The internet has become an integral part of our lifestyles. It is rare to find a home or commercial establishment without Wi-Fi or an internet connection.
As our dependence on the internet grows every day, it is only natural that you’ll want to access the web in more places in your home or office.
Setting up a mesh network or access point can help extend your network and boost coverage in the entire building. These internet technologies also increase the number of users who can connect to your active network.
This post explains the differences between mesh networks and access points to help you decide which is suitable for your connection needs. Keep reading to discover the best fit.
CONTENTS
What is a Mesh Network?
A mesh network is a networking solution consisting of multiple routing devices that “talk” to each other, forming one massive seamless network and improving your internet coverage.
These routing devices, also known as nodes, connect wirelessly or through wires to all nearby devices, creating a mesh-like network.
The primary objective of a mesh network is to eliminate dead zones in your space and guarantee uninterrupted internet connectivity throughout your home or business.

A mesh network may consist of multiple routers, hubs, switches, or bridges. These networking devices all work as nodes on a mesh system, and they connect to as many other nodes to efficiently route data back and forth between devices.
Each node separately relays data to your devices without depending on each other to broadcast signals. This means there won’t be internet interruptions if one node fails or malfunctions.
Mesh networks use various data transfer technologies such as routing and flooding to transmit signals to your devices.
The best part is that you don’t have to configure the nodes to establish a connection. The nodes self-configure and self-organize automatically, allowing for dynamic data transmission.
The nodes use artificial intelligence to determine the best data transmission method, ensuring stable internet connectivity and network coverage throughout the entire home or organization.
Mesh Wi-Fi Network Explained
How Does a Mesh Network Work?
Unlike a traditional Wi-Fi network that broadcasts signals from a single point, a mesh network transmits data from multiple points, providing blanket internet coverage throughout your space.
The system works by broadcasting signals using routing and flooding technologies. The nodes use artificial intelligence to determine the best data transmission method for your Wi-Fi network.
In routing, the nodes use sophisticated algorithms to move data from node to node using the shortest and least congested path until it reaches the target destination.
Conversely, in flooding, data packets repeatedly move from a specific node to all the neighboring nodes on the network until the data reaches its destination.
Mesh networks also use AI to decide which path the data will travel to the connected devices, ensuring faster speeds, broader coverage, and more stable internet connectivity.
What is an Access Point?
An access point or AP is a wireless hardware device that relays data between an existing wired local area network and internet-enabled devices.
An AP acts as a portal or hub for your wireless devices such as phones, tablets, laptops, and cameras, allowing them to connect to your wired local area network.
The access point connects to the main Wi-Fi router using a high-speed Ethernet cable but transmits data to your devices wirelessly.
If you have ample space, you might require multiple access points to extend network coverage to all the rooms. Its primary objective is to boost your internet coverage in areas with low Wi-Fi or no signal.

You must place the access points in strategic locations in each room to guarantee stable internet connectivity.
All the access points connect to a single router, which manages data transmission, meaning you do not need multiple routers for each access point.
The main advantage of using a single router with multiple access points is that it makes it easy to manage your network.
All network changes and configurations happen centrally on one router, saving time and reducing the hassle since you do not have to configure individual routers separately.
What is an Access Point?
How Does an Access Point Work?
An access point works by extending the Wi-Fi coverage of an existing network to areas with poor or no internet signals.
In essence, it eliminates dead zones in your space by enhancing the wireless coverage of your existing Wi-Fi network, allowing more devices to access the internet.
You must strategically place the access point in dead zones or areas with low signal strength for the device to transmit signals efficiently.
The access point connects to your main Wi-Fi router or a switch using a high-speed Power over Ethernet (POE) cable.
Your router or switch must have a PoE port to complete the connection. The POE transmits data back and forth and powers the access point.
The access point communicates directly with the Wi-Fi router via a data cable before transmitting signals to designated problem areas.
