Accessing the internet over Wi-Fi is common in many homes and businesses. The advancement of wireless technology resulted in routers transmitting signals over different frequency bands. For that reason, we look into what a frequency band is regarding your router’s signal transmission. Also, we will list and explain different ways to determine your router’s frequency.
CONTENTS
What is GHz?
Unit measurements can be confusing at times. Hence, to understand Gigahertz (GHz), we have to know about Hertz (Hz) first. Hertz is a unit of measuring frequency, and it is usually abbreviated as Hz. It is the unit for measuring frequency in the International System of units.
Hertz measures the rate of a cycle per second. We can use Hertz to measure the number of times something happens within a second. However, we use Hertz to measure frequencies of particular concepts more than others until it has become a measurement standard for said concepts.
Consequently, Hertz is used for measuring wave frequencies such as sound waves, light waves, and radio waves. Also, Hertz can measure computer speeds concerning how many instructions cycles the processor can conduct within a second.
In wireless connectivity, we use Hertz to measure the oscillation of electromagnetic waves that carry data from the router to a device with Wi-Fi capabilities. Electromagnetic waves consist of electronic and magnetic waves with varying intensities during transmission.
The variation leads to the formation of separate but related waves perpendicular to each other. When the electronic wave is oriented horizontally, the magnetic wave orients vertically, and the cycle continues as the waves are sent from the transmitter to the receiver.
A single perpendicular to horizontal orientation change is what we refer to as an oscillation.
Therefore, the number of oscillations per second is measured in a unit called Hertz.
Gigahertz (GHz) is a measurement of frequency that equals one billion Hertz. Other measurements include Kilohertz (kHz), equal to a thousand hertz, and Megahertz (MHz), equal to a million hertz.
Wi-Fi signals are measured in GHz and MHz because communication signals usually have very high frequencies.
What GHz Can Wi-Fi Transmit?
The range of the radio waves spectrum is from 3kHz to 300GHz. However, to minimize signal interruptions from other transmitters, the governments regulate radio wave frequencies through communication authorities in various countries.
