IP addresses are an integral component of communication between devices. Whether you intend to print documents from a computer or browse the internet, your devices will use IP addresses. It is essential to understand how IP addresses work so that we can easily troubleshoot devices if they encounter IP-related problems. Considering IP addresses’ role when connecting devices, there are settings related to IP addressing that can help establish better connections. Such settings include using a Static IP and using DHCP reservation. The two are quite similar but have a few key distinctions that we will look at in this article.
Keep reading as we go through the two settings and compare them and determine which is the more effective one.
CONTENTS
What Is an IP Address?
Since both Static IP and DHCP reservation settings revolve around IP addresses, it’s important to define an IP address briefly.
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a series of digits identifying a network device. The Internet Protocol is a set of guidelines governing communication over the internet. The guidelines handle various internet aspects, such as routing data to the necessary destinations.
The basic function of IP addresses is to ensure information is transferred to the correct device in a computer network. That is why devices mustn’t share an IP address, as it would cause connectivity issues.
There are two versions of IP addresses, i.e., Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPV4) addresses use 32-bit addresses, while Internet Protocol Version 6 addresses use 128-bit addresses. IPV6 succeeds IPV4 to compensate for the fast-diminishing available IP addresses thanks to increased IP utilizing devices.
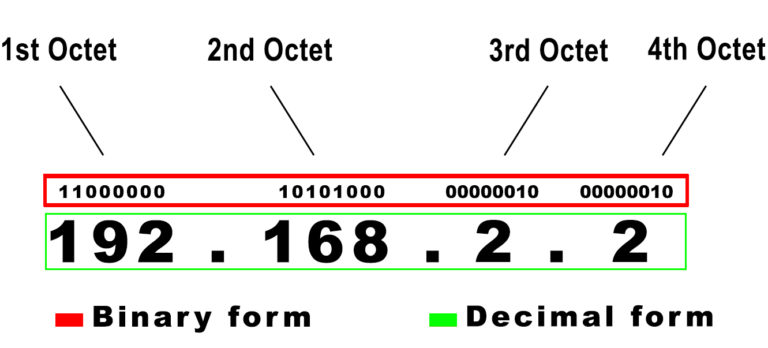
Example of an IPv4 Address (in binary and decimal form)
In the home setting, IP addresses can be categorized into Local (Private) and Public IP addresses.
Your router uses Public IP addresses to identify you to the internet. That way, any information transfer you conduct via the internet will get back to you and not to a random user elsewhere.
On the other hand, local or private IP addresses identify the specific devices in your local network, i.e., a phone or a laptop. That way, information in your local network is routed to the appropriate device thanks to Private IP addresses.
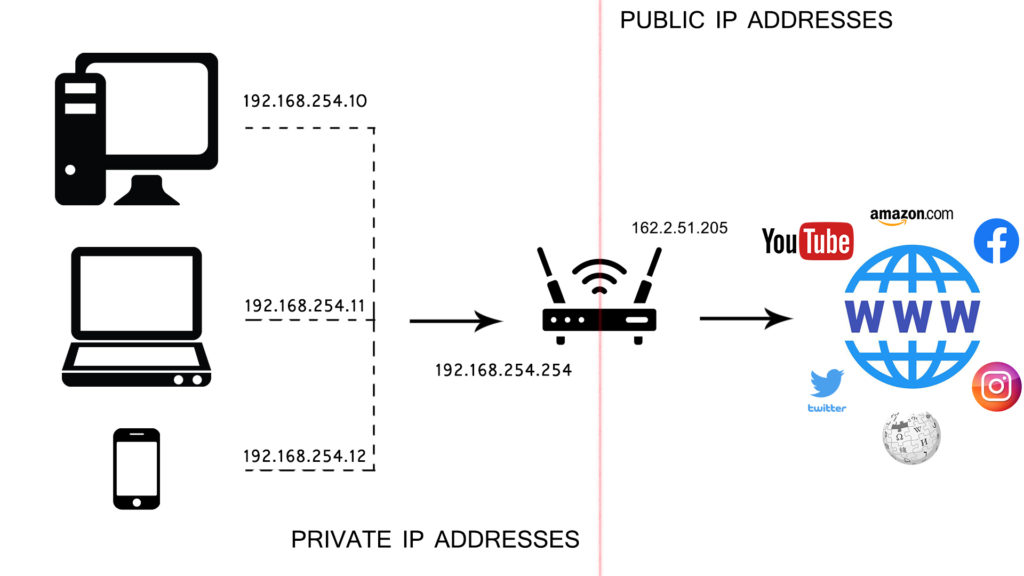
Public and Local IP addresses work in unison to ensure internet traffic is directed appropriately.
