As you may already know, Wi-Fi works using radio-wave frequencies. As such, it is susceptible to interference from other wireless devices working within the same frequency band. These include microwaves, smart TVs, cordless phones, and baby monitors.
Materials and solid obstacles such as metal, concrete, walls, doors, and furniture can also block Wi-Fi signals from reaching their destination.
Read on to learn how to deal with Wi-Fi signal interference to ensure you have a smooth experience.
CONTENTS
Why Are Wi-Fi Signals Prone to Interference?
Understanding how Wi-Fi technology works can help you know why it is prone to interference.
Wi-Fi transmits signals over the airwaves from the router to connected wireless devices using two radio frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Recommended reading: How to Block Wi-Fi Signals from Neighbors? (Ways to Reduce Wi-Fi Interference)
The 2.4 GHz band has an extended range and can pass through obstacles easily but is more vulnerable to electromagnetic interference since most wireless devices operate on this band.
The 5 GHz band is faster and less prone to interference since only a few devices operate on this network. Moreover, it has a shorter range meaning it is less likely to meet obstacles during signal transmission.

Wi-Fi signals are prone to interference because they travel in straight lines and are likely to encounter obstacles.
Moreover, the signals travel through a defined path or channel to the destination device. The further the distance between connected gadgets, the weaker the Wi-Fi signal becomes.
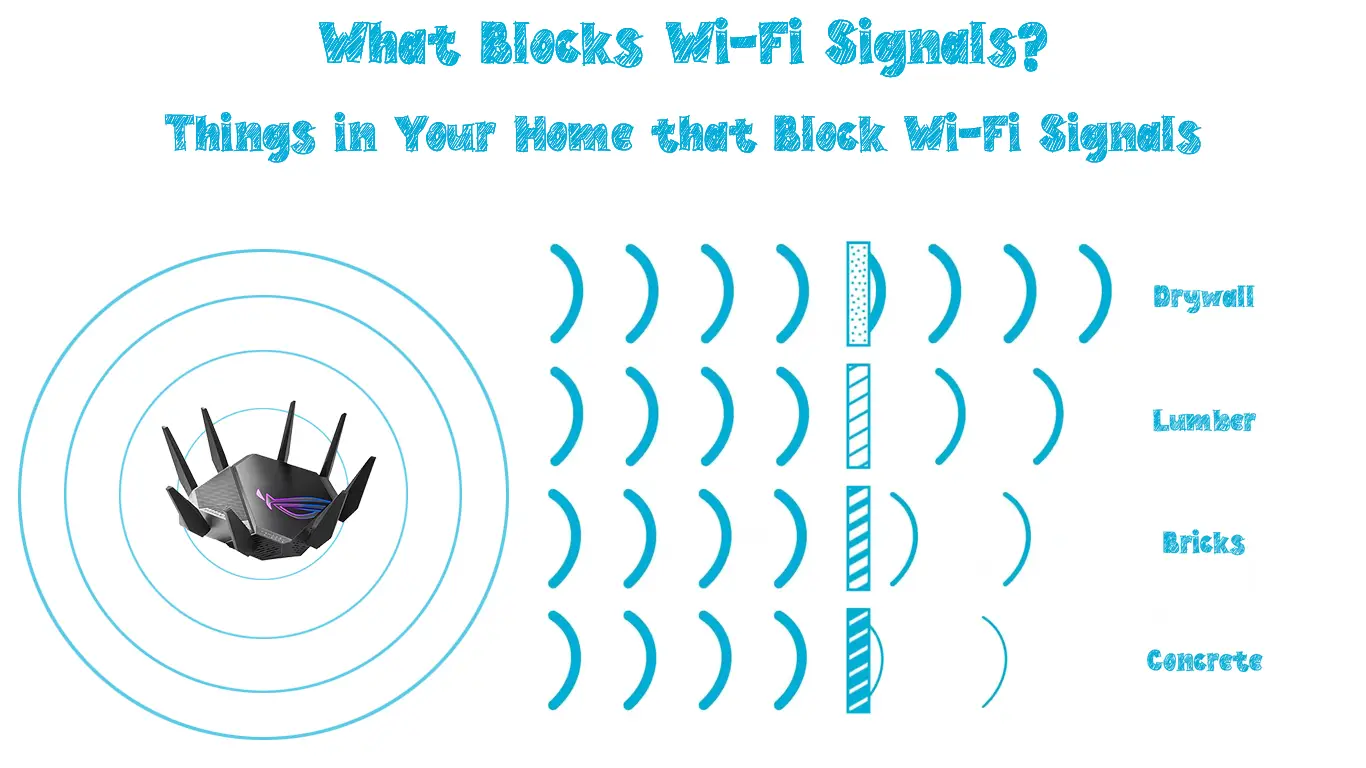
Materials and Physical Obstacles That Block Wi-Fi Signals
Wi-Fi signals can easily get blocked when they encounter various physical objects and materials during transmission.
Other wireless internet networks and technologies such as Bluetooth can also block Wi-Fi signals or cause electromagnetic interference.
Here are the top Wi-Fi signal blockers you should know about:
1. Metal
Building materials such as metals block Wi-Fi signals and significantly impede network coverage.
Metal is a conductor of electricity, making it difficult for Wi-Fi signals to penetrate.
