Wi-Fi technology uses radio waves to transmit data from the router to compatible devices via frequency bands.
Frequency bands are radio wave ranges within a wireless network that carry Wi-Fi signals, allowing your devices to access the internet.
The bands define how wireless data travel between connected devices.
The two primary frequency bands in Wi-Fi technology are 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, and they consist of several channels that send and receive data within a wireless network.
Your Wi-Fi router must support at least one of these two frequency bands to transmit internet signals to your wireless devices.
The first Wi-Fi routers were single band, which means they could only support one frequency band.
Following advancements in technology, you now have more options between a single band, dual-band, and tri-band router.
This post explains more about dual-band Wi-Fi while highlighting how it works, its benefits, and its downsides.
CONTENTS
- What Exactly is Dual-Band Wi-Fi?
- How Does Dual-Band Wi-Fi Work?
- Differences Between the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz Bands
- Are All Wi-Fi Routers Dual-Band?
- What is the Difference Between Single-Band and Dual-Band Wi-Fi?
- Is Dual-Band Wi-Fi Better Than Single-Band Wi-Fi?
- Can I Use 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz in a Dual-Band Router Simultaneously?
- Types of Dual-Band Routers
- How to Know If You Have a Dual-Band Router?
- Pros of Dual-Band Wi-Fi
- Cons of Dual-Band Wi-Fi
- Conclusion
What Exactly is Dual-Band Wi-Fi?
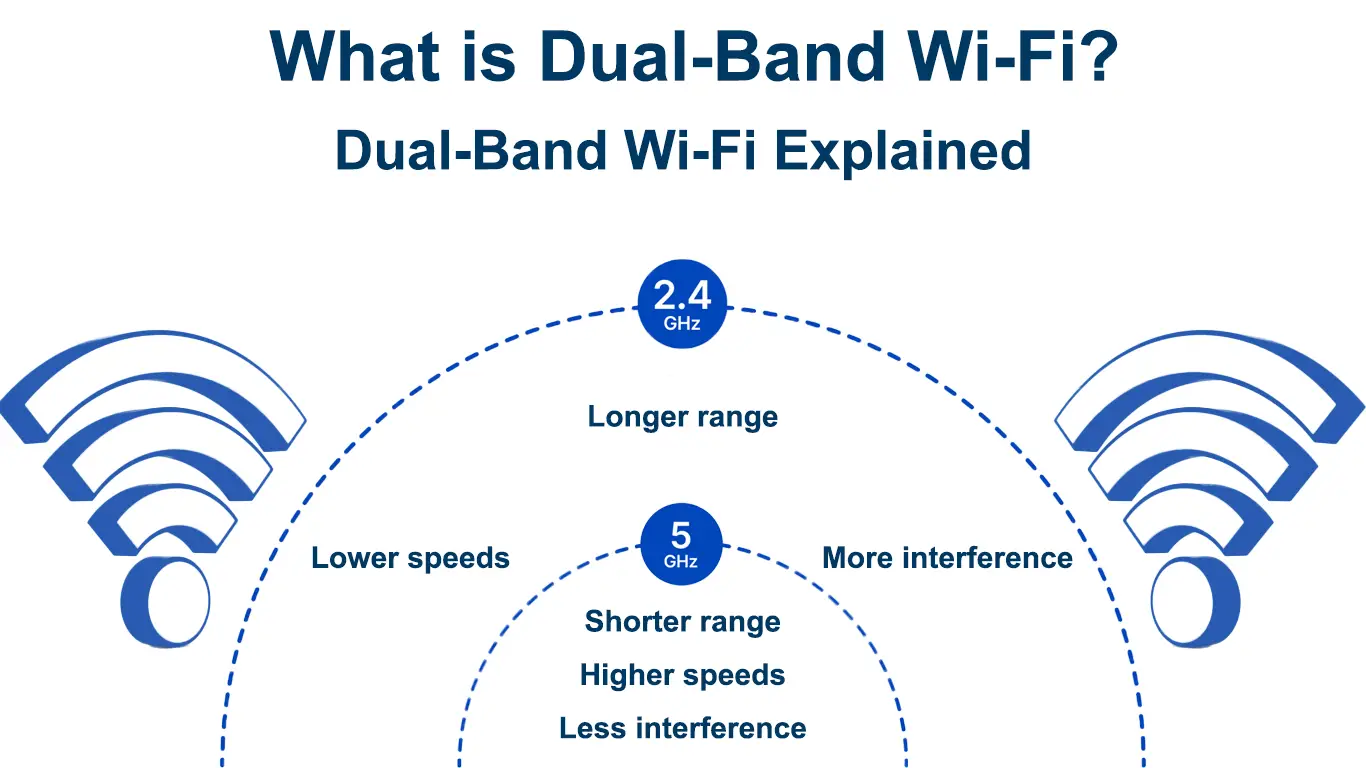
Dual-band Wi-Fi is a wireless internet network that supports the two primary frequency bands, including the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi bands.
