Is there a chance that my default IP is 192.168.16.1? How to check if this address is my default gateway? What manufacturers and devices use it as a default gateway?? What can I do with it if it is my default IP? Can I use this address as a client IP? All the answers can be found in this article. Keep reading and learn everything you need to know about 192.168.16.1.
CONTENTS
- Why Do We Need IP Addresses?
- What Does an IP Address Look Like?
- What Kinds of IP Addresses Are There?
- What Kind of Address is 192.168.16.1?
- Can This Address Be A Default IP Addresses?
- What Devices Use 192.168.16.1 as a Default IP?
- Is This Address My Default IP Address?
- What Can I Do with My Default IP Address? How to Use 192.168.16.1 as a Default IP?
- Can 192.168.16.1 be a Client IP?
Why Do We Need IP Addresses?
Every device (PC, laptop, phone) connected to any kind of network (LAN, corporate network, internet) must have an IP address, just like every phone comes with a phone number, and every house comes with an address (street name, street number). IP addresses are used to identify a device on a network. Without an IP address, a device wouldn’t be able to communicate with other devices – it wouldn’t be able to send or receive any data. The moment it connects to a network, an IP address is assigned to a device. That’s the only way for devices on the same network to communicate.
What Does an IP Address Look Like?
All the fundamentals of IP addressing, including the form of an IP address, are defined through IP protocols. There are two existing protocols (IPv4 and IPv6), but only IPv4 is currently in use. IPv6 is the future of IP addressing and still isn’t fully implemented.
IPv4 defines the form of an IP address. According to the protocol, every IP address is a string of 32 bits, divided into octets (groups of 8 bits – eight 1s and 0s). Every IP address in binary form can be translated into numeric values. We perceive IP addresses as 4 numeric values with dots between them. Computers and networking equipment perceive IP addresses as 32 bits.
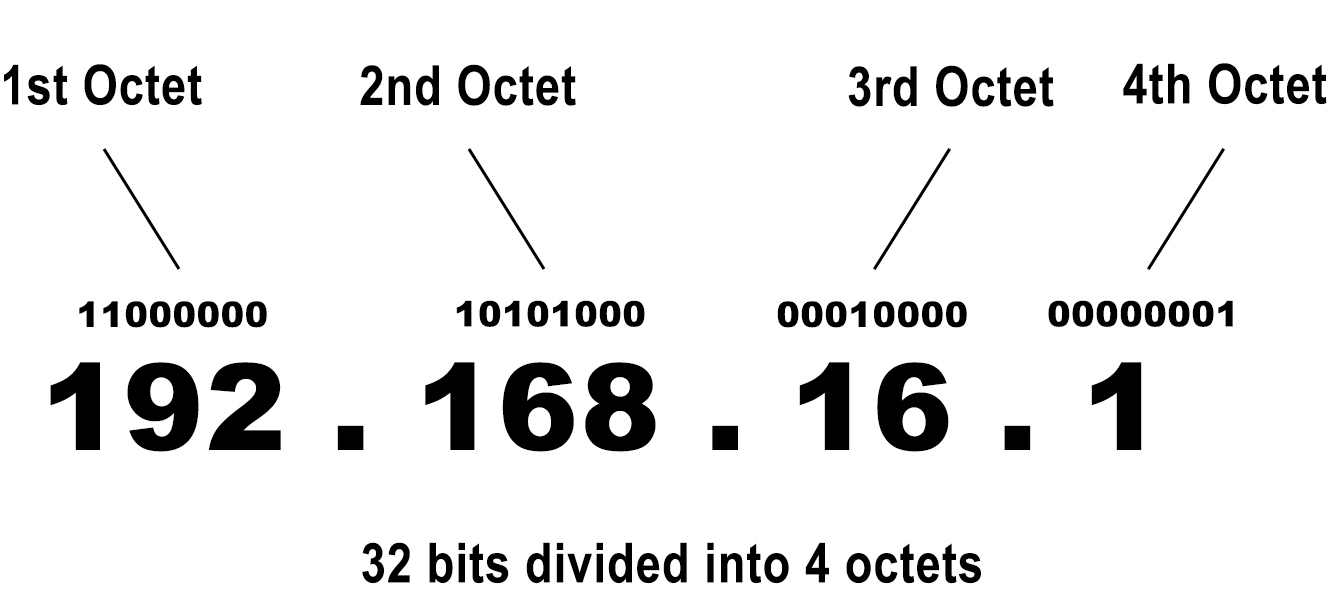
Each of the four numbers in an IP address ranges between 0 and 255. It can’t be a number larger than 255. Why? Because the smallest number you can write with 8 bits is zero (8 zeros), while the largest number you can write with 8 bits is 255 (8 ones). So, an IP address may look like this – 192.168.16.1. But it can’t look like this – 258.168.2.5.
