Ever since the first Wi-Fi standard came out in 1997, Wi-Fi technologies have evolved allowing more people and wireless devices to access the internet and stay connected seamlessly.
With the emergence of Wi-Fi hotspots, you can now enjoy instant, high-speed internet access from anywhere at the palm of your hand.
A hotspot is an internet access point that lets you connect to a wireless network via your phone, tablet, computer, and other compatible devices.
Hotspots are everywhere, including airports, restaurants, libraries, malls, hospitals, schools, and most public spaces, allowing you to connect your devices and access the web seamlessly.
As much as Wi-Fi hotspots are fast, easily accessible, and convenient, they have their limitations.
Most of the current Wi-Fi technologies do not support roaming, meaning you have to select a new network and log in your credentials afresh when moving from one Wi-Fi hotspot to the next, taking much of your time.
Fortunately, Wi-Fi hotspot 2.0 is here to change this scenario by addressing these specific issues and other Wi-Fi challenges.
This post explains everything you need to know about the game-changing Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0.

CONTENTS
What Exactly is a Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0?
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is an interoperable Wi-Fi standard that allows compatible mobile devices to automatically detect and connect to available Wi-Fi hotspots without entering authentication information afresh.
Hotspot 2.0, also known as Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint or HS2, is a roaming standard for Wi-Fi networks. This Wi-Fi technology allows mobile devices to switch between Wi-Fi networks and cellular networks seamlessly without requiring additional authentication.
With Hotspot 2.0 technology, you can move from one Wi-Fi hotspot to another or from a cellular network to a Wi-Fi network and vice versa, without the need to select a network or enter your passwords again. The switch is automatic and does not require additional user sign-on.
The primary objective of Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is to facilitate roaming for Wi-Fi networks similar to cellular roaming. Your HS2-compatible device can automatically connect to available public hotspots whenever you enter a Hotspot 2.0 area.
Hotspot 2.0 aims to offload the strain on cellular networks, reducing outages and improving quality and efficiency. It also cuts support costs, allowing communication service providers to increase their systems’ capacity and offer better and more efficient services.
That’s not all. Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is more secure and convenient as it facilitates your device to detect and connect to real Wi-Fi networks when in public hotspot areas.
What is Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0?
History of Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is a public access Wi-Fi specification by the Wi-Fi Alliance in collaboration with the Wireless Broadband Alliance. It first came out in 2011 with Hotspot 2.0 capable devices certified in 2012.
This Wi-Fi authentication technology is based on the IEEE 802.11u standard, tailored for interworking with external networks. IEEE 802.11u is a set of protocols designed to facilitate cellular-like roaming among Wi-Fi networks.
IEEE 802.11u protocols also support improved network discovery and selection, QoS map distribution, enhanced data link rates, and service on demand for Wi-Fi networks.
Following the advent of smartphones, tablets, and other wireless devices, data consumption has increased significantly.
Close to one billion Wi-Fi compatible devices hit the market every year, resulting in increased demand for internet connectivity. This increase means more strain on wireless and cellular networks.
It also causes safety concerns and inconsistent service quality since communication providers cannot meet the growing demand and guarantee the security of wireless networks.
The primary goal of Hotspot 2.0 is to address these challenges. Hotspot 2.0 reduces the burden on cellular networks by allowing roaming between Wi-Fi networks, and Wi-Fi and mobile networks.
Hotspot 2.0 also helps service providers to improve their systems’ capacity and band together with Wi-Fi providers for better service delivery.
How Does a Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 Work?
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 works similarly to a cellular network by facilitating roaming services. It allows Wi-Fi users or devices to wirelessly connect to a Hotspot 2.0 whenever they are within range.
When traversing the globe with your mobile phone, you can activate or purchase a roaming subscription to allow your phone to connect to any cellular network while abroad. Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 works in a similar fashion.
The only difference is that it allows your wireless device to switch between different Wi-Fi networks when within range. It also lets you move from mobile data offered by your cellular network to a Wi-Fi 2.0 network.
