Wi-Fi technology has been around for a decade and a half, with many end-users now enjoying the benefits of fast, secure, and wireless internet access.
If you have Wi-Fi in your home or office, you do not need to run any wires on your walls. Wi-Fi allows you to seamlessly connect your wireless devices, including smartphones, smart TVs, printers, security cameras, gaming consoles, and computers.
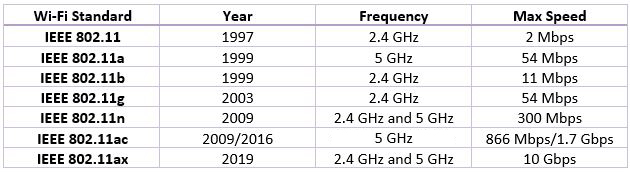
As you know, there are different Wi-Fi standards available today. The first Wi-Fi specification was Wi-Fi 1, but now we have Wi-Fi 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. The first three Wi-Fi versions are almost obsolete as most people use Wi-Fi 4, 5, and 6.
This post explains everything you need to know about Wi-Fi 5 and why you should consider upgrading your router to this specification. Keep reading to learn more.

CONTENTS
What Exactly Is Wi-Fi 5?
Wi-Fi 5 is one of the latest wireless networking standards. This 5th generation of Wi-Fi also goes by the name 802.11ac, but many people prefer to use the simplified naming protocol, Wi-Fi 5.
Since its launch and subsequent adoption in 2014, Wi-Fi 5 has become popular because of its fast speeds, high data throughput, and better WLAN range to keep up with the increasing number of users and wireless devices.
Even though Wi-Fi 5 uses the 5 GHz frequency band only, it is incredibly fast, with maximum link rates ranging from 433 to 6933 Mbps. These speeds are a noteworthy upgrade to the 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) standard, only capable of supporting top rates of 600 Mbps.
The only possible reason many end-users are stuck on Wi-Fi 4 instead of upgrading to Wi-Fi 5 is that most wireless devices still run on the 2.4 GHz network.
Wi-Fi 5 only supports the 5 GHz frequency bands, which is one of its most significant flaws. Other than that, anyone with a 5 GHz-compatible device should switch to Wi-Fi 5 right away.
A Brief History of Wi-Fi 5
Wi-Fi 5 does not need any introductions as it has been around since 2014. Besides, it ranks highly as a wireless networking standard that has transformed Wi-Fi technology in data transmission rates and overall performance.
Even though its predecessor, Wi-Fi 4, does not have any serious flaws, it still falls short in data transmission speeds, signal modulation, and network security. This not-so-new Wi-Fi standard addresses all these issues through its improved features.
If you didn’t know, Wi-Fi 5 is available in two different versions (waves). The first version is 802.11ac Wave 1, released in 2014, and the second version is 802.11ac Wave 2, certified in 2016.
The difference between 802.11ac Wave 1 and 802.11ac Wave 2 is the channel bandwidth. While Wave 1 supports up to 80 MHz, Wave 2 supports a maximum of 160 MHz, double the channel bandwidth of the first Wi-Fi 5 release.
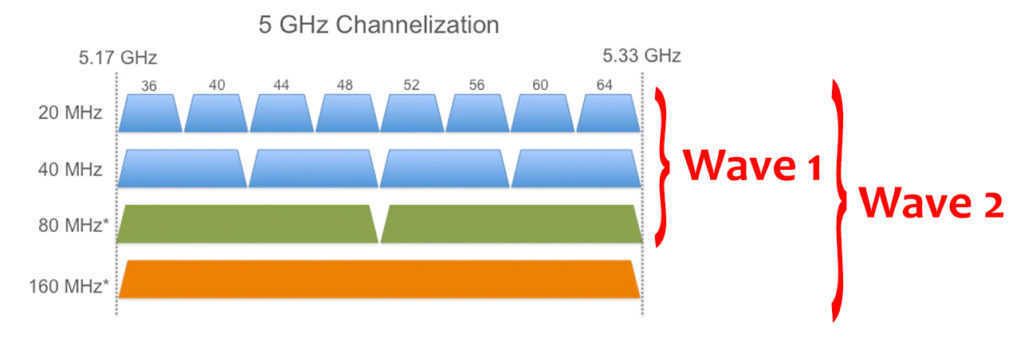
Image source – Cisco
Data transmission rates are significantly greater with Wave 2 than with Wave 1. You can experience maximum speeds of 6.9 Gbps on the 802.11 ac Wave 2 network. Since Wave 2 is superior to Wave 1, it is what we use now as Wi-Fi 5.
How to Check if You Have Wi-Fi 5?