This Wi-Fi feature broadcasts internet signals over both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands from a router to compatible wireless devices for faster and less congested internet connectivity.
Recommended reading: What is VZW Wi-Fi? (Do I Want VZW Wi-Fi Calling ON or OFF?)
Dual-band Wi-Fi is a step up from the old single-band Wi-Fi that only supports the 2.4 GHz band.
Even though the 2.4 GHz frequency band has a broader range and can penetrate through thick walls and solid obstacles, it is more prone to electromagnetic interference.
What is Wi-Fi Interference and How to Deal With It?
Besides, most wireless devices, such as baby monitors, cordless phones, and microwaves, operate on the 2.4 GHz band, which means the frequency is also susceptible to congestion.
The 5 GHz band addresses its predecessor’s shortcomings as it is faster and less prone to interference. Moreover, only a few gadgets operate on the 5 GHz frequency band, making it less crowded.
Most of today’s Wi-Fi routers are dual-band, transmitting two wireless signals simultaneously to connected devices.
These routers use artificial intelligence to determine the best frequency band for data transmission to a connected device.
If your smartphone or laptop supports the 5 GHz band and you are closer to the router, the router will automatically connect your device to the network via the 5 GHz band.
Since dual-band Wi-Fi routers broadcast data over the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, it guarantees better and faster internet connections.
How Does Dual-Band Wi-Fi Work?
Dual-band Wi-Fi works by transmitting two internet signals to your connected devices over the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz frequency bands.
It creates two wireless networks within one network, allowing your devices to connect to either the 2.4 GHz band or the 5 GHz band, depending on their capabilities.
Recommended reading: What is 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi? (When Should I Use 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?)
If your device supports the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz frequency bands, your router will automatically steer it to the best band via smart connect.
Most dual-band routers that use smart connect prefer the 5 GHz network since it is faster and less congested.
Band Steering Explained
The essence of dual-band Wi-Fi is to ensure your internet connection and devices perform at their best without performance drops.
With a dual-band router, you can browse the internet on one band (2.4 GHz) and stream HD videos on the other band (5 GHz), essentially preventing your wireless network from unnecessary congestion.
Even though dual-band Wi-Fi broadcasts two signals, you do not have to give the different bands separate passwords.
The transmission occurs within the same wireless network using two different frequency bands, meaning both bands share an SSID name.
Differences Between the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz Bands
Dual-band Wi-Fi simultaneously broadcasts signals over the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz frequency bands.
As much as these bands have striking similarities, they also have slight differences.
Understanding these differences can help you make the most of your dual-band router for an impeccable Wi-Fi experience.