What Kinds of IP Addresses Are There?
There are different ways to classify IP addresses. First of all, you have 5 classes. Each class is of a different size and is designed for a different purpose. Then, you have private and public addresses. Finally, you have static and dynamic IP addresses. Let’s start with classes.
There are five classes (from A to E). The first three classes are used for networks of different sizes. The fourth class (Class D) is reserved for multicast purposes, while the fifth class (E) is reserved for experimental purposes.
Of all the available IP addresses (4.3 billion addresses), half belong to the Class A. Class A addresses are reserved for large networks with numerous clients. 8 bits in these addresses define the network, while 24 bits define the host/client.
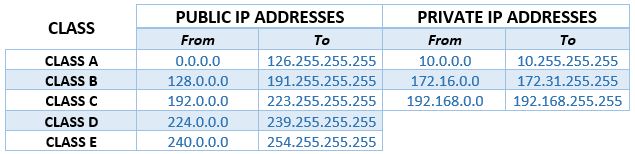
Class B addresses are reserved for medium and class C for small networks. In class B addresses, the first 16 bits (the first two numbers) define the network, while the other 16 bits define the host. In class C addresses, you have 24 bits defining the network and 8 bits defining the host.
Class A allows you to have a smaller number of networks with a huge number of clients, while Class C allows you to have a larger number of networks with a smaller number of clients on each network.
Based on their application and characteristics, IP addresses can be divided into two groups – private and public. Public addresses can be routed over the internet – they are visible online. Private addresses are not routable – they are not visible online.
Your computer, your phone, your tablet, and any other device connected to your wi-fi has a private IP address. Every device on every private wi-fi network has a private IP address. Websites and servers, on the other hand, have public IP addresses.
There’s a dedicated block of private IP addresses within the first three classes (A, B, and C). These blocks are used only on local area networks (like your home wi-fi network). In total, there are 18 million private IP addresses.
Now, let’s talk about the purpose of private addresses. The first question we are going to answer is – why do we need private addresses? The answer is – to prolong the use of the IPv4 protocol. There are already much more devices connected to the internet than available IP addresses (10 billion VS 4.3 billion). So, giving a unique IP address to every single device connected to the internet is simply impossible.
Similar Articles:
As you know, the address of your device must be unique. Having two devices on the same network (on the internet) with the same IP address creates a conflict, and the information doesn’t know where to go. The solution introduced by the IPv4 protocol are private addresses. The advantage of private addresses is that they can be reused an unlimited number of times on an unlimited number of networks (but can be used only one time on one network).
Every device connected to your wi-fi (including your router) has a private IP address. That applies to every home wi-fi network. One private address is preassigned to your router by the manufacturer. This address is called the default IP address. Your router holds a scope of addresses (from the same subnet) and assigns them to your devices. These addresses are only used for communication within your wi-fi network (within your home LAN network). On that single network, you mustn’t have two devices with the same private address. But there can be a device on your neighbor’s wi-fi (which is a different LAN) using the same address as one of your devices. There’s no conflict since the two devices are on two separate LANs.
While all of your devices have private IP addresses, they don’t use these addresses for internet access. They all, in fact, use your router to access the internet. You see, the router uses its default IP to communicate with other devices connected to your home network, but the router (your network) also has a public IP address. This address is assigned to your network by your internet provider. Your router uses this single public IP address to access the internet and respond to requests sent from all the connected devices.
