCP server to initiate a new connection with a new IP address. You could also restart the router to ensure it renews the lease time for all clients, whether wireless or wired.
Does Renewing the Lease Change My Device’s IP Address?
Renewing an IP lease does not necessarily change the client’s IP address. As mentioned, the procedure’s primary function is to notify the router that a client device is still using a particular IP address, so the router should reserve it for the device for a longer duration.
The router will offer a new IP if the configuration information on the first IP has errors or if it mistakenly offers the current IP to another device on the same network.
Conclusion
Renewing leases on IP addresses is essential in maintaining an internet connection and ensuring devices access the internet. Usually, the router handles lease renewal automatically, and you do not need to do it manually.
However, you can initiate lease renewal if your devices have issues connecting to the internet, or you can resolve to use a static IP or DHCP reservation.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.