Creating faster products, one launch after another has been a trend for decades. Faster cars using less energy, faster smartphones with longer-lasting batteries, and faster Wi-Fi continuously fill up popular reviews. Wi-Fi technology has evolved from the initial Wi-Fi 1 to the current Wi-Fi 6, with each version boasting a faster internet signal than the preceding version.
Wi-Fi 6 is still new, and only a few latest smart devices are compatible with it. Therefore, many users still retain Wi-Fi 5 although Wi-Fi 6 is much faster. But do you know how fast Wi-Fi 6 actually is? Well, you’re about to find out.
A home network with fast Wi-Fi is always in demand, especially when each family member has multiple high bandwidth-consuming online activities such as UHD/4K/8K video streaming, online gaming, and AR/VR applications. For instance, a typical family of four would have at least three devices each.
When you count in smart TVs, smart home appliances, and a CCTV system, the number of connected devices could easily reach 25 or more. With each device demanding more bandwidth, you need a Wi-Fi capable of delivering faster internet evenly to all connected devices, and not just to a limited number of devices. Wi-Fi 6 technology has bettered Wi-Fi 5 in that division.

CONTENTS
Wi-Fi 6 Explained
IoT has been increasingly associated with our lives during the last decade. An important technology that makes IoT possible is the wireless internet or Wi-Fi.
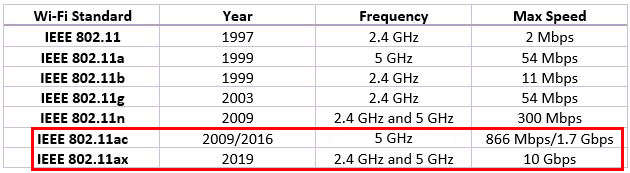
Created in 1997, Wi-Fi is a group of wireless network protocols that are built on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards. It allows surrounding devices to gain internet access and exchange data using radio waves.
The first version of the technology is 802.11b, and Wi-Fi 6 is the latest version, also identified as 802.11ax. Originally, the naming convention was 802.11XX, where the ‘XX’ denotes the version. Later, the convention changed to a more meaningful (and easier) naming – Wi-Fi 1, Wi-Fi 2, Wi-Fi 3, etc.
Wi-Fi 6 Explained
What Wi-Fi 6 Brings
Wi-Fi 6 provides a huge upgrade over Wi-Fi 5 and all the previous generations. Although the way we set up and use the Wi-Fi network does not change much, there are tons of improvements that make it a substantial upgrade. The first and foremost upgrade is definitely faster connection speed. Below, we have listed the most important upgrades.
Speedier Internet Connection
Wi-Fi 6 provides increased bandwidth that gives faster download and upload speeds. It’s crucial considering the increased file sizes and increased bandwidth demands, especially when it comes to high-quality video streaming, multiple-player online gaming, and AR/VR applications.
While Wi-Fi 5 can give you a maximum speed of 1.7 Gbps, Wi-Fi 6 boasts a maximum speed of 10 Gbps. Of course, in a real-life application, you won’t reach the maximum theoretical speeds, but Wi-Fi 6 can still offer much better speeds than Wi-Fi 5. It’s the result of applying better techniques like improved data encoding efficiency and smarter use of wireless spectrum.
Lower Latency
Efficiency is the key to Wi-Fi 6 gaining better performance than the previous Wi-Fi versions. It efficiently handles huge network traffic and brings down latency, much to the joy of online gamers. It also means quicker game downloads and seamless multitasking experience.
Closing the Gap Between Wired and Wireless Signals
Heavy users like gamers and AR/VR operators prefer to connect their devices directly to the router using Ethernet cables for the speed and stability of the internet connection. The wireless network seems to lack efficiency and reliability compared to the wired Ethernet connection, but Wi-Fi 6 manages to close the gap. As a result, more and more users will shift to the wireless signal due to its flexibility and the freedom of connecting without cables.