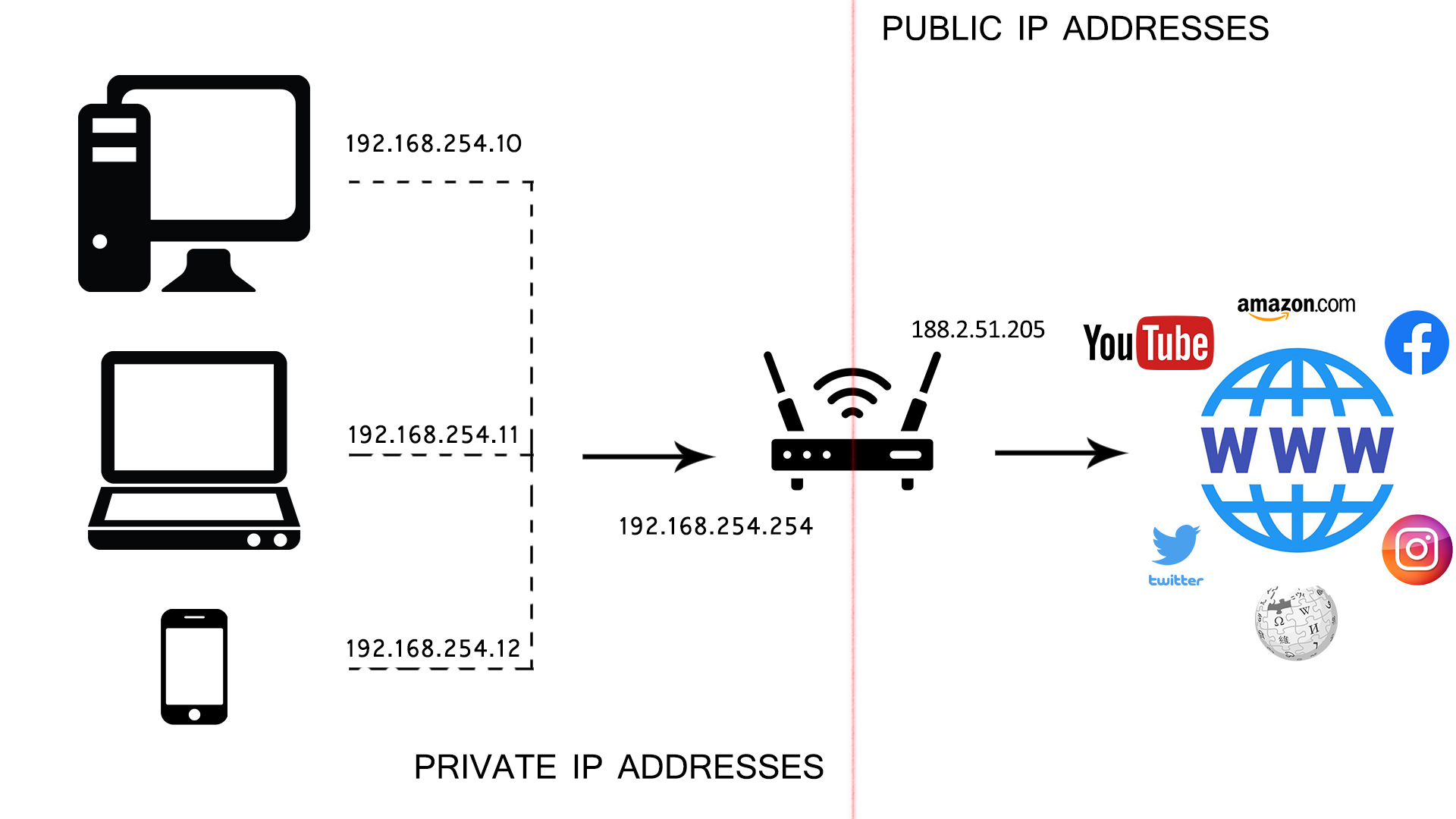
So, when you type in some web address and press Enter, your request is sent to your router (router and your PC use private IP addresses for this communication). The router then uses a public IP address to access the DNS server and get the info you requested. The router gets a response from the server, forwards this response to your device, and the website opens. The introduction of private addresses allowed us to use one (private) IP address an unlimited number of times and to use one public address for multiple devices (all devices on a single LAN) without creating a conflict.