Here are the differences between the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz frequency bands:
- Frequency Range
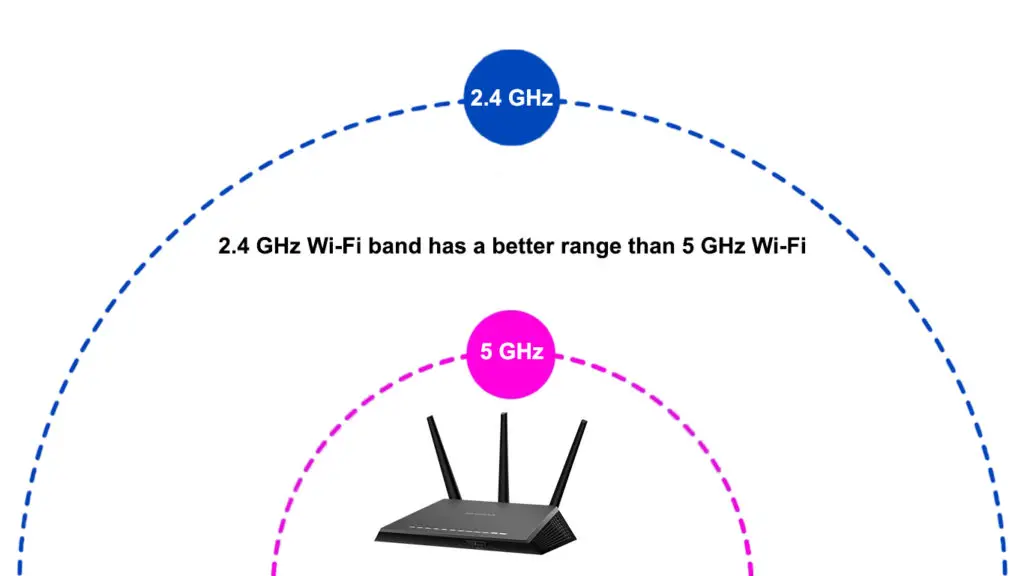
Even though the 2.4 GHz band transmits lower frequencies, it has a broader coverage area, averaging 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors.
2.4 GHz signals are stronger and penetrate through solid obstacles such as thick walls, doors, and floors, providing broader network coverage.
The 5 GHz band transmits higher frequencies but cannot maintain a strong signal over long distances, translating to a smaller coverage area.
Dual-band routers operating on the 5 GHz band can only reach 75 feet indoors and 150 feet outdoors.
- Channels
A Wi-Fi channel is a “mini frequency band” within a band that carries data from the router to connected devices.
The number of channels per band and the width of each channel determines data throughput and link rates.
The 2.4 GHz band has 11 channels, with three non-overlapping channels, while the 5 GHz band has 45 wireless channels, whereby 24 of these are non-overlapping.
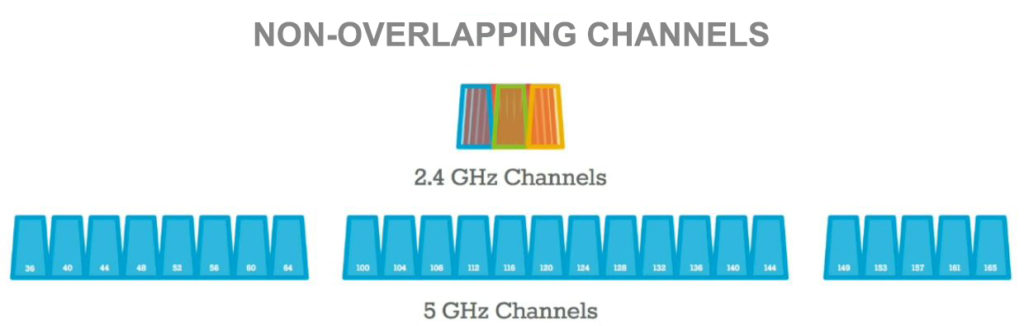
The difference in the number of channels explains why the 2.4 GHz band is slower than the 5 GHz frequency band.
Wi-Fi Channels Explained
- Channel Width
The channel width determines data transfer speeds and the number of devices supported over the different frequency bands.
The width of each channel on the 2.4 GHz band is 20 MHz, while the channel width on the 5 GHz band varies between 20 MHz, 40 MHz, and 80 MHz.