For instance, the FCC (Federal Communications Commission) is responsible for frequency allocation in the United States. The allocated or licensed frequencies are long-range frequencies and are mainly used by various organizations to speak to their client devices.
On the other hand, some unlicensed frequencies are intentionally left free for use by different gadgets and transmissions. These frequencies fall under the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) purposes frequencies. That means you do not need a license to use those frequencies hence why they are commonly used in router and access point transmissions.
The ranges of radio wave frequencies that Wi-Fi can use to transmit data are known as the Wi-Fi frequency bands.
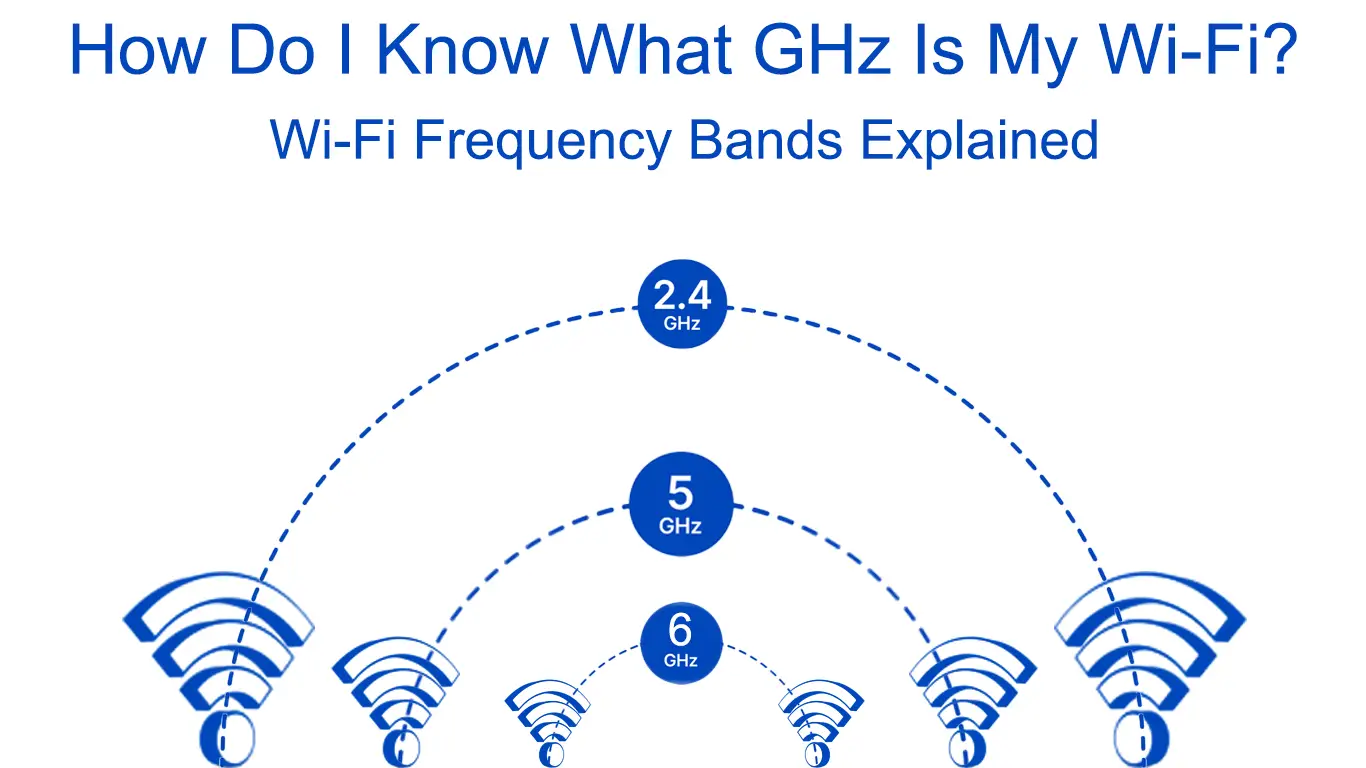
Routers and access points use two Wi-Fi bands: the 2.4GHz Wi-Fi and the 5GHz Wi-Fi band. The recent addition of the 6GHz band is less susceptible to signal interference and is faster, although by a small margin.
What GHz Is My Wi-Fi?
Since Wi-Fi uses electromagnetic signals to transmit data, we can determine what GHz an access point is transmitting.
Before finding out what GHz your Wi-Fi is, we must know the different common Wi-Fi frequencies used. They include:
2.4GHz
Every router supports a 2.4GHz frequency band, which is the most common on all devices. It consists of frequencies ranging from 2401 to 2484MHz. The range might slightly differ depending on the frequency regulations of your area.
The 2.4GHz band is preferable because it is cheap to install and use. Additionally, it can penetrate obstacles, increasing the distance over which the frequency band can still be helpful. For this reason, 2.4GHz devices have evolved to include microwaves, baby monitors, and security cameras.
The only downside of this Wi-Fi frequency is that it’s overcrowded, and many devices use the frequency range to carry out their normal functions. The congestion is also caused by the few channels available on the 2.4GHz frequency band.
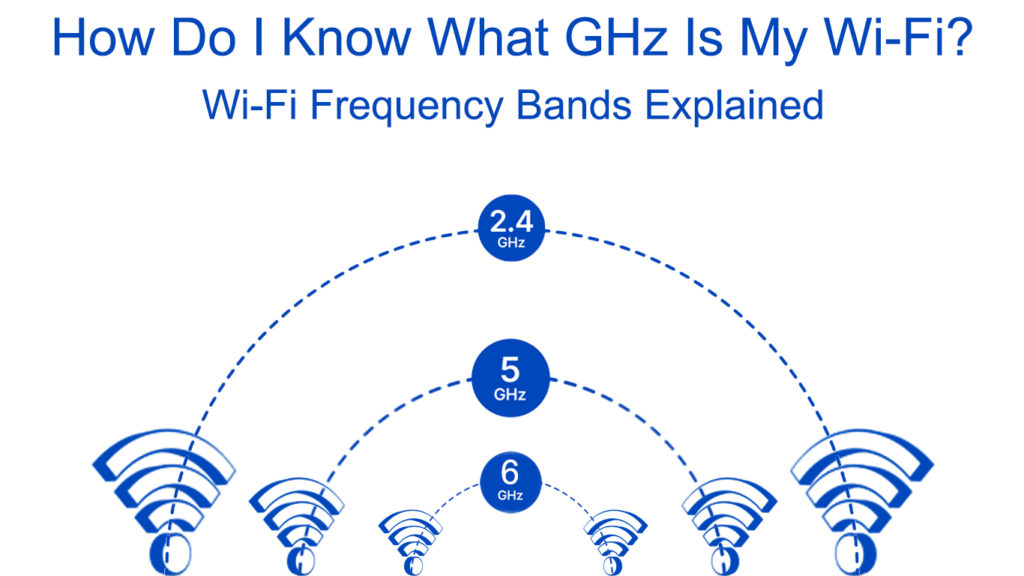
Channels in wireless internet connectivity entail smaller bands within a more prominent band like the 2.4 and 5GHz. Channels in the 2.4GHz band have a 5MHz width and a 16.25 to 22MHz range per channel.