What Kind of Address is 192.168.16.1?
192.168.16.1 is the second IP address in the 192.168.16.0/24 subnet. This is the first address in this subnet that can be assigned to some device since 192.168.16.0 is the network address for this subnet. It belongs to a reserved block of private IP addresses (192.168.x.x) within the Class C. All Class C addresses (both public and private) are used on smaller networks. Private addresses, like 192.168.16.1 are only used on smaller local area networks or LANs.
Can This Address Be A Default IP Addresses?
Yes, it can. As you may know, the starting (and ending) addresses in a subnet are the most common choice for default IP. Even though all the private addresses are equally viable options, manufacturers simply prefer to assign starting and ending addresses in a subnet to their routers. The most popular choices are, by far, 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.1.1. Numerous manufacturers also use 10.0.0.1, 192.168.0.254, and 192.168.1.254.
192.168.16.1 is the starting address of the 192.168.16.0/24 subnet, which makes it a somewhat better choice than other addresses from the same subnet.
What Devices Use 192.168.16.1 as a Default IP?
Even though it’s not commonly used, we have found a manufacturer that assigns two addresses from the 192.168.16.0/24 subnet to its routers, access points, and range extenders. That’s a Chinese company called LB Link.
Some of the LB Link devices using 192.168.16.1 as a default gateway are BL-W1200, BL-WDR4600, BL-WR4000, BL-310R, BL-WR3000. These are all wireless routers.

Is This Address My Default IP Address?
Unless you’re using one of the LB Link routers, it probably isn’t. But you can find your default IP address quickly by checking the label on the bottom of your router or the user manual.
You can also find your default IP address in a few simple steps on your Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, or Linux device. Don’t know how? Read our guide and learn everything about it.
What Can I Do with My Default IP Address? How to Use 192.168.16.1 as a Default IP?
Your default IP address gives you access to your router’s configuration page. Whether you just want to monitor your network and check the status, or change your network settings (LAN, WAN, DHCP settings), QoS settings, Firewall settings, sharing settings, etc., you need your default IP to access all those settings.
Most people don’t use advanced settings, but one thing we all do is changing the network name and protecting the network with a password. We’ll show you how to do this on devices that use 192.168.16.1 as a default gateway.
How to change the network name and wi-fi password on LB Link routers?
The first thing you’ll have to do is type in your default IP (in this case – 192.168.16.1) in your browser’s address bar.
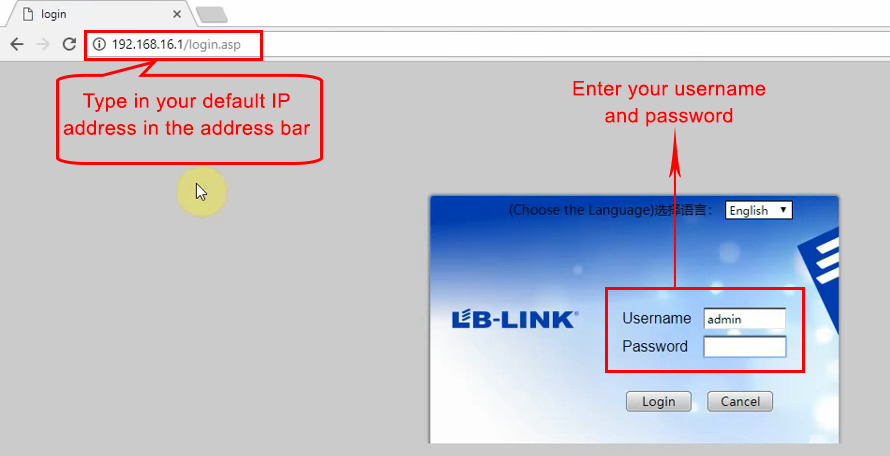
When you press Enter, the Login window will appear. You will have to enter the username and password. If you are accessing this page for the first time, you’ll have to use your default username and password. For most LB Link routers, you’ll use admin/admin as username/password. If you have changed the defaults, you will have to use your new username and password and, if you can’t remember them, you will (unfortunately) have to reset your router. Have in mind that once you reset your router all the previous changes will be lost.