- Interference
Co-channel interference is one of the most significant differences between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Since the 2.4 GHz band has only 11 channels, 3 of which are non-overlapping, it is prone to overcrowding.
Besides, most wireless devices such as cordless phones, microwave ovens, Bluetooth speakers, and baby monitors operate on the 2.4 GHz band, increasing the likelihood of congestion.
Recommended reading: What is EVDO? (Guide to EVDO Telecommunications Standard)
The 5 GHz band has up to 45 wireless channels, whereby 24 of these are non-overlapping, making it less prone to interference and congestion.
Since most appliances and devices operate on the 2.4 GHz band rather than the 5 GHz band, the latter does not experience much overcrowding or interference.
- Speed
Speed is another notable difference between the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz bands.
Since the 2.4 GHz band has lower frequencies, it is slower than the 5 GHz band with higher frequencies.
The maximum practical speeds on the 2.4 GHz band are less than 400 Mbps, while the 5 GHz band supports top transfer rates of 1,300 Mbps.
The good news is that a dual-band router gives you the best of both worlds, and you can switch between bands depending on your device’s capability.
Dual-band Wi-Fi uses AI features like Smart Connect to connect your devices automatically to the most suitable band, effectively ensuring stable internet connectivity.
Differences Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Frequency Bands
Are All Wi-Fi Routers Dual-Band?
Not all Wi-Fi routers are dual-band. The first Wi-Fi routers were single-band, meaning they could only transmit signals over the 2.4 GHz frequency band.
However, single-band routers have their fair share of downsides, including slow transmission speeds, network congestion, and electromagnetic interference.
For these reasons, manufacturers came up with dual-band and tri-band routers to mitigate these shortcomings.
You can now use dual-band and tri-band routers for Wi-Fi connectivity.
What is the Difference Between Single-Band and Dual-Band Wi-Fi?
The primary difference between single-band and dual-band Wi-Fi is the supported frequency band.
Single-band Wi-Fi uses one frequency band, usually the 2.4 GHz band, to transmit data between connected devices.
In contrast, Dual-band Wi-Fi transmits data over two frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), ensuring users experience the best of both worlds without unnecessary slowdowns or performance drops.
Another notable difference between single-band and dual-band Wi-Fi is the speed. Single-band Wi-Fi is considerably slower than dual-band Wi-Fi since it only supports one frequency band.
Dual-band Wi-Fi provides users with more options regarding data transmission speeds since it uses both the 2.4 GHz band and the faster 5 GHz band.
Since single-band routers work using the 2.4 GHz frequency band only, they can maintain signal strength over long distances.
Moreover, single-band routers are cheaper than dual-band routers.
Is Dual-Band Wi-Fi Better Than Single-Band Wi-Fi?
From the above comparison, dual-band Wi-Fi is undoubtedly better than single-band Wi-Fi.
It allows internet users to enjoy a better Wi-Fi experience without frequent downtimes and network drops.
After all, dual-band Wi-Fi supports both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, allowing your router to select the best band for your device.
Dual-band Wi-Fi accommodates older and newer wireless devices and equipment so that you won’t experience challenges accessing the internet.
Can I Use 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz in a Dual-Band Router Simultaneously?
You can simultaneously use both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands on your dual-band router.
However, the possibility of using both frequency bands comes down to the type of dual-band router and if your wireless device supports both bands.
Some wireless devices, particularly the older ones, only support the 2.4 GHz band, while others support both and allow you to switch between the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, depending on your needs.
Types of Dual-Band Routers
There are two types of dual-band routers:
- Selectable dual-band router
- Simultaneous dual-band router
Selectable Dual-Band Router
Selectable dual-band routers operate on one frequency at a time.
These routers allow you to choose between the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz bands, depending on your preferences and needs.
Selectable dual-band routers have a similar bandwidth size as single-band routers, making them prone to interference.
However, you can switch between the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz bands from the router’s web configuration page.
