Wi-Fi standards continue to emerge every few years, with the Wi-Fi Alliance not relenting on its quest to provide end-users with faster, more efficient, and more secure Wi-Fi versions.
After the launch of Wi-Fi 5 in 2014, it took only 5 years for Wi-Fi 6 to become a reality. Wi-Fi 6 is now here with us, with many upgrading from previous Wi-Fi versions to the latest Wi-Fi specification.
This post explains everything you need to know about Wi-Fi 6 and why you should consider upgrading to this standard. Keep reading to learn more.

CONTENTS
What Exactly Is Wi-Fi 6?
Wi-Fi 6, also called the 802.11ax standard, is a wireless networking protocol renowned for its incredible speeds, greater data throughput, and high performance.
This 6th generation of Wi-Fi has been around since 2019 and is already making headlines with its impressive features.
Unlike its predecessor, Wi-Fi 6 supports multiple frequency bands, including the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz bands. The new Wi-Fi 6E supports the recently launched 6 GHz band, giving end-users more options to choose their preferred frequency band.
What makes Wi-Fi 6 popular is its remarkable speeds. It has maximum link rates ranging from 600 to 10,000 Mbps. The highlight of the 802.11ax standard is that it can support dozens of wireless devices without compromising on speed or performance.
Wi-Fi 6 Explained
A Brief History of Wi-Fi 6
As you know by now, Wi-Fi 6 came out in 2019 and has been around for slightly over two years. This wireless networking standard stands out in data transmission speeds, signal modulation, and network security.
It is an improvement of the Wi-Fi 5 standard as it addresses some, if not all, of the flaws associated with its predecessor. The first enhancement was the speed, with Wi-Fi 6 supporting transmission rates of close to 10 Gbps.
However, speed improvements were only secondary. The primary objective of the 802.11ax standard was to improve its capacity to perform better in dense environments when multiple devices connect to it.
Connected gadgets do not have to wait in line to receive data packets since transmission is simultaneous across the entire network. The multiple devices in the network also share internet and LAN speeds without causing slowdowns or Wi-Fi drops.
How to Check if You Have Wi-Fi 6
There are many myths surrounding Wi-Fi 6, with many people claiming it is not compatible with older devices. However, nothing could be further from the truth. Wi-Fi 6 is backward compatible, meaning it can support legacy routers and older gadgets.
Nevertheless, you need to verify if your device is compatible with Wi-Fi 6 to avoid performance issues.
Checking the Wi-Fi version on your Windows PC
You can check if your PC supports Wi-Fi 6 using three different methods:
Method 1 – Network Settings
- Right-click the Start button
- Click Settings
- Choose Network and Internet
- On the left navigation panel, click on Wi-Fi
- Click on Advanced Options
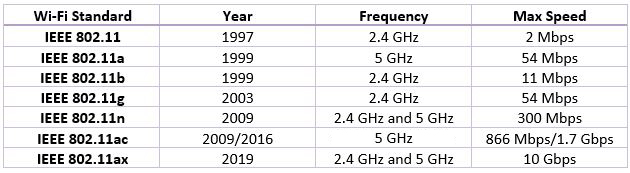
- Scroll down and check the Wi-Fi description (802.11ax means your PC’s network is running on Wi-Fi 6)
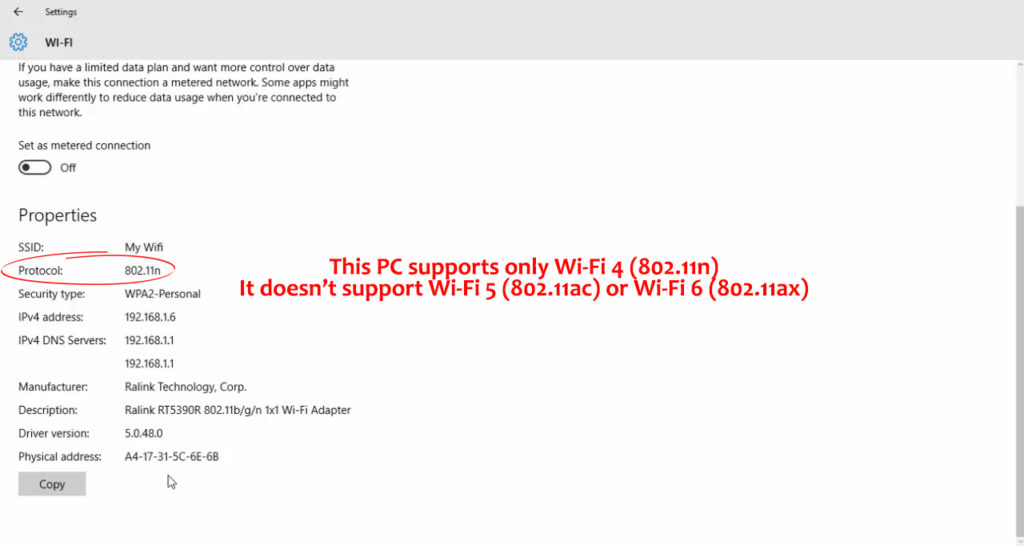
Method 2 – Device Manager
- Right-click the Start button
- Next, click the Device Manager option
- Go to Network Adapters
- Double-click Network Adapters to expand the menu
- Select your Wi-Fi adapter. The name of the adapter usually indicates the supported Wi-Fi standard. If you see N in the name, your adapter supports only Wi-Fi 4. If it’s AC, your adapter supports Wi-Fi 5, and if it’s AX, your adapter supports Wi-Fi 6.
