There are many discussions about the default gateway FE80 online. Many people are curious enough to read about their network settings and look into what’s going on with their network.
To understand what default gateway FE80 is, you need to understand a little about internet protocols and how they work, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), and what a default gateway is.
CONTENTS
Internet Protocols
IPs are protocols required for network communication to send and receive datagrams. A payload and a header comprise a datagram. Because internet protocols establish network communication, they are the fundamental part of the internet.
Without the protocols, there would be no internet. They’re a set of rules that data and information traveling the network have to abide by. There’s another cardinal piece of networking called TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). It works with the IP, so we usually refer to them as TCP/IP.
How Does IP Work?
The TCP/IP has two layers. TCP is the protocol responsible for fragmenting the information into data packets before sending them to the receiving computer. Then, once the data packets reach the computer, they re-assemble into the information, i.e. any kind of content.
The other layer is the IP, which basically manages the addresses of the computers. When the computer sends the information, it has the IP info, the IP address of the computer that receives it, in the header of the data packet.
TCP/IP Explained
TCP/IPv4
The first public IP address was introduced as the IPv4 in 1980. This is the standard protocol of internet communication. IPv4 protocol supports 32-bit IP addresses. It was a great way to use addressing on the internet until critical mass was reached.
There are many strategies for IP address preservation. However, the space has grown too little for IPv4 IP addresses in the public domain, as there’s an increasing number of people using the internet, and there are more and more devices connecting to the IoT (Internet of Things).
TCP/IPv6
The IPv6 was first enabled on the 6th of June, 2012. The reason IPv6 was developed and enabled is what we mentioned previously. There are too many devices connecting to the internet and the public IP addresses with IPv4 are becoming exhausted.
This is the key difference between IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses. The IPv6 are 128-bit hexadecimal addresses. There’s a large combination of numbers and letters that can fit into an IPv6 IP address, and that’s why they’re so great.
IPv4 VS IPv6 Addresses