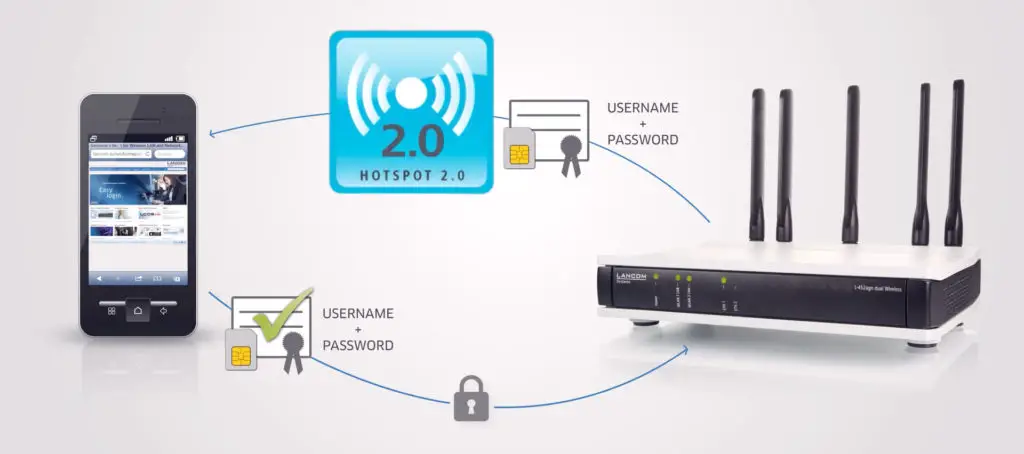
The entire process is automatic and seamless. Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 technology facilitates network discovery, selection, and registration, allowing your device to automatically connect to the available wireless network without requiring additional authentication.
You do not have to enter your password or login credential again. Instead, Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 uses 802.11u protocols to transfer your pre-connection details to all available devices within range, eliminating the need to enter your authentication info again.
Nevertheless, connecting to Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 networks is not as smooth and seamless as it seems.
First, you must have a device that supports the IEEE 802.11u standard to allow for interworking with external networks. Moreover, you must be within a Hotspot 2.0 area to establish a connection.
The Wi-Fi profile applied on the wireless access point must have Hotspot 2.0 enabled. The network providers must configure the corresponding settings to allow the access point to advertise available hotspots and enable 802.11u-certified devices to discover and select the ideal Wi-Fi network.
Passpoint or Hotspot 2.0 compliant devices can search and discover Hotspot 2.0 operator networks within an area and automatically connect to the best network for which they have valid user credentials.
Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 Features
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 facilitates cellular-like roaming for Wi-Fi networks, requiring minimal or no manual intervention as far as authentication is concerned.
This Wi-Fi 802.11u standard is an enhancement of the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard and it comes with various improved interworking features, including:
- Network Discovery and Selection
The Wi-Fi 802.11u standard facilitates automatic network discovery and selection. This Hotspot 2.0 feature uses a generic advertisement service to allow communication between your Passpoint-compliant devices and an external network without associating an access point. With this feature, your phone or tablet will detect, discover, and select the appropriate network to connect to.
- Inter-Carrier Wi-Fi Roaming
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 supports inter-operator roaming, enabling new value streams and allowing for the expansion of the existing subscriber base. ISPs, mobile carriers, and hotspot providers can now work together to provide seamless Wi-Fi connectivity for new devices using SIM and non-SIM credentials for authentication. With inter-carrier Wi-Fi roaming, operators can determine if users are on mobile or Wi-Fi.
- Layer 2 Inspection and Filtering
Even though Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is highly secure, it is not immune from security breaches. To mitigate the possibility of hacking, Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 uses Layer 2 inspection and filtering to protect mobile devices against hacking or cybersecurity attacks. This feature prevents data frames between devices from being delivered by the wireless network without going through inspection and filtering.
- P2P Cross Connection
Another significant feature associated with the 802.11u standard is P2P Cross Connection. Point-to-Point cross-connection allows devices to communicate directly without going through an access point for faster packet transmission.