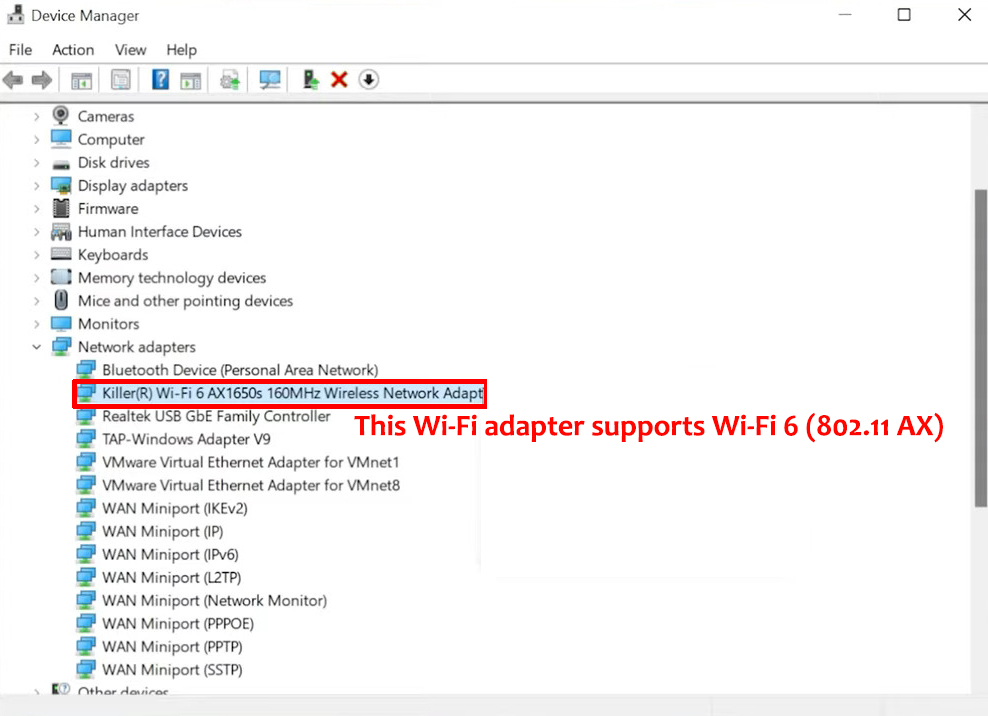
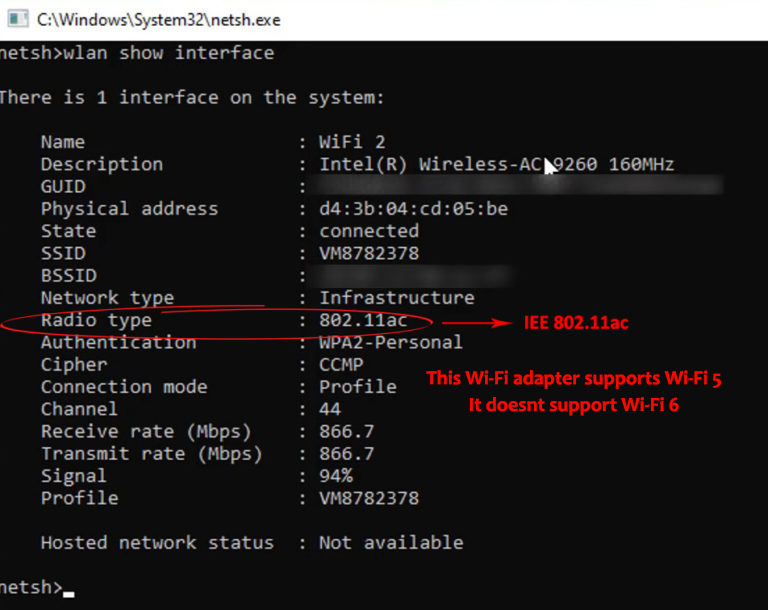
Method 3 – Command Prompt
- Right-click the start button on your Windows PC
- Select Command Prompt or type Command Prompt in the search bar
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator
- Type: “netsh wlan show drivers” and press Enter
- Check the Radio types supported section to see your Wi-Fi version
Checking the Wi-Fi version on your Linux PC
- Open a Linux terminal by pressing the Ctrl+Alt+T Function keys simultaneously
- You can also open a terminal by typing the word “terminal” in the Ubuntu search box
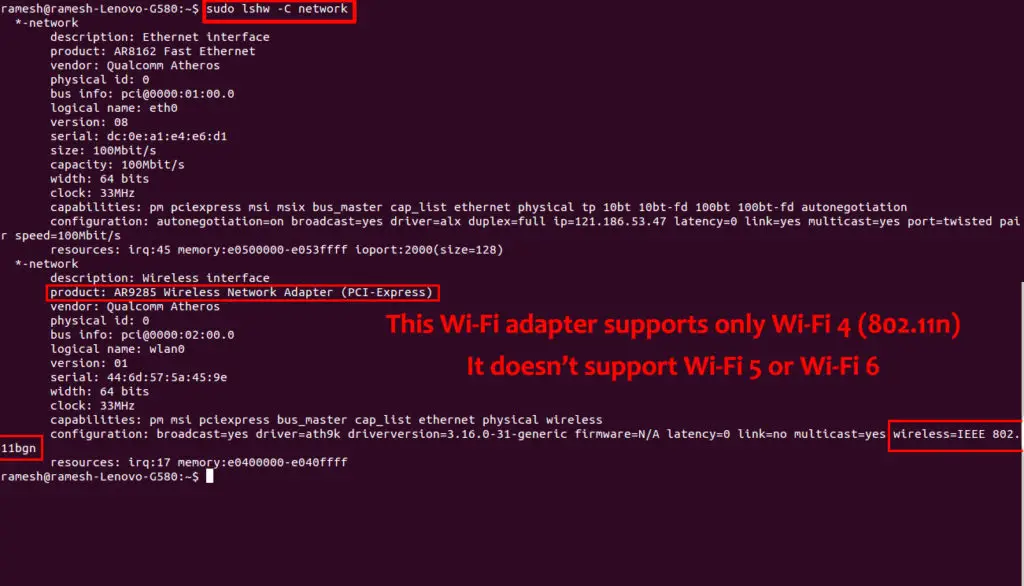
- After launching the terminal, type: sudo Ishw –C network
- Scroll down to view the displayed hardware information
- Under network devices, you’ll see your Wi-Fi version from the router name
Checking the Wi-Fi version on your Smartphone
Since Wi-Fi 6 came out in 2019, most devices, particularly the older models, might not support this new Wi-Fi standard.
Even though Wi-Fi 6 is backward compatible, your wireless devices might endure performance issues, and you may not make the most of the impressive features this Wi-Fi version offers.
The quickest way to check whether or not your smartphone supports Wi-Fi 6 is to visit a reputable third-party site like gsmarena.com.
You only need to enter your phone’s make and model in the search bar and check the supported Wi-Fi versions on the specifications page. You can also check your phone’s specs by perusing the user manual that came with it.
How to Upgrade to Wi-Fi 6
You do not have to do anything special to upgrade to Wi-Fi 6. Buying an 802.11ax router can resolve the issue within no time. The only concern is that Wi-Fi 6 routers are outrageously expensive, but many people expect the prices to come down in the coming years.