Not all wireless devices are compatible with Wi-Fi 5. In any case, Wi-Fi 5 only supports the 5 GHz band. Older phones and equipment rely on Wi-Fi 4 and other previous Wi-Fi standards since they mostly use the 2.4 GHz band.
Before investing in a Wi-Fi 5 router, you must confirm that all your devices are compatible with the 802.11ac standard. If not, you won’t access the internet, or you might have connection challenges.
Here is a comprehensive guide you can use to check your Wi-Fi version on your Windows or Linux PC and smartphone.
Checking the Wi-Fi version on your Windows PC
- Right-click the Start button on your Windows PC
- Click Settings
- Click Network and Internet
- Click on Wi-Fi on the left navigation pane
- Click on Advanced Options
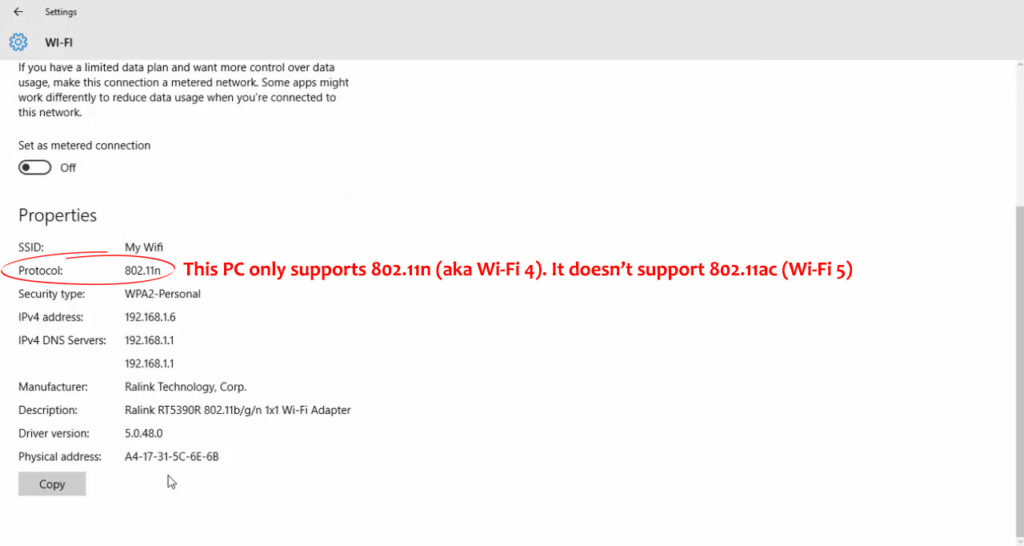
- Navigate to the bottom of the Advanced Options page and check the description (802.11ac means your PC is running on Wi-Fi 5).
Method 2
- Right-click the Start button
- Go to Device Manager
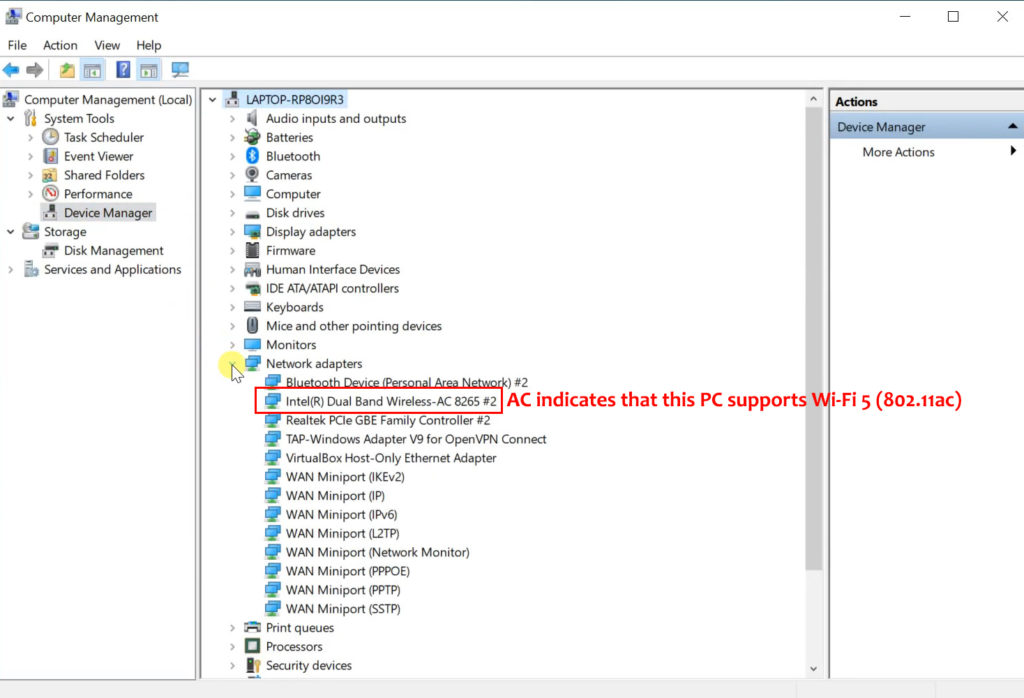
- Navigate to Network Adapters
- Expand the Network Adapters menu by double-clicking on it. The name of your network adapter may indicate your Wi-Fi version. If the name contains AC, it means it supports Wi-Fi 5. You may also see the letter N (Wi-Fi 4) or AX (Wi-Fi 6)
Checking the Wi-Fi version on your Linux PC
- Open a Linux terminal by pressing the Ctrl+Alt+T Function keys simultaneously
- You can also open a terminal by typing the word “terminal” in the Ubuntu search box
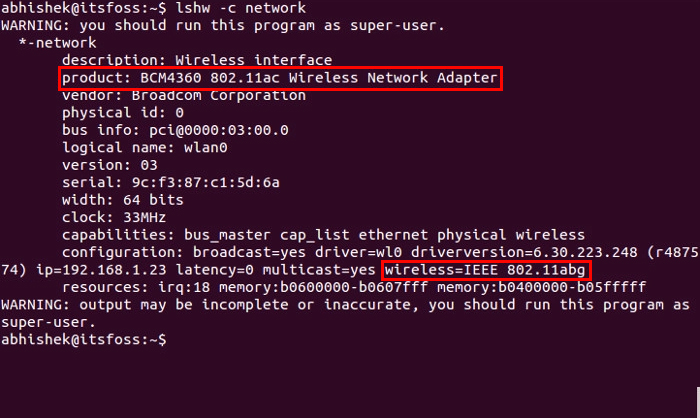
- After launching the terminal, type: sudo Ishw –C network
- Scroll down to view the displayed hardware information
- Under network devices, you’ll see your Wi-Fi version from the wi-fi interface name
Checking the Wi-Fi Version on Your Smartphone
You cannot tell the Wi-Fi version on your smartphone through the settings app. You can only check supported Wi-Fi standards by perusing the specifications page on your phone’s user manual.
A quick search on Google or any other reputable search engine can also give you reliable results. Enter your phone’s name and model in the search bar and visit review sites that display the full specifications of various phones.