Maintaining High Speed on Busy Networks
In the early days of Wi-Fi, you’d probably have no more than five devices connected to the network. As more and more devices were added to the network over the years, the traffic congestion caused by the increased number of devices has taken its toll on the network.
Wi-Fi 5 may still be able to provide high-speed signals to individual devices, but it cannot handle the ever-increasing bandwidth requests from a multitude of devices such as TVs, PCs, laptops, tablets, games consoles, AR/VR devices, and even household items like fridges, dishwashers, washing machines/dryers, CCTVs, bulbs and many more. So much so that it’s not uncommon for a home network to have 50 to 100 connected devices simultaneously.
Recommended reading: How to Use Wi-Fi Direct? (A Complete Guide to Wi-Fi Direct)
Luckily Wi-Fi 6 has come to the rescue. It won’t necessarily increase the signal speed on individual devices, but it can maintain the bandwidth allocation to each device, where Wi-Fi 5 has struggled.
Why Wi-Fi 6 is Faster Than the Earlier Versions?
Firstly, it’s MU-MIMO (Multi-User-Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output) technology. As the name suggests, it allows multiple transmissions by multiple users simultaneously without sacrificing its stability. Although this technology has been introduced in Wi-Fi 5, the previous MU-MIMO version was not as capable as the MU-MIMO version in Wi-Fi 6.
Wi-Fi 6 uses MU-MIMO to transmit to up to eight devices simultaneously, compared to Wi-Fi 5’s four. Also, MU-MIMO technology was only available on downstream channels. In Wi-Fi 6, MU-MIMO is available on both – downstream and upstream channels.
What is MU-MIMO Technology?
Another distinguishing technology is OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access). It permits a single transmission to send data to multiple devices simultaneously, resulting in more efficient use of bandwidth. Consequently, other devices would have a chance to share more bandwidth.
The Difference Between OFDMA and MU-MIMO in Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 has also improved the beamforming technology to promote faster internet speed. Beamforming may sound too futuristic but it’s actually a straightforward new data transmission process. Traditional routers disperse a wireless signal to reach devices scattered in your home.
On the other hand, the beamforming technology directs the signal towards the exact device that requested it. As a result, you get a faster internet connection speed. Although the beamforming technology was present in the earlier Wi-Fi version, it has been improved in Wi-Fi 6 and it’s now more efficient.
What is Beamforming?
Wi-Fi 6 Progress
Similar to the 5G broadband cellular network, Wi-Fi 6 has not been implemented as fast as we would expect due to many hiccups and device/facility readiness issues. However, it has started to pick up the momentum with most new device launches carrying Wi-Fi 6 capability. Routers equipped with Wi-Fi 6 used to cost a bomb, but now the prices have gone down, and you can easily find one with an entry-level price tag.
Internet Service Providers have also joined the Wi-Fi 6 bandwagon by supplying the upgraded router to its subscribers. Inevitably, everyone would have to shift to Wi-Fi 6 technology to keep abreast with the progressive IT revolution.
Wi-Fi 6E
Yes, it sounds like a Wi-Fi 6 facelift. And, yes, it’s already in operation. Unlike Wi-Fi 6, which operates on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi bands, the latest Wi-Fi standard operates on a much faster 6 GHz band. Offering similar capabilities to Wi-Fi 6, like high performance, low latency, and fast signal speed, Wi-Fi 6E has the extra edge in the amount of bandwidth – it offers four times higher bandwidth.
However, you won’t see that many devices equipped with Wi-Fi 6E yet in the market since users are just getting accustomed to Wi-Fi 6. Also, Wi-Fi 6E devices and routers may not be compatible with Wi-Fi 6 devices.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi technology may not advance as fast as cell phones, tablets, and laptops. You may not see a new Wi-Fi version upgrade year-in and year-out since it involves a system, not just a device.
That said, in this fast-moving IoT era, systems need to keep pace with the demands of smart devices. Wi-Fi 6 brings Wi-Fi performance to a whole new level and enables further IoT development.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