It receives the signals from the router and transmits them wirelessly via the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands to all your compatible devices.
Difference Between a Wireless Router and a Wireless Access Point
Differences Between Mesh Network and Access Point
Even though mesh networks and access points work to improve signal strength and network coverage, they differ slightly in how they function.
Here are notable differences between mesh networks and access points:
- Infrastructure
Mesh networks consist of several nodes that communicate directly with each other instead of relying on network signals from a central router.
In contrast, access points connect to the main router via a high-speed Ethernet cable. The access points do not link to each other, like nodes in mesh networks.
- Installation
Access points require professional installation since the process entails drilling holes and laying Ethernet cables from the central Wi-Fi router to the access points. Moreover, you must mount the access points on the ceiling or walls for optimum efficiency and performance.
In contrast, you can install mesh networks without professional assistance. After all, mesh networks can work wirelessly, meaning you don’t need to drill holes or lay cables. Besides, mesh networks use artificial intelligence to operate, reducing installation overheads.
- Operation
Access points and mesh networks operate differently. While access points extend your network by connecting to a central router through an Ethernet cable, mesh networks do not rely on a single router. Instead, they operate via interconnected nodes that work and transmit signals independently.
- Configuration
Mesh networks consist of several nodes that have an integrated software program. This program automatically configures the node, meaning you do not need to manually set up the mesh system.
Access points, on the other hand, do not use AI. You have to configure the devices manually to extend your network coverage.
- Efficiency and Performance
Mesh networks and access points are both highly efficient. However, mesh networks have the upper hand performance-wise since they do not rely on data transmission from a single node.
Moreover, each node can communicate with every other node on the network, ensuring a stable and reliable internet connection. In a mesh system, node failure does not affect the network, unlike in an access point configuration.
- Cost
The cost of setting up a mesh network and an access point system is more or less the same. The overall amount depends on the number of rooms you want to extend the network. However, mesh networks are comparatively more expensive, especially when installing several nodes.
Pros of a Mesh Network
Easy Installation
Mesh networks are easy to set up since they do not require professional installation. You do not need to drill holes or lay cables like other network range extenders. You can also choose between a wired or wireless network setup for your mesh system for enhanced flexibility.
Self-Configuring
After installing and setting up your mesh network, you do not need to configure the nodes. After all, they come with a pre-installed software program that automatically configures and organizes the devices ensuring optimum performance and enhanced Wi-Fi coverage throughout the building.
Self-Healing
One of the most beneficial features of a mesh network is self-healing. A mesh network consists of multiple self-healing nodes, meaning if one of them fails, it won’t affect the network. Instead, the system will isolate the malfunctioning node and discover a new path to transmit signals while the defective node “heals.”
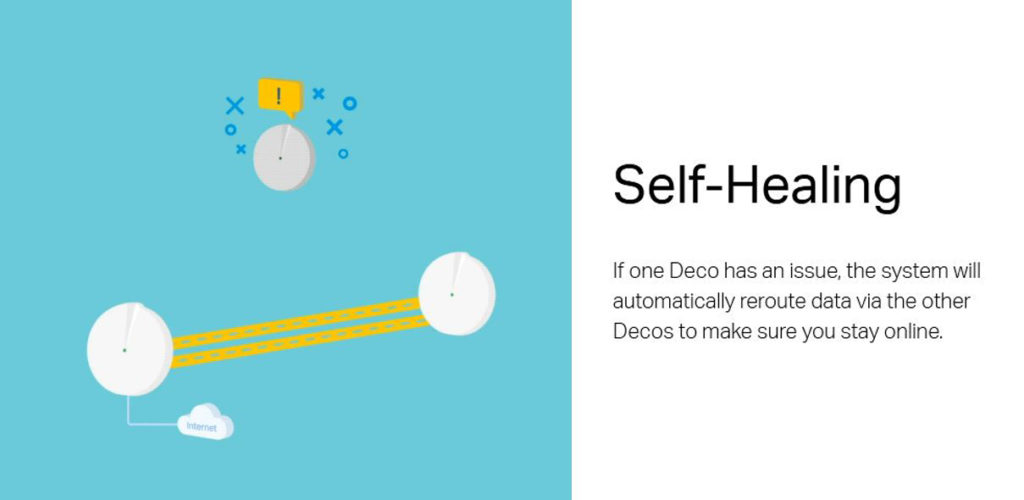
Source – TP-Link Mesh Systems
Enhanced Security
Let’s face it. Most Wi-Fi networks are not secure despite the numerous security mechanisms. It’s very easy for an experienced hacker to intercept data over a wireless network using various sophisticated tools. However, mesh systems are highly secure since you can isolate any compromised node to safeguard the network.