What is the Range of Wi-Fi 5?
Even though Wi-Fi 5 is fast and efficient, it has a poor range since it runs on the 5 GHz band. Its network coverage is only 35 meters (115 feet) indoors and 80 meters (260 feet) outdoors.
The 5 GHz frequency band has a limited range and cannot penetrate well through solid obstacles such as thick walls, doors, floors, and furniture.
Your home or office might have a lot of dead zones due to Wi-Fi 5 lousy network coverage. However, installing a Wi-Fi booster or extender can help fix the problem.
What Speeds Can You Achieve with a Wi-Fi 5 Router?
The speeds you can achieve with a Wi-Fi 5 router are remarkable compared to its predecessor. Your 802.11ac router can attain maximum theoretical link rates between 433 and 6933 Mbps (6.9 Gbps).
Of course, these speeds are not actual, and they depend on various aspects, including your ISP, router model, and the number of connected devices, among many other factors.
A point worth noting is that your Wi-Fi 5 router won’t increase your internet speeds but only facilitate your devices to make the most out of the available bandwidth and transmission rates.

How to Upgrade to Wi-Fi 5
If you desire faster internet speeds, greater bandwidth, and smoother connections, consider upgrading to Wi-Fi 5. The 802.11ac standard is ideal for streaming and gaming enthusiasts since it supports heavy data transfers.
Upgrading to Wi-Fi 5 is as simple as buying an 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) router. But first, you must ensure your devices support this standard before investing in a Wi-Fi 5 router.
Pros of Wi-Fi 5
Wi-Fi 5 is an upgrade to Wi-Fi 4, and it comes with several new features and numerous benefits worth considering. Here is a breakdown of the pros of Wi-Fi 5:
Gigabit Speeds
Wi-Fi 5 opens a world of possibilities as far as Gigabit speeds are concerned. This Wi-Fi standard supports maximum rates of 6.9 Gbps for seamless browsing, streaming, and gaming, without lagging or buffering issues. These transmission speeds are almost ten times what the 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) specification supports. Nevertheless, the actual transfer speeds attainable depend on your ISP.