What Devices Support Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0?
Very few devices currently support Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0. Fortunately, plans are underway to produce more Passpoint-compliant gadgets.
Examples of Passpoint-compliant devices include:
- Windows 10 devices
- MacOS 10.9 devices
- Some Samsung Galaxy devices running on Android 11 and above
- Apple mobile devices on iOS 7
- Windows 8 and 8.1
How to Set Up Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0?
Configuring Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is a straightforward process but your device must support this functionality to set it up appropriately.
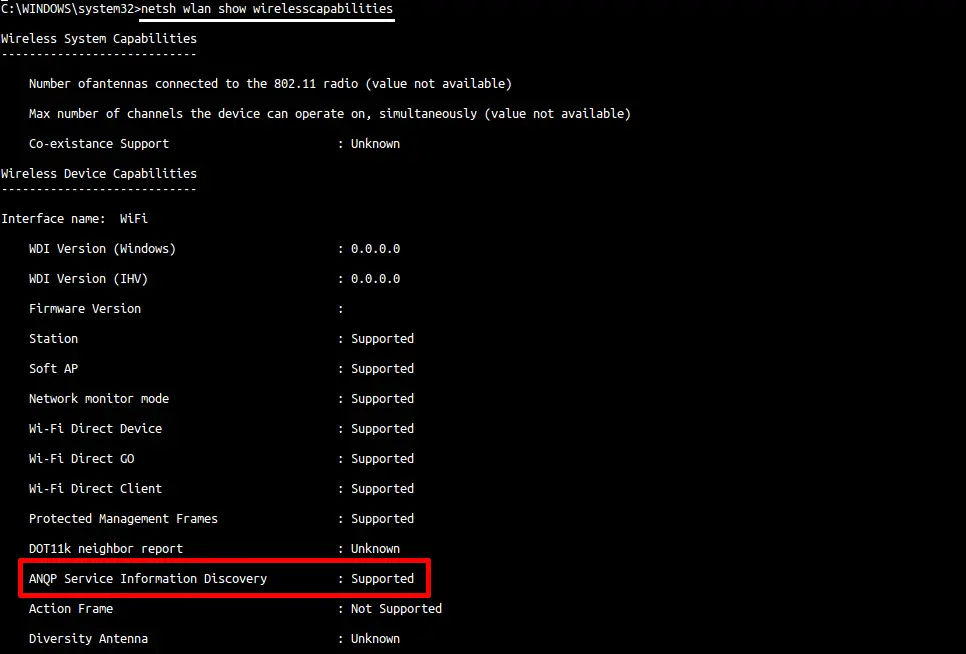
Follow these steps to know if your device (Windows 10 PC) supports Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0:
- Click Start
- Search Command Prompt
- Select Run as Administrator
- Type: netsh wlan show wirelesscapabilities
- Press the Enter key
- If the results show ANQP Service Information Discovery, your device supports Hotspot 2.0
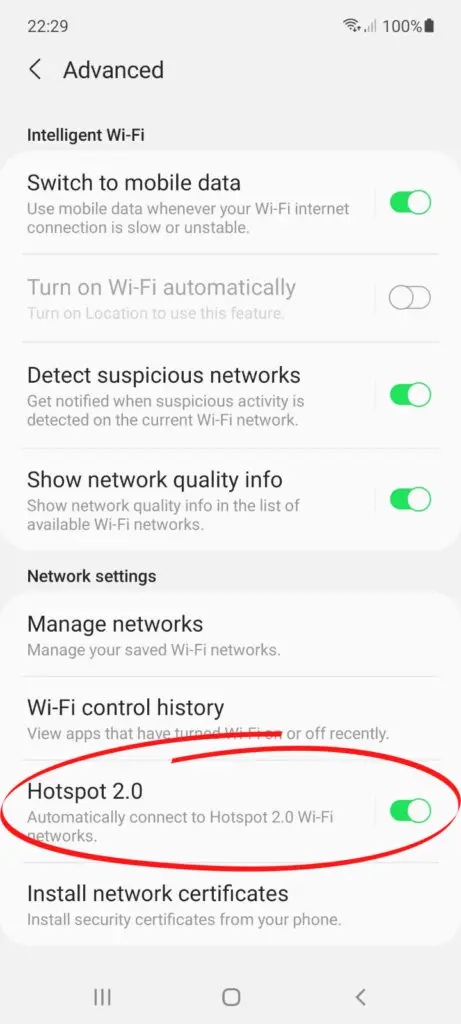
To check if your phone supports Hotspot 2.0, simply:
- Activate Wi-Fi on your device
- Go to Wi-Fi settings
- Tap Advanced or More, depending on your device model
- You should see the Passpoint or Hotspot 2.0 option, if not, your device does not support Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0
If your device supports Hotspot 2.0, you must set it up before connecting to the network. Here are the steps:
- Right-click the start menu
- Click Settings
- Click Network & Internet
- Click Wi-Fi on the left panel
- Under Hotspot 2.0 networks, enable “Let me use Online Sign-Up to get connected.”