Pros of Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 has revolutionized how we access the internet. You no longer have to experience Wi-Fi drops or slowdowns when gaming online or streaming your favorite movies, no matter how many devices are on your network. Wi-Fi 6 is the epitome of internet connectivity. Here are the top reasons to upgrade to this Wi-Fi standard:
Breakneck Speeds
Wi-Fi 6 supports breakneck speeds and fast data transmission rates with every connection. It delivers higher data throughput than all other Wi-Fi generations, and it is 40% faster than its predecessor, Wi-Fi 5. Maximum link rates reach 10000 Mbps (10 Gbps), making it the fastest Wi-Fi specification globally. Thanks to these incredible speeds, you can play online games and stream 4K UHD movies without issues.
Reduced Latency
Latency refers to the time delay in transmitting data from one point to another. Many wireless networks experience some degree of latency during data transmission. The delay is usually unnoticeable since it does take more than a few milliseconds.
The average latency of Wi-Fi 6 is 2 milliseconds. This Wi-Fi standard uses Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) technology to simultaneously transmit data to numerous devices, reducing latency and overheads.
Support Multiple Frequency Bands
Unlike Wi-Fi 5, which only supports a single frequency band, the 802.11ax standard (Wi-Fi 6) uses multiple bands for data transmission. It supports the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz bands, ensuring users make the most out of both worlds. Besides, the new Wi-Fi 6E standard supports the recently introduced 6 GHz band. If you want to experience faster speeds, you can switch your device to the 5 GHz band. The 2.4 GHz band is ideal for extended network coverage.
Wi-Fi 6 VS Wi-Fi 6E
Higher-Order Modulation
While Wi-Fi 5 supports 256-QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation), Wi-Fi 6 upholds 1024-QAM. This feature lets your router combine multiple amplitude modulation signals into a single channel, boosting signal strength, increasing transmission speeds, and reducing interference.
Enhanced MU-MIMO Technology
Another technology that Wi-Fi 6 uses is MU-MIMO, which stands for Multi-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output. This technology made its debut with Wi-Fi 5. It allows multiple devices to communicate with your wireless router simultaneously.
MU-MIMO Explained
However, MU-MIMO on Wi-Fi 5 is only available downstream and can only support four simultaneous streams. In contrast, MU-MIMO on the 802.11ax standard is available downstream and upstream and can support twelve simultaneous streams.
Supports Beamforming Technology
Legacy Wi-Fi standards usually send transmissions in any direction, leading to lost signals. Wi-Fi experts introduced beamforming technology with the Wi-Fi 5 standard to help curb this problem. Wi-Fi 6 also supports beamforming, a technique that transmits data in a specific direction. It sends data packets directly to the connected devices, improving signal strength and eliminating dead spots.
Beamforming Explained
Better Network Coverage
Since Wi-Fi 6 supports multiple frequency bands, it has better network coverage than its predecessor, Wi-Fi 5. It uses the 2.4 GHz band, renowned for its extended range of about 150 feet indoors and 300 feet outdoors. The 2.4 GHz frequency band can also effortlessly penetrate through solid obstacles, thick walls, and floors without creating dead zones in your space.
Lower Energy Consumption
Wi-Fi 6 routers are energy-efficient and can help reduce the power consumption in your household or commercial premises. With higher transmission rates and more efficient signal allocation, your devices do not have to consume much power. The smooth and seamless data transfer can help conserve energy since you do not have to stay online for prolonged periods.
Backward Compatible
Another benefit of upgrading to the 802.11ax standard is backward compatibility. You do not need to worry whether or not your devices support Wi-Fi 6 since it is backward compatible and can work with older, legacy versions and gadgets. Moreover, Wi-Fi 6 is also future-proof, and many people predict it will remain in use for years, although Wi-Fi 7 is just around the corner.
Basic Service Set Coloring
Wi-Fi 6 is less prone to interference, and it can minimize disruptions from nearby networks using a technology called Basic Service Set Coloring (BSS). For instance, if you and your neighbor have Wi-Fi routers, the signals from the two neighboring networks can overlap and cause interference. BSS technology colors the signals from your network and distinguishes them from your neighbor’s signals, ensuring it goes to the intended recipient.