Therefore, with the common 5MHz width and 22MHz range per channel, we have 13 channels. Unfortunately, we cannot use all those channels. Instead, we would use non-overlapping channels 1, 6, and 11.
While determining the available channels, we should remember that 2MHz is left out to act as the channel spacing to reduce signal interference from older routers that might occupy those frequencies. The 802.11 b/g/n/ax standards are built to work with the 2.4GHz frequency band.
Wi-Fi Bands and Channels
5 GHz
The 5GHz frequency band consists of frequencies ranging from 5GHz to 5.8GHz. The wide range of frequencies also indicates that there are more channels available in this band compared to the 2.4GHz band. There are 23 channels on the 5GHz band that do not overlap; therefore, there will be less signal interference.
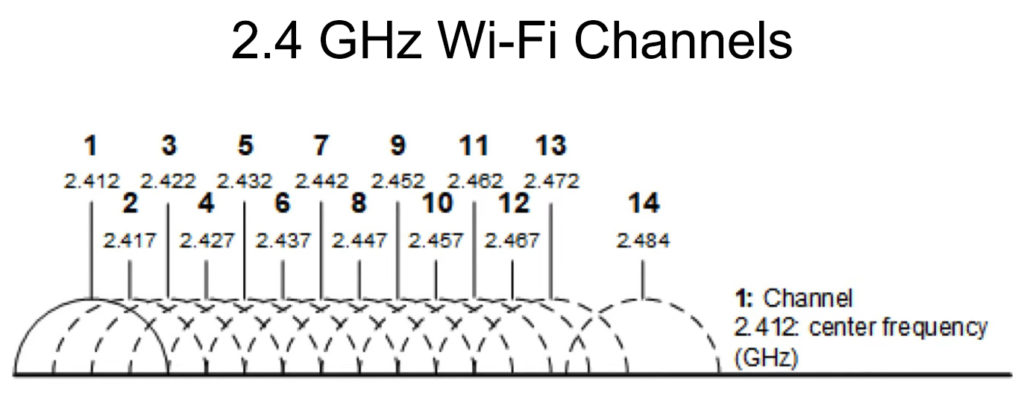
5GHz can also transmit more data because it does more oscillations per second. However, it transmits data over shorter distances compared to the 2.4GHz band.
The 5GHz band can also transmit more than 1Gbps, while the 2.4GHz band can transmit up to 600Mbps. Notably, devices compatible with 5GHz are expensive compared to those of the 2.4GHz band.
The a/h/j/n/ac/ax 802.11 wireless standards are compatible with 5GHz Wi-Fi connections.
Differences Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi Bands
6GHz
The 6GHz frequency band is a new standard that is still carving its niche in the market. It is the frequency band between 5.925 GHz and 7.125GHz, making it the highest frequency range band of 1200MHz.
The FCC has recently made the band free or available for unlicensed use mainly because of the influx of wireless devices that can congest the available frequency bands. The band also incorporates technology such as OFDMA that facilitates more reliable simultaneous connections.
The band is less prone to interference since few devices are compatible with the protocol. Also, the Wi-Fi band locks out devices from legacy bands meaning the connected device will stay unbothered for a long time to come. The band’s goal is not to increase Wi-Fi speed but to increase the network’s throughput.
Introduction to 6 GHz Wi-Fi
How Do I Know What GHz Is My Wi-Fi?
Now that you know what GHz is, in terms of your wireless connection, the next obvious question is how to tell what band you’re connected to? Fortunately, a few hacks can help you determine your Wi-Fi band without a fuss.