Throughout this quest to contrast and compare Static IP and DHCP reservation, we will be referring to private IP addresses unless stated otherwise.
Basics of IP Addressing (IPv4 vs. IPv6)
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP)
Your router or modem has a way of assigning IP addresses to devices in your home network to ensure devices are not sharing IP addresses.
The Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) is a set of guidelines for assigning dynamic IP addresses from a pool of available addresses to devices on a network.
A DHCP server works on various networks ranging from home networks to business networks.
DHCP servers can be separate computers that handle large corporations’ IP address assigning. But the router or gateway has DHCP server capabilities; hence they handle IP addresses in a home network.
A DHCP server assigns an IP address and additional network configuration information like the Default Gateway and Subnet.
Also, an IP address is leased temporarily to allow the reuse of addresses that are not in use. The server can renew the lease time to enable a device to keep using an IP address before the original lease time expires.
The protocol assigns IP addresses within a certain range to reduce the chances of IP collision.
What Is DHCP
Sometimes users might prefer using the same IP address for a particular device every time they join a network. DHCP reservation and Static IP are features that will let client devices use the same IP address every time, as we shall see.
What Is a Static IP?
As the name insinuates, a static IP is an IP address that does not change, unlike a dynamic IP address that changes from time to time.
Therefore, you can update the devices’ settings in your home to always use a particular IP address whenever they connect to the router.
However, remember to set an IP address out of the router’s scope to avoid IP collisions that will cause connectivity problems.
On the other hand, if you want your router/gateway to have a Static Public IP, you will have to contact your Internet Service Provider. That is because most ISPs charge for that kind of service.