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
There are two configuration protocols on most networks. There’s DHCP and DHCPv6. The regular DHCP is a host configuration protocol that configures IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) hosts with their route, their IP addresses, prefixes, etc.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6 is the one that is used to configure all these settings on IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) supported networks. E.g. networks that run on IPv6 require different IP prefixes and other configurations.
DHCP Explained
What Is a Default Gateway?
A default gateway is the default route that the data packets take when communicating with other networks. It’s usually a request that travels through the gateway first, and once it reaches a web page, we wait for the answer.
We come across the default gateway term when we look at our network settings. The default gateway’s IP address is usually our router’s IP address. Now, the reason why we’ve mentioned all these things is the default gateway that has FE80 in it.
Default Gateway FE80
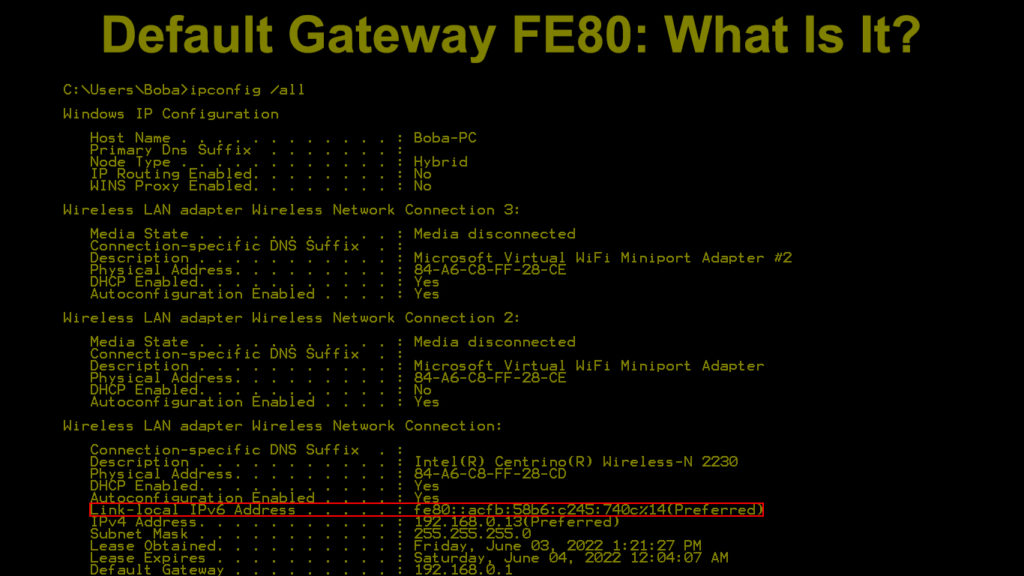
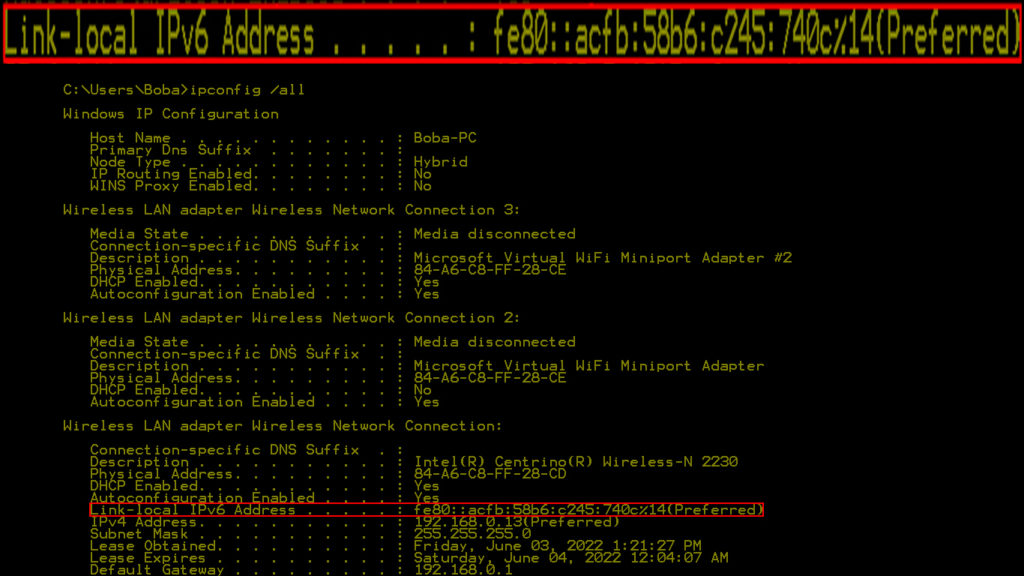
If you go to the Command Prompt by typing cmd in the Search box next to the start menu, and then type the command ipconfig /all and hit Enter, you can see the link-local IPv6 address, e.g. fe80::45a7:2cd8:f7a5:bf2a%16.
There’s going to be a ton of other information displayed. The default gateway FE80 prefix is the link-local IPv6 address, and it is assigned automatically by the DHCP. That’s the reason the prefix is FE80.
However, there are three more prefixes that can be used, the FE90, the FEA0, and the FEB0 prefixes. The only reason we always see the FE80 prefix is the fact that the DHCP automatically assigns this address.
Link-Local Address vs. Unique Local Address
A link-local address is usually a part of a segment of a network, whereas a unique local address is an address that can be part of a domain. The link-local address can detect duplicate addresses, discover neighbors, and other link protocols.
ULA (Unique Local Addresses) are the ones used to assign numbers to resources in the company’s administrative domain. Unique local addresses will stay the same if you change your ISP.
Conclusion
There you have it. Now you know a little more about IP addresses, the DHCP, and what a default gateway is. Remember, the default gateway FE80 prefix is always assigned automatically by your DHCPv6.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.