How to Enable Hotspot 2.0 in Windows 10
To configure Hotspot 2.0 on your phone or tablet, simply:
- Turn on Wi-Fi on your smartphone or tablet
- Go to Wi-Fi settings
- Tap Advanced or More, depending on your device model
- Select the Hotspot 2.0 or Passpoint check box
How to Enable Hotspot 2.0 on a Samsung Phone
How to Connect to a Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0?
Connecting to a Hotspot 2.0 network is not different from other Wi-Fi hotspots. The process is equally fast and straightforward.
The only difference from other Wi-Fi networks is that connecting to Hotspot 2.0 is a one-time sign-in process.
Your device will save your login credentials and automatically connect to other Hotspot 2.0 networks by transferring these details to them whenever you are within range.
To connect to Hotspot 2.0 on your PC:
- Right-click the Wi-Fi icon to view the list of available networks
- Click your preferred network from the list
- Select Connect
- Enter your credentials
To connect to Hotspot 2.0 on your smartphone:
- Go to Settings
- Tap Network & Internet
- Turn on Wi-Fi to see available Wi-Fi networks
- Tap on a Hotspot 2.0 network to connect
- Enter your login details
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 Pros
- Cellular-Style Roaming
Previously, roaming services were only available on cellular networks. With the emergence of Hotspot 2.0, users can now roam between different Wi-Fi networks seamlessly. Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 also allows people to switch between cellular and Wi-Fi networks, reducing the strain on the former.
- Enhanced Security
Hotspot 2.0 provides high-level security for all connected devices via Layer 2 inspection and filtering. This feature prevents data frames between devices from being delivered by the wireless network without going through inspection and filtering.
Moreover, encryption is mandatory on all Hotspot 2.0 networks, meaning your data is safe from hackers. Your device can also tell which is the real Wi-Fi network when visiting public spaces such as malls, libraries, and cafes.
- Fast Internet Connections
Hotspot 2.0 networks do not require multiple authentications, making it easy to connect compatible devices. Since connecting to a Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is a one-time process, you can enjoy instant internet access whenever you’re within range.
- Reduced Support Costs
Reduced churn and improved customer contentment often lead to decreased support costs. Service providers no longer have to spend money visiting their clients’ premises since their services meet customers’ expectations.
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 Cons
- Not Readily Available
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 is not available everywhere and not many devices support this Wi-Fi standard.
Conclusion
Network providers and carriers have continued to research and produce interoperable solutions to help automate hotspot authentication and make Wi-Fi technology as easy to use and secure as ordinary cellular networks.
The primary goal of these efforts is to offload data traffic and reduce the strain on cellular networks. Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 has come at the right time as it allows roaming between Wi-Fi networks. It also allows you to switch from cellular to Wi-Fi networks, reducing the burden on the former.
Wi-Fi Hotspot 2.0 has become an enabler and an equalizer. It makes roaming possible within Wi-Fi networks and it allows cellular operators to expand their roaming footprint and improve their systems’ capacity.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.