When you click on Log in, the status window will appear. If you’re accessing the Configuration page for the first time, you may have to select the operation mode and go through the initial settings.
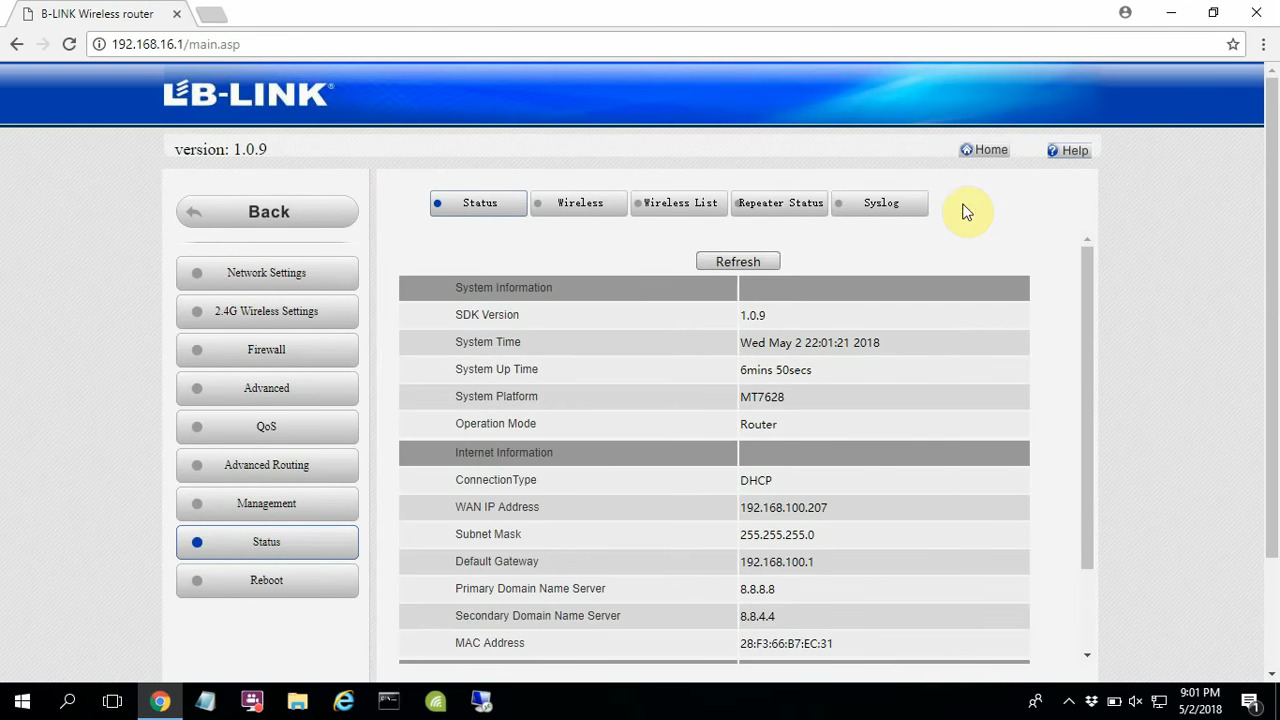
LB Link router status window
To change the network name and password, you will have to select the 2.4G settings (or 5G settings) tab on the left.