Greater Data Throughput
Another significant benefit associated with Wi-Fi 5 is its greater data throughput capacity. The increased data throughput is a result of the improved channel width. Wi-Fi 5 supports a maximum of 160 MHz channel bandwidth. Broader Wi-Fi channels mean your 802.11ac router can swiftly send and receive more data.
Supports MU-MIMO Technology
Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) was a breakthrough technology associated with Wi-Fi 4. MIMO allows simultaneous data transmissions to single devices at a time.
Wi-Fi 5 improved this innovation by adopting Multi-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO). MU-MIMO allows simultaneous data transmission to multiple devices. Essentially, your 802.11ac router can simultaneously communicate with several devices without interruptions.
MU-MIMO Explained
Increased Spatial Streams
Wi-Fi 5 routers have multiple antennas to ensure the efficient execution of MU-MIMO technology. These antennas send and receive signals simultaneously in your wireless network via spatial streams. Wi-Fi 5 uses several spatial streams to transmit data. Using multiple spatial streams helps to prevent collisions during data transmission.
Low Power Consumption
Many people overlook the aspect of energy consumption when comparing different Wi-Fi standards. Since Wi-Fi 5 supports simultaneous data transmission and allocates signals more efficiently, devices operating on the network consume less power. With improved energy efficiency, the batteries in your wireless gadgets can last longer.
Reduced Interference and Congestion
Wi-Fi networks operating on the 2.4 GHz band are usually prone to electromagnetic interference from smart wireless devices such as baby monitors, cordless phones, Bluetooth speakers, and microwaves. Since most gadgets support the 2.4 GHz band, they might congest your network, leading to painstakingly slow internet speeds. Fortunately, Wi-Fi 5 is here to resolve these issues. It uses the 5 GHz band, which is less susceptible to interference.
Stable Signal Strength
Since Wi-Fi 5 has wider channels and increased spatial streams, you are less likely to experience slowdowns or connectivity issues associated with your router. Wi-Fi 5 is stable and reliable since it allocates signals more efficiently than other Wi-Fi standards. It stabilizes wireless signals before transmitting them to connected devices.
Supports Backward and Forward Compatibility
When shopping for a Wi-Fi router, consider one that is backward and forward compatible, meaning it can work with older and newer equipment without any major issues. Wi-Fi 5 is compatible with legacy versions and newer standards, including Wi-Fi 6. The performance will, however, conform to the older specification.
Beamforming Technology Support
Another significant breakthrough associated with Wi-Fi 5 is beamforming technology. Older wireless standards usually transmit data 360 degrees in all directions, leading to wastage, interference, and slowdowns since the signals go to unintended areas. Beamforming sends data directly to connected devices, helping improve speed and range.
Beamforming Explained
Enhanced Security
Security is a significant concern in wireless networking. It is easy for hackers to intercept signals in a wireless network. Fortunately, Wi-Fi 5 has improved security features like Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) and Advanced Encryption Standard technology for enhanced protection.
Cons of Wi-Fi 5
Even though Wi-Fi 5 has numerous benefits, it also has a few downsides that we can’t ignore. Some of the most notable downsides of Wi-Fi 5 include:
Incompatible with 2.4 GHz Devices
One of the primary concerns about Wi-Fi 5 is that it only supports the 5 GHz band. Devices that operate using the 2.4 GHz frequency band only cannot work with Wi-Fi 5 routers. You may have to replace your router or purchase a compatible device.
Limited Range
Since Wi-Fi 5 uses the 5 GHz frequency band, its network coverage is pathetic. The 5 GHz band can only reach 35 meters (115 feet) indoors and 80 meters (260 feet) outdoors. Even though beamforming technology can help cover more ground, you may still need a Wi-Fi extender or booster to eliminate dead spots and improve wireless network coverage.
No Support for Higher Modulation Schemes
Wi-Fi 5 supports 256-QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation), allowing for combining multiple amplitude modulation signals into a single channel to boost signal strength, increase speed, and reduce interference.
What is 256-QAM?
Even though this modulation scheme is better than that of Wi-Fi 4 (64-QAM), it is still not sufficient. Upholding a higher modulation scheme like 1024-QAM would be ideal for preventing connectivity issues.
No MU-MIMO Support in the Uplink
Wi-Fi 5 supports MU-MIMO technology on the downstream link only and not on the upstream channel. This limitation means you might experience slower upload speeds when transferring large files such as videos and photos.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi 5 or the 802.11ac standard is worth considering if you have a compatible wireless device. This Wi-Fi specification supports breakneck transmission speeds for smooth and seamless browsing, streaming, and gaming experience. You’ll never have issues with lagging or buffering when on the Wi-Fi 5 network. Upgrade your wireless network today and notice the difference.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