In any case, Wi-Fi signals are radio waves that happen to be electromagnetic, meaning the metal will absorb them and inhibit their transmission to connected devices.
2. Windows and Mirrors
Windows and mirrors block Wi-Fi signals by reflecting them instead of allowing them to pass through.
Moreover, some windows and mirrors have a thin metallic film that blocks or reflects Wi-Fi signals and other radio signals.
It is also important to note that the size of the window or the mirror determines the level of interference. As such, a small window causes less interference than a larger one.
3. Concrete
Concrete walls, blocks, and floors can similarly block Wi-Fi signals and interfere with your connection.
Even though concrete does not conduct electricity, its thick density can prevent Wi-Fi signals from penetrating seamlessly.
It gets worse if the concrete wall has metal laths and supportive structures.
4. Ceramic Tiles
Ceramic tiles do not necessarily block Wi-Fi signals but weaken them, making it difficult to establish a stable connection.
Not only that. Mastic, the adhesive material used to install ceramic tiles and walls, is also an impediment and can cause interference.
5. Household Appliances
Household appliances such as microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to perform their functions.
Some appliances operate exclusively on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, and this may cause network congestion and interference.
6. Bluetooth Devices
Devices that communicate and operate via Bluetooth e.g. Bluetooth headsets, speakers, keyboards, and mice can block Wi-Fi signals since they operate via frequency hopping.
Consider turning off any Bluetooth device that you are not using to improve your Wi-Fi network coverage.
7. Smart TVs and Electronics
Your smart TV and other electrical devices such as baby monitors, refrigerators, and stovetops can block Wi-Fi signals.
These electronics have components that impede W-Fi traffic, causing network and connectivity issues.
Besides, most of these electronics operate on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, resulting in network interference and congestion.
8. Furniture
The furniture pieces in your home or office can block Wi-Fi signals, depending on their thickness, size, shape, and the materials used to make them.
Furniture items consisting of wood and metal are obstacles to wireless signals since they absorb the Wi-Fi waves instead of allowing them to penetrate easily.
9. Water
As absurd as it seems, water can block Wi-Fi signals and interfere with your wireless network.
The water in your aquarium, fish tank, or indoor waterfall contains impurities that conduct electricity.
The electromagnetic effect of this means that the water will absorb Wi-Fi signals instead of transmitting them to connected devices.
10. Neighboring Wi-Fi Network
Wi-Fi signal blockage and disturbance can occur because of having several wireless networks nearby.
Your neighbor’s Wi-Fi network or a separate wireless network in your home can block Wi-Fi signals and interfere with your connection.
Most Wi-Fi networks work on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, resulting in significant interference.
How to Reduce Wi-Fi Interference
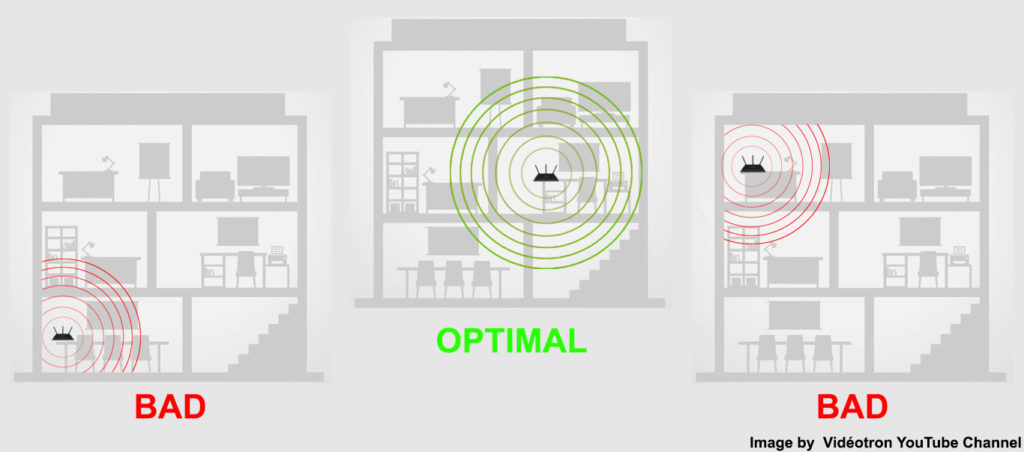
1. Reposition Your Router
The position of your router determines the efficiency of signal transmission. Consider placing the router in a central location, away from physical obstacles and other electrical devices.
2. Switch off Bluetooth Devices
Bluetooth devices can significantly interfere with your wireless network since they operate via frequency hopping. Turn off Bluetooth devices you are not using to reduce Wi-Fi signal interference.
3. Create a Mesh Network
Creating a mesh network is an excellent way to boost Wi-Fi coverage and reduce interference. A mesh network is a local networking solution in which several nodes connect and communicate with each other, providing better internet coverage.
4. Invest in a Wi-Fi Booster, Repeater, or Extender
You can also invest in a Wi-Fi booster to eliminate dead zones and spots in your space and reduce Wi-Fi signal blockages.
A Wi-Fi booster, repeater, or extender enhances your Wi-Fi coverage, ensuring the entire building has internet connectivity.
Conclusion
Weak or blocked Wi-Fi signals can lead to a frustrating connection experience. You have to contend with slowdowns, network lags, and buffering issues.
Fortunately, dealing with Wi-Fi signal obstruction does not have to be complicated so long as you follow our recommended tips.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.