- Check Your Router’s Available Wireless Networks
The easiest and quickest way to find your router’s frequency band is by checking SSIDs broadcasted from your router. In most cases, routers have dual-band capabilities; therefore, they can support both – the 2.4 and 5GHz, frequency bands. Also, some routers have tri-band support and can transmit signals either over two 5GHz bands and a 2.4GHz band or over 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6GHz bands.
If your router supports three Wi-Fi bands on three Wi-Fi networks, you will see three SSIDs. For example, if you are at home and using a triband router, the SSIDs might look like: Homewifi2.4, Homewifi5GHz, and Homewifi6GHz.
The Wi-Fi names can be anything appended with the numbers ‘2.4GHz’,2G,’2.4G’, ‘24G’ for the 2.4GHz band. The same goes for the 5 GHz band.
Some routers, however, use the same SSID for all the available bands. If that’s your case, there are other ways to tell your frequency band. Or, you can simply name each Wi-Fi band in your router settings differently.
- Go to the Router’s Settings
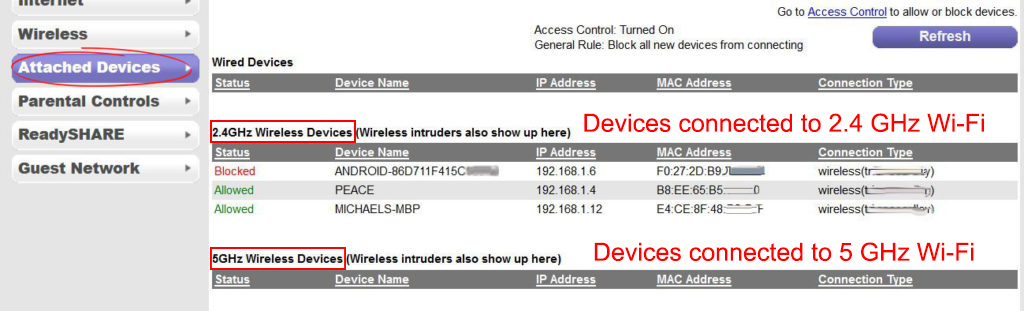
Another easy way to determine your Wi-Fi band is to access the router’s settings through a webpage.
To do this, open a web browser while the device is connected to the Wi-Fi. You have to use the default IP address to log in. Ensure you have the correct IP since they are not the same for every router model. The most popular ones are 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, and 10.0.0.1.
Also, you have to enter the correct admin password and username. If you have never changed the password and username, enter the default values before proceeding.
Once you log in, go to the wireless settings tab and see what frequency bands are active. Some routers can allow you to view the devices connected to a particular band. You can also switch off a particular band and use the one you prefer now that you know what they entail.
- Use Third-Party Apps
There are also freely available apps that can scan your wireless signal and determine the band and channel of your router. These apps include Wi-Fi Analyzer, available for Android and iOS devices. Once you download and install the app, you can scan your Wi-Fi network to determine various aspects, including channel number and wireless band.
iPhone users can also download the app Airport Utility from the Appstore, and it will help them know more about their Wi-Fi networks.
Windows users can also download the Wi-Fi Info View program that scans nearby Wi-Fi connections without connecting.
- Use the Device Settings
In most cases, you won’t be able to tell whether your device (phone, laptop, PC, tablet) is connected to 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz Wi-Fi. If your device supports both bands, it will prioritize the 5 GHz band when in range, and it will switch to 2.4 GHz when you’re too far away from the router. If your device supports only one band, then it’s pretty obvious what band you’re connected to.
While you can’t see the Wi-Fi band you’re connected to, you can (on some devices) force the 5 GHz Wi-Fi connection. Doing so will give you better speeds and overall performance when you’re close to the router, but it will be tricky if you tend to move your device around the house. Remember, the 5 GHz band has a shorter range than the 2.4 GHz band. So, if you force the 5 GHz band, you may lose your Wi-Fi connection when if you move away from the router.
On some devices (like Windows PCs), you can select the preferred band, which is a better option than forcing one band since it doesn’t eliminate the other band.
How to Select the Preferred Wi-Fi Band in Windows 10
Conclusion
The different Wi-Fi bands have varying capabilities that make the wireless technology interesting. We can now tell the Wi-Fi band we’re connected to with a few taps on a screen or a few clicks on a computer. It is even better because you will know the effects of changing your wireless band frequency.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.