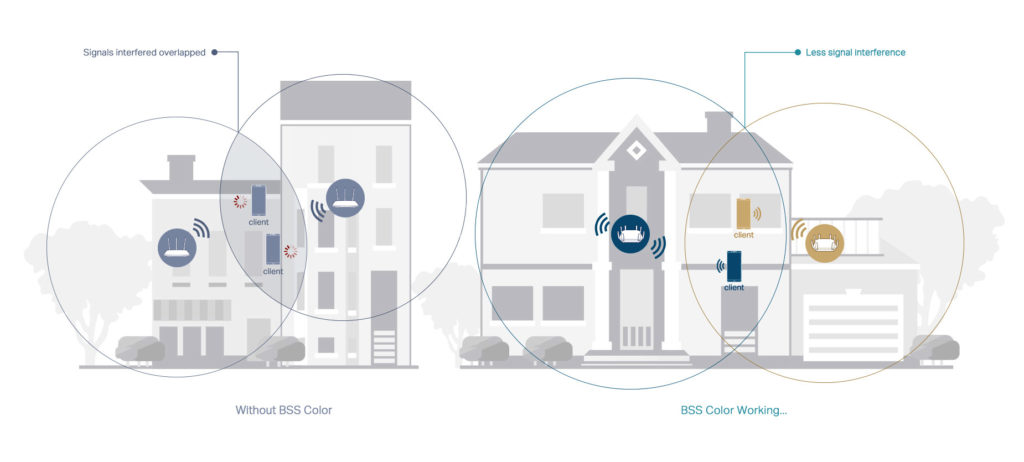
Image source – TP-Link
Enhanced Battery Life
Aside from conserving power, Wi-Fi 6 can help extend the battery life of your wireless devices through the Target Wake Time function. This feature schedules time when your router should send data to your wireless devices. It allows your gadgets to sleep and wakes them up at scheduled times, subsequently extending battery life.
Enhanced Security Features
Wi-Fi 6 has the most advanced security features in Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3). This security standard for wireless networks provides cutting-edge features that enable a more robust authentication process, preventing hacking attempts. For one to certify your router has Wi-Fi 6, it must have WPA3.
Cons of Wi-Fi 6
The excitement surrounding Wi-Fi 6 can make someone assume this Wi-Fi standard has no faults. However, Wi-Fi is not immune to shortcomings. Here are a few drawbacks to consider:
Narrower Sub-Carrier Spacing
Wi-Fi 6 uses Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) to transmit data simultaneously to multiple devices. It subdivides channels into smaller subcarriers called resource units.
While these carriers deliver data to multiple devices more efficiently, their spacing is narrow at 78KHz, making them prone to Wi-Fi noise. For this reason, you might require phase noise oscillators to deal with this issue.
Requires Gigabit Broadband Connection
If you do not have a Gigabit broadband connection plan, do not waste time investing in a Wi-Fi 6 router. After all, Wi-Fi 6 is the fastest Wi-Fi standard, with maximum transmission rates exceeding 10 Gbps. A fast broadband connection plan will ensure you fully exploit Wi-Fi 6 technology for a fantastic internet experience.
Not Readily Available
Even though Wi-Fi 6 has been around for more than two years, Wi-Fi 6 routers are not readily available. Many shops and online stores are stuck with Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5 routers, perhaps because most customers prefer these two Wi-Fi standards. Besides, many people consider Wi-Fi 6 a preserve for commercial use.
Pricey
If there’s a router that will force you to dig deeper into your pockets, it has to be a Wi-Fi 6 router. They do not come cheaply, with most costing hundreds of dollars, making them out of reach for many casual Wi-Fi users. However, if you can afford it, go for it since Wi-Fi 6 routers are worth every dime.
Conclusion
If you want to connect multiple devices to the internet without overwhelming your wireless network, consider installing a Wi-Fi 6 router. The primary objective of Wi-Fi 6 is not to increase transmission speeds but improve connections and performances in dense wireless environments.
It doesn’t matter how many gadgets you want to connect. Whether you have a laptop, smartphone, tablet, thermostat, refrigerator, or security camera, Wi-Fi 6 can support these devices without compromising performance or slowing down your network.
So, what are you waiting for? Upgrade to Wi-Fi 6 today!

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