You can navigate the connectivity settings of devices in your home and update them to use a static IP. But remember to assign an IP outside the DHCP scope (but from the same subnet) so that the router does not reuse IP addresses already in use.
When isolating an IP address, you must update additional information regarding the Subnet and Gateway addresses.
Static IPs are convenient for devices to easily establish a connection to a network since the required IP is already known.
Static IPs are convenient for business settings, while dynamic IPs are popularly used in home networks.
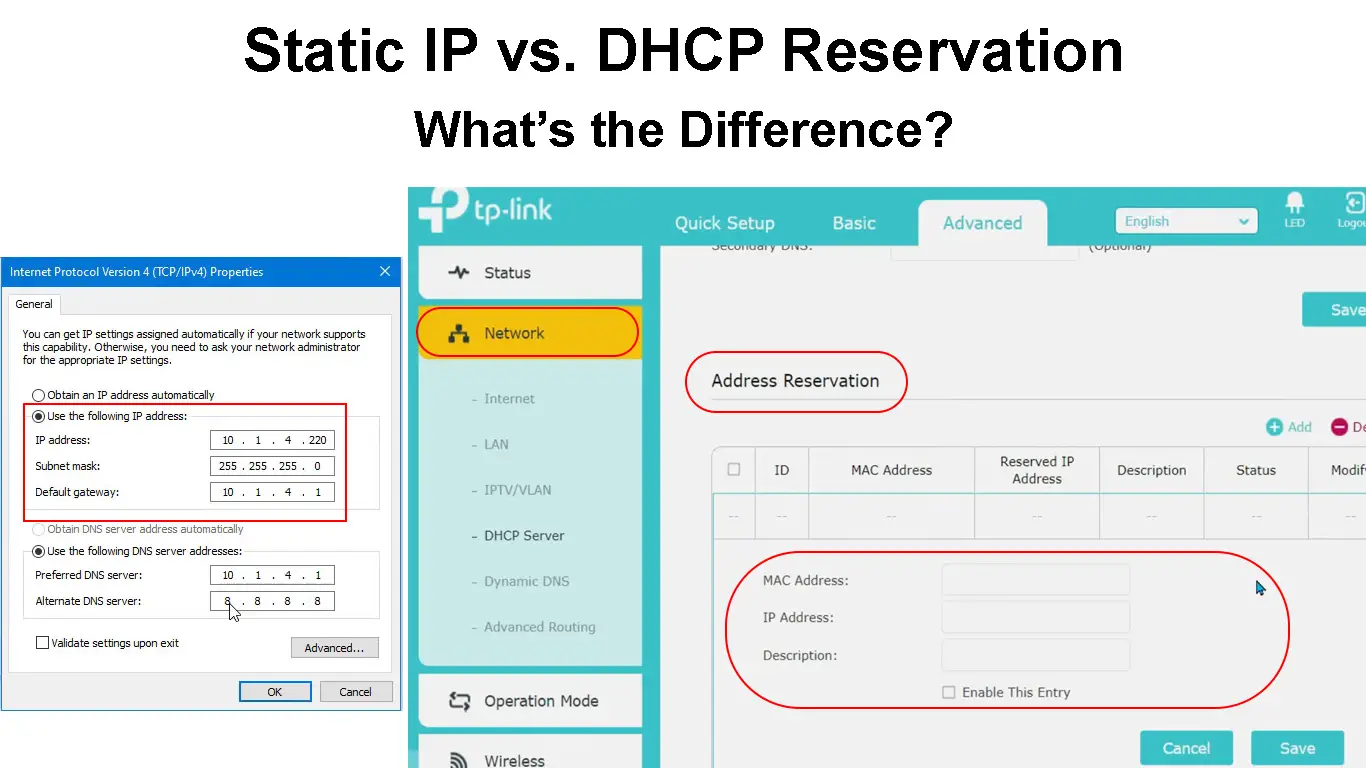
Assigning Static IP to a Windows 10 PC
Instances Where Static IP Addresses Are Necessary
Static IPs are necessary for setups where connectivity is critical and should be at its best. Businesses mostly use static IP addresses when hosting servers or websites to enhance connectivity. A static IP would ensure you know the exact address you need to access a server or website.
Essentially most general services like VoIP and streaming that are said to require static IPs can work with dynamic IP addresses.
You can also use static IPs if you have external devices or services, e.g., Network Attached Storage (NAS) or a printer, that you wish to connect to a network using an IP instead of the domain name. In that case, you assign a static IP to the device/service and use that IP to connect to said device or service.
Static IPs also enhance remote access through Virtual Private Networks (VPN) and Port Forwarding services.
A static IP is also helpful when adding a new router to a home network as it ensures traffic is routed correctly.
What Is DHCP Reservation?
DHCP reservation is what most would consider a convenient alternative to using a static IP.
DHCP reservation and static IP will achieve the same result of isolating a specific IP address for a specific device.
The difference is that DHCP reservation is made at the router/gateway while IP isolation is done in the client device.