Ensure your wireless devices and adapters support the 5 GHz network before selecting it as the default frequency band.
Simultaneous Dual-Band Router
Simultaneous dual-band routers receive and transmit signals over both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands simultaneously, hence the name.
They create two separate and independent wireless networks within the same Wi-Fi network, providing more flexibility and higher bandwidth.
Recommended reading: What is Panoramic Wi-Fi? (Introduction to Cox Panoramic Wi-Fi)
The best part is that you do not have to rename your router’s network name or provide a password for each band.
The router will automatically select the appropriate band for data transmission for each device on the network.
With a simultaneous dual-band router, you can set one network or band for regular browsing and the other network for online gaming, watching videos, and heavy streaming.
Selectable VS Simultaneous Dual-Band Routers
How to Know If You Have a Dual-Band Router?
Even though some router’s come with a sticker indicating they are dual-band, you cannot quickly tell if you have a dual-band router by just looking at it.
You have to visit your router’s web configuration page or check via your PC using the command prompt to confirm if your router and PC are dual-band compatible.
Here’s how to check if your PC supports dual-band:
- Type CMD on the Windows search bar near the Start button
- Select Open Command Prompt as Administrator
- From the Command Prompt Window, type “netsh wlan show driver” without the quotes
- Press the Enter key
- Look for Radio types supported. If your router supports only 802.11 b and g, i’’s a single-band router. If it supports 802.11 b/g/n, there’s a chance that it is a dual-band, but it’s probably just a single-band. If it also supports 802.11ac or 802.11ax, your PC is dual-band compatible
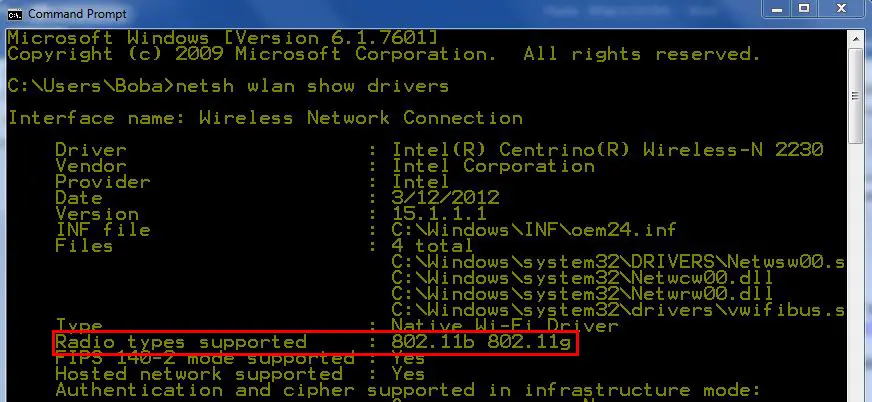
This PC supports only 802.11b and 802.11g – it is not dual-band-compatible
How to check if your router is dual-band from the web configuration page:
- Connect your PC to your Wi-Fi network
- Launch your preferred browser and enter the default IP address to access the router’s admin site
- Enter your login credentials
- Go to Wireless Settings
- If you have the option to select the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, your router is dual-band compatible
You can also check if your router is dual-band compatible by visiting the manufacturer’s website and entering your router’s model number.
Another easy way is to check the user manual that came with the router for any relevant information regarding the router type.
Pros of Dual-Band Wi-Fi
- Multiple frequency bands for optimal performance
- Less prone to interference
- Reduced network congestion
- Provides higher bandwidth and more flexibility
- Smart Connect selects the ideal band automatically
Cons of Dual-Band Wi-Fi
- Dual-band routers are more expensive
Conclusion
Deciding whether you need a dual-band router or not should be an easy choice. After all, dual-band Wi-Fi addresses the shortcomings of single-band Wi-Fi by providing faster and more stable internet connectivity.
Dual-band Wi-Fi is more flexible and reduces network congestion for a better and more enjoyable internet experience.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.