Slow internet speeds happen because of many reasons, and we relate one of these to home wireless routers. However, the main question here is – Can a bad router cause slow internet?
It’s best to first look at the possible reasons we have a slow internet connection and what might be the solutions for these issues. After that, we’re going to explain bad routers and slow internet.
CONTENTS
Slow Internet Causes
Sometimes we don’t need to look that far to know what’s causing our slow internet speeds. It’s a known fact that most ISPs use data caps as a part of their fair usage policy. This means that all subscribers get the same amount of data they can spend.
If this is the reason your internet connection is slow, there’s not much you can do. You can always change your ISP, but all the providers usually implement the policy. What are the other reasons for slow internet?
Slow Internet – Router Position
The most likely reason that you’re getting a slow internet connection is that the position of your router is not good. It’s important that the router is in a position where there are no barriers between it and most devices at home.
For WI-FI networks, the signals get interrupted by concrete objects. Because these block the signals that provide internet access, try to move the router to a more open location.
Slow Internet – Too Many Devices
It’s not a secret that when many people connect to the same network, they get a poor reception. Why? Because they overload the network. We get low-quality videos, slow internet surfing (more like floating), and other frustrating issues.
Imagine a really fast car, it’s a two-seater, and 5 people get into it. It will not drive at the same speed it would with only two people in it. We’ve added mass that wasn’t accounted for during the development of the car.
This happens with an internet connection as well.
Slow Internet – Bad VPN
A bad VPN (Virtual Private Network) can cause many more problems than just slow internet speeds. VPNs are a very safe way to browse the internet, but our data has to go through a VPN server.
So, if we get slow internet speeds when using a VPN, this either means that we chose a slow VPN, or that we didn’t configure it appropriately. When we choose a wrong VPN, it puts us at risk.
Why have a VPN at all if it’s not working properly or it’s slowing down our internet connection?
Slow Internet – Piggybacking
Piggybacking is using someone’s internet access without their permission. For example, you invite your next-door neighbor over, and they ask you for your Wi-Fi password, you provide it, and now your neighbor uses your internet access instead of his.
It sounds silly, but it happens more often than not. It’s a practice that definitely slows down your internet speed. You can always regulate this by assigning a maximum number of devices allowed on the router or blocking MAC addresses that aren’t yours.
Slow Internet – Outdated Routers
The only bad router is an outdated router. So, outdated routers cause slow internet speeds that can’t support the full capacity of the modern day connections. The router needs to support the latest network standard.
If one of the fastest internet speeds is 980 Mbps (Megabits per second), and you’re still using an old router from 2009, the internet is slow. It’s because the router from 2009 supports an outdated Wi-Fi standard with the maximum data rate of 600 Mbps.
As internet speeds and connectivity develop overall, new standards are released, and new hardware to meet those standards is necessary. It’s quite logical actually, when you’re a child you outgrow your first sneakers, the same happens with connection capacities.
Wi-Fi Standards Overview
The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) invented Wi-Fi standards for ease of categorization. With the current standards in place we know which hardware supports which standard, and we know the characteristics of each standard.
Two main things characterize each standard. These are speed and frequency. Speed handles how fast it transmits data, while frequency is the radio frequency through which data is transmitted.
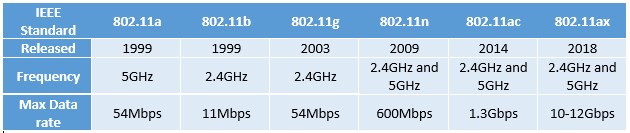
Based on these two factors, we have:
- IEEE 802.11a: Established in 1999, it transmits data through the 5 GHz (GigaHertz) frequency, and it supports up to 54 Mbps (Megabits per second).
- IEEE 802.11b: Also released in 1999, it transmits data through the 2.4 GHz frequency, but the speeds can reach only 11 Mbps. 2.4 GHz can reach larger distances, but is significantly slower than 5 GHz.
- IEEE 802.11g: It was released in 2003 based on a 2.4 GHz frequency, and it allows speeds up to 54 Mbps.
- IEEE 802.11n: Released in 2009, and it supports both 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz, plus it reaches amazing speeds of up to 600 Mbps.
- IEEE 802.11ac: Established in 2014, it runs on both frequencies, and it supports speeds of up to 1.3 Gbps (Gigabits per second)
- IEEE 802.11ax: This is the newest Wi-Fi standard, and the first router that supports it was released in 2018.
The latest standard is also called Wi-Fi 6E, it supports the 6GHz frequency. So, it’s actually quite simple. If you have a router that’s over 3 or 4 years old, you’re probably not getting the fastest internet speed. It might be time for an upgrade.
Conclusion
If your router is one of the latest routers on the market, and it meets the current standard, then it’s likely that you just need to reboot it as a quick fix to any slow internet speed. If that’s not the case, contact your ISP.
Also, you can try moving the router or installing Wi-Fi extenders, but you should only do this after you contact your ISP’s support. It might not be the router at all, it can be one of the other reasons that we listed.

Hey, I’m David. I’ve been working as a wireless network engineer and a network administrator for 15 years. During my studies, I also worked as an ISP field technician – that’s when I met Jeremy.
I hold a bachelor’s degree in network engineering and a master’s degree in computer science and engineering. I’m also a Cisco-certified service provider.
In my professional career, I worked for router/modem manufacturers and internet providers. I like to think that I’m good at explaining network-related issues in simple terms. That’s exactly what I’m doing on this website – I’m making simple and easy-to-follow guides on how to install, set up, and troubleshoot your networking hardware. I also review new network equipment – modems, gateways, switches, routers, extenders, mesh systems, cables, etc.
My goal is to help regular users with their everyday network issues, educate them, and make them less scared of their equipment. In my articles, you can find tips on what to look for when buying new networking hardware, and how to adjust your network settings to get the most out of your wi-fi.
Since my work is closely related to computers, servers, and other network equipment, I like to spend most of my spare time outdoors. When I want to blow off some steam, I like to ride my bike. I also love hiking and swimming. When I need to calm down and clear my mind, my go-to activity is fishing.
