If you are reading this, you probably came across some issue that requires changing the NAT type to fix the problem. Before we explain how to change the NAT type, let’s see what NAT is and why you need to change the NAT type to fix some connectivity issues.
So, let’s take it from the top:
CONTENTS
What is NAT, and why do we use it?
Every computer or other device on the internet needs an IP address as an identifier. Look at it as a home address. This address is required so other computers and devices can know who is sending the data and where to send the answer.
IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4) is one of the core internet protocols, and It uses 32-bit address space. To put it in numbers, it can generate a unique address for 4,294,967,296 devices. Now, this may sound like a considerable number. However, keep in mind how many mobile phones, PCs, TVs, servers, and other devices need IP addresses to connect to the internet in the entire world. Do the simple math, and you will soon realize that these 4,29 billion addresses are not enough. This is where NAT comes in handy.
NAT allows you to use only one public IPv4 address for your entire network, thus preserving the IPv4 pool. If two same IP addresses appear in the network an IP conflict will occur. All the devices connected to your network use a single public IP address to communicate with the rest of the internet.
This feature of the NAT won’t cause you any connectivity issues. However, NAT also plays the role of the firewall, and this feature is what causes your connectivity problems.
Possible Issues With Using NAT to Access the Internet
Since it plays the role of the firewall, NAT decides what data packages can go in and out of the network. Depending on the settings, e.g., NAT type, those rules can vary from open to strict. The more rigid the NAT type is, the more connectivity issues can pop up, especially if you’re trying to play some online game with migrating hosts.
Types of NAT
Like we mentioned earlier, there are more possible NAT settings. Three, to be exact. OPN, MODERATE, and STRICT. Each setting applies more restrictions to what can go in and out of the network than the previous one.
NAT Type 1 – OPEN
This type places no restrictions on the traffic. Everything goes in and out, but this type presents a security risk because there is no control. Hackers can have free for all on your network and computer.
NAT Type 2 – MODERATE
This setting allows some ports to be open and places some restrictions. If the NAT on the other end is set to moderate or open, there will be little or no issues with connectivity.
NAT Type 3 – STRICT
Any data entering the network will be severely restricted. Since this is the default setting for most routers, it can present an issue since the NAT type 3 can connect only to the user with the NAT set to OPEN.
How to change NAT Type?
As you can see from above, changing NAT type is necessary in some cases to establish a connection. Here are a few common ways to do it effectively
UPnP
UPnP, or Universal Plug and Play, is a feature that allows different devices on the network to connect and communicate. Doing what it is designed for allows automatic port forwarding, making it easy to get the data packages in and out of the network. However, this way of changing the NAT type presents a significant security threat due to its open nature.
To turn the UPnP on, you’ll need to log in to your router’s admin panel.
Find your router’s IP address by typing in the “ipconfig” into the Command Prompt (type in cmd into the search bar next to the windows logo and select Command prompt) and pressing enter. The router’s IP address will be next to the “default gateway,” It should be something like 192.168.1.1 or similar.
Write/copy this address and enter it into the address bar of the internet browser.
A log-in screen will open where you will be asked for the admin username and password to proceed.
Default admin username and password can usually be found printed on the sticker at the back of the router.
Once you enter the admin panel, browse through the options and look for menu “WAN,” “Internet,” or “Local.” You should find the UPnP option in one of them. Enable it and save the settings by following the instructions in the admin panel.
Network discovery in Windows
This one is pretty straightforward. Just do the following:
- Click the Start Menu (Windows logo)
- Open Settings by clicking on the settings icon
- Click Network & Internet
- Click Sharing options.
- Expand the network profile assigned to the network connection (private or public).
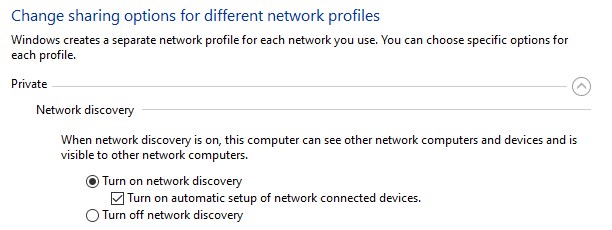
- In the Section of Network discover, select the “Turn on network discovery.” Also, tick the box “Turn on automatic setup of network-connected devices.”
- Click Save changes
Port Forwarding
This method requires you to log in to the router’s admin panel, just like with UPnP. So, enter the router’s IP address into the browser, and use the administrator credentials to enter.
Once you’re there, look for advanced settings or similar and try to find the “port forwarding” option.
Once you find it, you’ll need to enter the specific port for the program or the game.
Enter your IP address next to it.
Select the device you wish to point (Server IP). Select both TCP and UDP.
Save or apply and reboot the router.
DMZ
DMZ stands for DeMilitarized Zone. Enabling this feature on the router will fix your NAT problem, but it is highly unsafe. If you turn it on and enter the IP address of your computer as a demilitarized zone, you will become unprotected from all incoming traffic.
You can enable it by entering the router’s admin panel, finding this option, enabling it, and entering the IP address of your PC.
Keep in mind that your PC’s IP address will change every time you turn it off. If you want to keep your PC’s NAT set to OPEN, you’ll need to assign a static IP address to it.
Summary
NAT or Network Address Translation is used to preserve the IPv4 address pool and keep private IP addresses hidden from the internet. It acts as a firewall. There are three different NAT types. Open, moderate, and strict. To establish communication between various networks, you’ll need to change your NAT type to open.
The most common ways to do this change are by activating UPnP, port forwarding, or DMZ on the router or turning on automatic network discovery in the Windows network settings.

Hey, I’m David. I’ve been working as a wireless network engineer and a network administrator for 15 years. During my studies, I also worked as an ISP field technician – that’s when I met Jeremy.
I hold a bachelor’s degree in network engineering and a master’s degree in computer science and engineering. I’m also a Cisco-certified service provider.
In my professional career, I worked for router/modem manufacturers and internet providers. I like to think that I’m good at explaining network-related issues in simple terms. That’s exactly what I’m doing on this website – I’m making simple and easy-to-follow guides on how to install, set up, and troubleshoot your networking hardware. I also review new network equipment – modems, gateways, switches, routers, extenders, mesh systems, cables, etc.
My goal is to help regular users with their everyday network issues, educate them, and make them less scared of their equipment. In my articles, you can find tips on what to look for when buying new networking hardware, and how to adjust your network settings to get the most out of your wi-fi.
Since my work is closely related to computers, servers, and other network equipment, I like to spend most of my spare time outdoors. When I want to blow off some steam, I like to ride my bike. I also love hiking and swimming. When I need to calm down and clear my mind, my go-to activity is fishing.