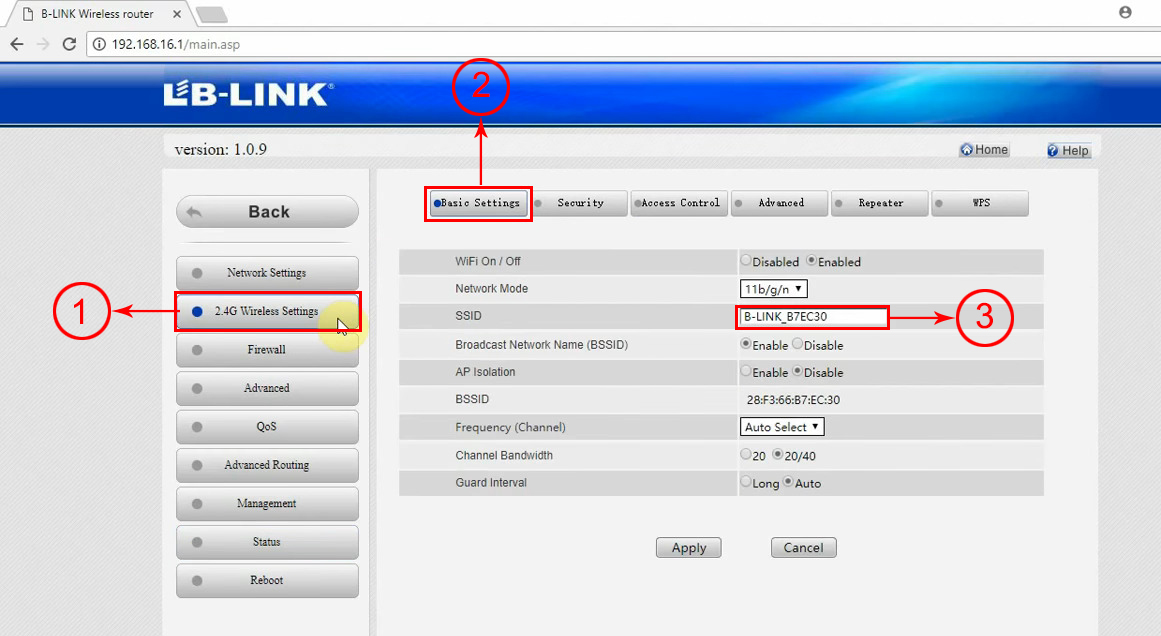
In 2.4G settings, go to the Basic tab (2), and enter the desired network name in the SSID textbox (3). Once you enter the name, click Apply.
To change the password, go to the Security tab. Select WPA2-PSK as a security mode, enter the password and click Apply.
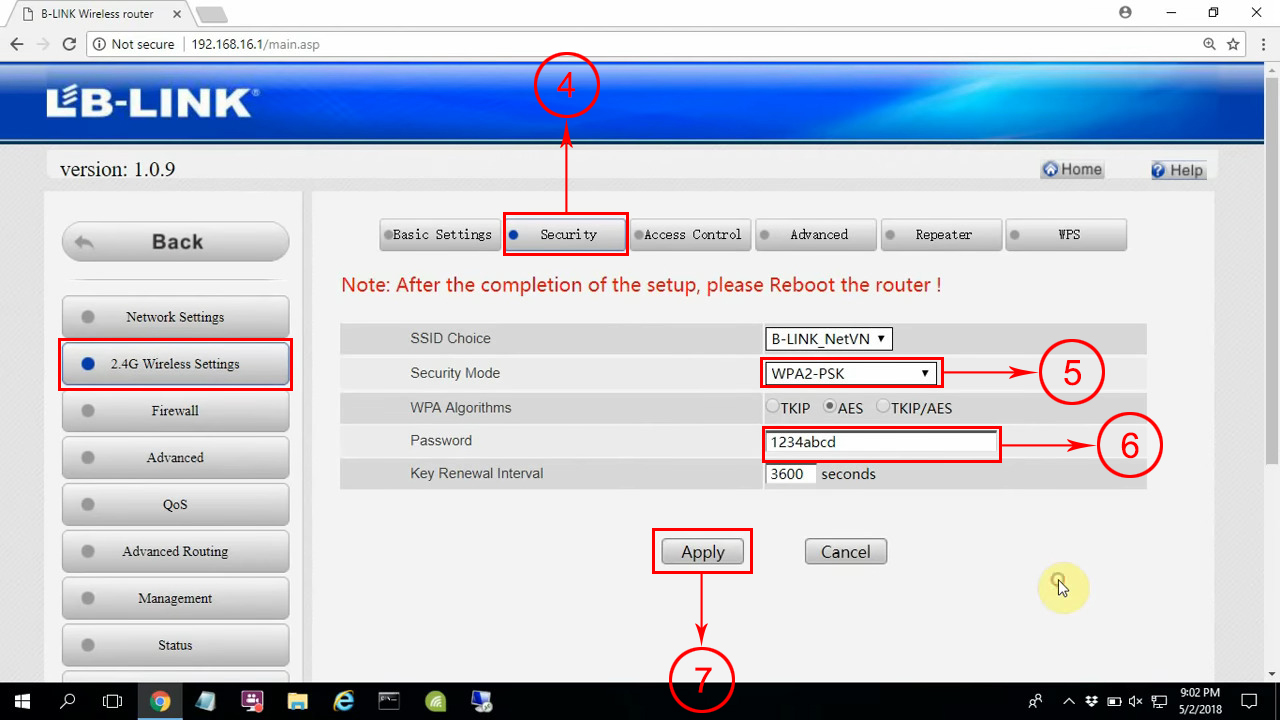
Once you change your network name and password, you will have to reboot your router. The changes will take effect after rebooting.