Easily Expandable
Another benefit of a mesh system is that it is easily expandable. You can add as many new nodes to the network to enhance your Wi-Fi coverage and ensure stable internet connectivity. The downside of adding more nodes is that it makes the network complex to troubleshoot in case of any issues.
Reduced Power Consumption
The different nodes on a mesh network consume less power since they don’t communicate through a single far-flung access point. They do not have to transmit data signals forcefully or intensely to a central router or access point, reducing power consumption.
Cons of a Mesh Network
Can Be Pricey
Mesh networks are generally inexpensive, but they can be pricey if you need to set up more nodes. You might require additional routers, bridges, hubs, or switches to act as nodes for your expansive mesh network.
Complex Troubleshooting
Even though mesh networks are self-healing and self-discovering, troubleshooting the system can be complicated if it involves numerous nodes. You can replace defective nodes, but identifying them can be an issue if you have an expansive mesh network.
Pros of an Access Point
Scalability
Wireless access points are scalable meaning you can easily add multiple access points to your Wi-Fi network to eliminate dead zones and extend coverage.
Real-Time Performance Monitoring
Access points allow you to monitor your network and measure performance in real-time via the control panel.
The best part is that you can see the number of users on the network at any given time. It also shows the type of devices and applications currently in use.
High-Capacity Load Balancing
Access points also support high-capacity load balancing. If one access point is overloaded, the system will shift some users from one access point to another, depending on the available capacity. Load balancing reduces congestion, ensuring fast and stable internet connectivity.
Indoor and Outdoor Coverage
Unlike other Wi-Fi boosters or network extenders that primarily function indoors, access points provide Wi-Fi coverage indoors and outdoors.
Besides covering your indoor space, you can set up an access point system to extend your internet connection to your outdoor spaces, including your patios, courtyards, and parking lots.
Low Latency
Access points offer fast internet speeds with low latency since they use an Ethernet cable to establish a connection with the primary router. A wired connection is less prone to interference than a wireless Wi-Fi connection, leading to lower latency.
Easy to Manage
Access points are easy to manage. All network changes and configurations happen centrally on one router, saving time and reducing the hassle since you do not have to configure individual routers separately.
Cons of an Access Point
Requires Ethernet Cabling
Access points must connect to the central router via an Ethernet cable, meaning you must drill holes and lay wires in your home or office to establish and extend your network.
Requires Professional Installation
Setting up an access point system might require the expertise of a professional since most of the configuration is manual.
Should I Use a Mesh Network or Access Point?
Choosing between a mesh network and an access point depends on several factors, including installation costs, network configuration, and connection needs.
Consider installing access points if you have an expansive space and want to experience fast and consistent internet speeds throughout the building.
This networking solution uses an Ethernet cable to connect to the main Wi-Fi router, reducing latency and slowdowns and guaranteeing stable internet connectivity.
Mesh networks are suitable for mid and large-sized businesses since they require a lot of equipment to make up the nodes. Even though these nodes work automatically to extend your Wi-Fi, configuring the network can be an issue when dealing with multiple nodes.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.