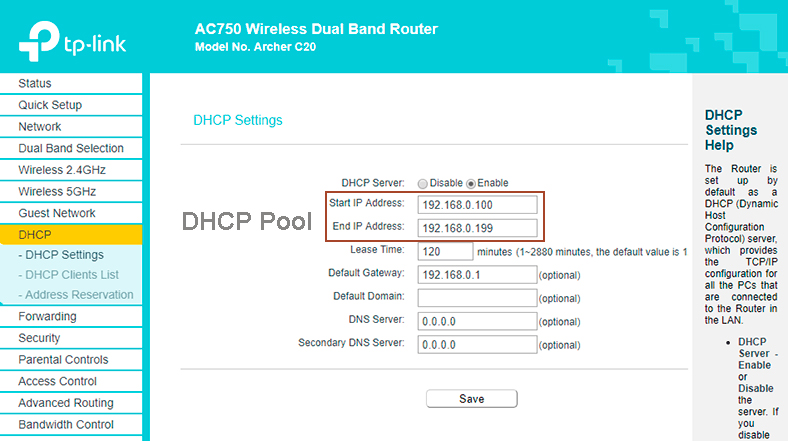
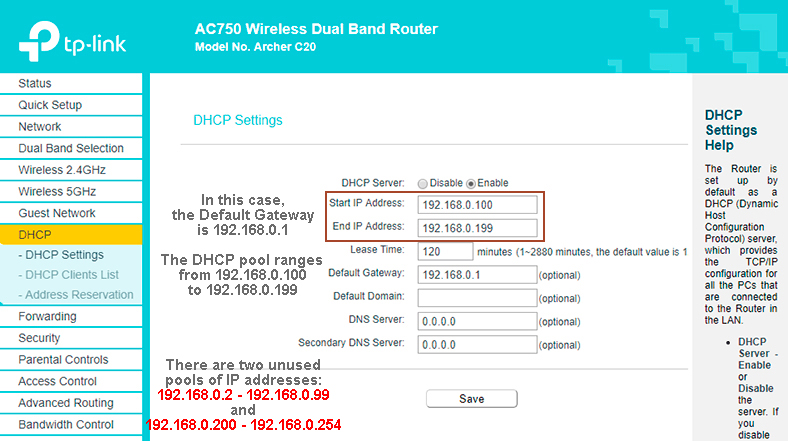
DHCP reservation entails setting aside (reserving) an IP address to be used by one specific device. Therefore, the server will issue the reserved address when a client device reaches out to a pre-configured DHCP server for an IP.
When using DHCP reservation, you will also have to include the physical Media Access Control (MAC) address of the target device in the DHCP server.
A MAC address is attached to a device’s Network Interface Controller (NIC), uniquely identifying devices on a network. Hence the MAC address will assist the server in identifying the device it has reserved an IP for.
Most ISPs and router/gateway manufacturers provide instructions on how to enable DHCP reservations on their websites. Similarly, you can find instructions in the router’s user manual.
Making a DHCP Reservation (TP-Link Router)
When to Use DHCP Reservation
DHCP reservation can be used in most instances where you use a static IP. However, the IP address you choose when using either method should be outside the scope of the DHCP server pool of IP addresses. That will ensure the chosen IP is not re-assigned to another device on the network.
Which Is Better: DHCP Reservation or a Static IP?
DHCP reservation is a preferable method of setting a permanent IP for a particular device since it allows you to manage the IP addresses centrally.
In comparison, if you use static IPs on many devices on a network, it would be cumbersome to manage them individually. Instead, you can reserve the IP from the server, automatically keeping a record of reserved IP addresses.
That way, you can easily change the address without going through the settings of each device.
DHCP reservation also greatly reduces the chances of simultaneously using one IP address for two devices.
Also, using a static IP on devices like mobile phones and laptops can cause problems if you switch to another network. The static IP might already be in use in the new network.
There are very few instances where using static IPs is exclusively necessary, but such are very rare to come across in a home network setting.
When using DHCP reservation, you will not have to update additional information such as the subnet, unlike when using a static IP.
Therefore, if you have an option to choose between the two, a DHCP reservation is a more convenient way to go.
You can also mix both configurations but be careful not to reserve an IP already used as a static IP. Although, there are very rare instances that might require you to do this.
The bottom line is you should rely on DHCP reservation and use Static IPs if there is no alternative.
A major drawback of DHCP reservation is that some DHCP servers (routers) do not support the feature, and you might be forced to use static IPs.
DHCP Reservation vs. Static IP
Conclusion
Using a static IP or reserving one at the router are options that work best in their respective circumstances. However, reserving an IP at the DHCP server is more convenient than assigning a static address through devices’ settings. Since you are familiar with the two options, settling on one that will serve your specific needs should be easy. But do not interfere with IP settings if you do not understand them to avoid causing long-lasting damage to your network.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.