Can 192.168.16.1 be a Client IP?
It rarely is, but 192.168.16.1 can theoretically be a client IP address – it can be assigned to some of your devices. For that to happen, you will need a router with the default IP address from the same 192.168.16.0/24 subnet. LB Link, for example, also makes routers that use 192.168.16.254 as a default IP. Such a router may have a DHCP pool that includes 192.168.16.1. If the address is inside the DHCP pool, then it can be assigned to some device – it can be a client IP address.
Now, any client IP address can be dynamic or static. If the address is assigned without your intervention, then it’s considered dynamic. That means that the address is assigned automatically and that it doesn’t stay with one client/device forever. The dynamic IP address is leased to a device. When the lease time expires, the router will check if the address is still in use (if your device is still connected) and, if it’s not connected, the router will take it back. When the address returns to the DHCP pool, it can be assigned to some other device.
If you want one IP address permanently assigned to one device, you have to assign it manually and make it static.
How to assign 192.168.16.1 as a static IP
Assuming that you’re using an LB Link router and that your router’s default IP address is 192.168.16.254, 192.168.16.1 could be one of the available addresses in the DHCP pool. And, even if the DHCP pool doesn’t include this address, you can expand it to include it.
When you log in, you have to go to network settings, and then to the DHCP server. Enable the DHCP server and adjust the scope – make 192.168.16.1 your starting IP address.
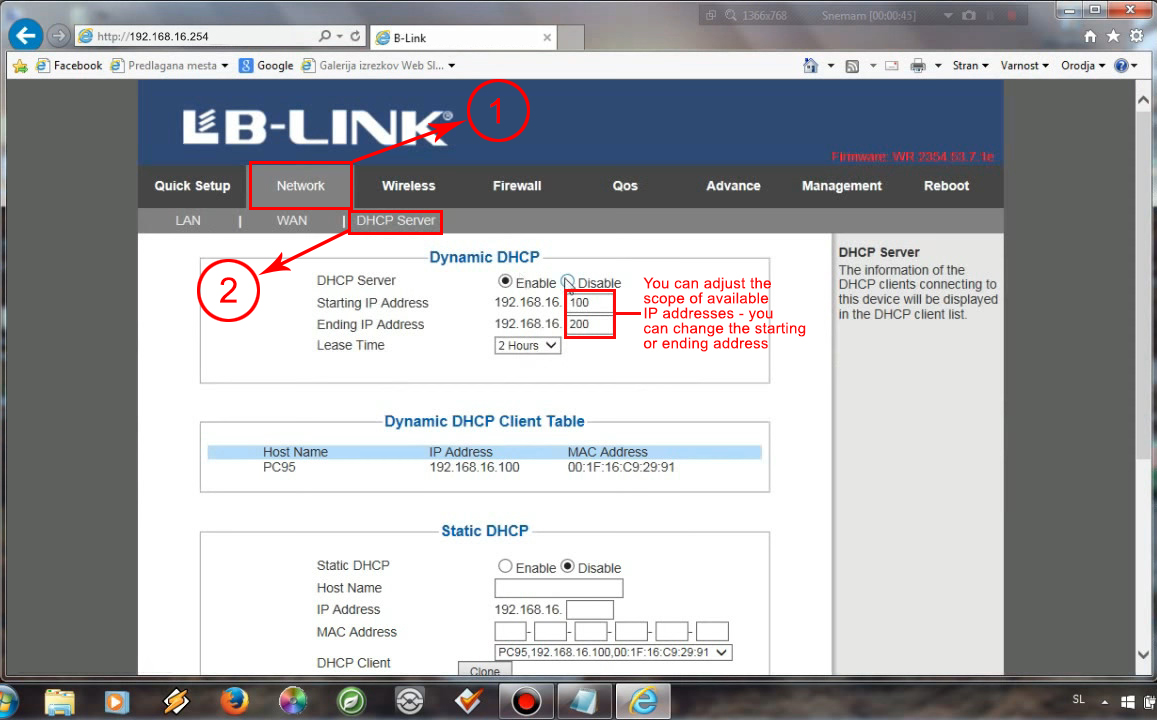
Once you adjust the DHCP pool, you can scroll down (or select the Static lease tab or Static DHCP tab) and enter the required data. You will have to enter the device’s hostname and MAC address, and you’ll have to enter the IP address that you want to assign to that device. When you enter all the required info, you just have to click Apply and log out.
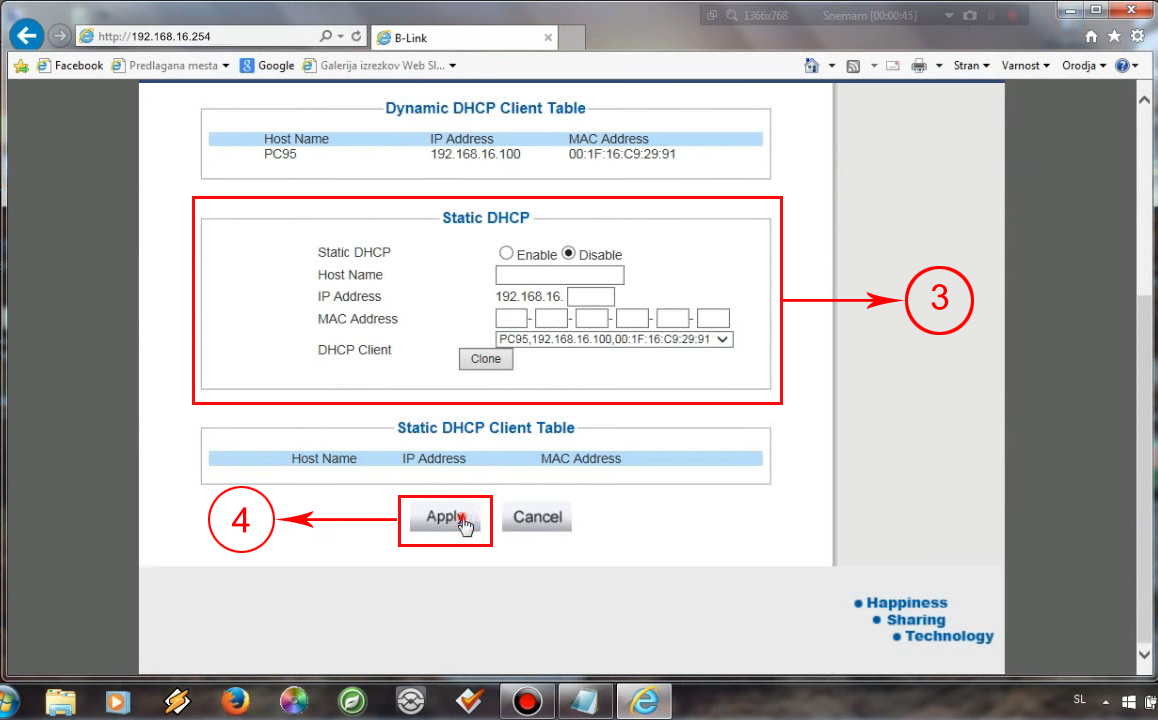
The next time you connect it to your wi-fi, your device will get the address you assigned to it.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.
