Do you want to find out what kind of address is this and what can you do with it? This article will give you all the necessary info. You will learn how to find your default IP, what devices use 192.168.1.3 as a default IP, how to use this address if it’s your default IP, and how to use it as a host IP address. Let’s start with the basics.
CONTENTS
192.168.1.3 – What Kind of Address is This?
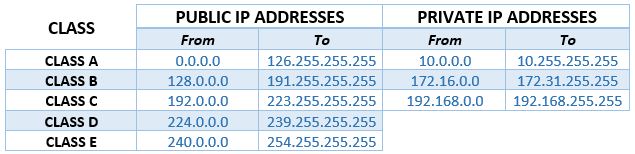
192.168.1.3 is an IPv4 IP address. IPv4 is a protocol (a set of rules) that defines the form of the address and the way the addresses are assigned. There are almost 4.3 billion IPv4 addresses like this one. They all have the same form – 4 numeric values ranging from 0 to 255 separated by dots. IPv4 addresses are divided into five classes (A-E). Each class is used for a different kind of network – class A for huge networks, class B for large corporate networks, class C for small businesses, Class D for streaming services, and class E for research. 192.168.1.3 belongs to class C.
IPv4 addresses are also divided into two groups – public and private. Public addresses are routable over the internet, while private ones are not. 192.168.1.3 is a private IP address. In fact, all the addresses that start with 192.168 are private, just like all the addresses that start with 10 (10.x.x.x addresses).
The fact that it’s private means that it can only be used on small local area networks. It is not used for internet access. At least not directly. You’re probably wondering – what does that mean? Here’s an explanation.
The device you’re using to read this article and visit other websites may have 192.168.1.3 assigned to it. That’s your device’s IP address. But your device uses that address just to communicate with your router (and other devices connected to the same router), and then the router does the rest of the job for you. Your router has a private address (default IP) and uses it to communicate with the devices on your LAN, but it also has a public IP (assigned by your ISP) and uses it to access the internet. To be more specific, your router receives the requests from all the devices connected to it and forwards them to a DNS server. DNS server finds the website you were looking for (it finds a public IP address of a website that you want to visit) and sends it to your router. Your router receives the feedback from a DNS (via its public IP) and forwards it to your device (via private IP).
Because you can only use private addresses on LANs, one private address (like 192.168.1.3) can be used on any (or every) LAN. However, you can’t have two devices on the same LAN using the same address (because of communication issues).
Can 192.168.1.3 Be a Default IP Address? What Devices Use It as a Default IP?
Yes, it can, but that’s rarely the case. A default IP address is the address assigned to your router (access point, range extender, or some other device). This address is preassigned to a networking device by the manufacturer.
The manufacturers can choose just any private address. So, 192.168.1.3 is a viable choice, just like any other private address. However, some addresses happen to be more popular than others. Most manufacturers prefer using the first available address (or the last available address) in a subnet. That’s why 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.1.1 are, by far, the most popular choices. Other popular default IPs are 192.168.2.1, 192.168.10.1, 10.0.1.1, 10.0.0.1, 192.168.1.254, 192.168.254.254, 192.168.3.1, etc.
There are just a few devices using 192.168.1.3 as a default IP. One of the devices with this IP is the Zyxel PLA5236 access point. The same address is also used by some range extenders.
Is 192.168.1.3 My Default IP Address?
Having in mind what we’ve just said, this address is probably not your device’s default IP, but there’s an easy way to find your default IP and be sure. The easiest way is to check the label on the bottom of your device. All the important info about your device (including default IP, MAC address, the default username and password) is listed on this label. It’s not a problem if the label is damaged or if there’s no label. You can try finding the manual – all the info and instructions on how to use the default IP address are in the manual, too. Can’t find the manual? Don’t worry – you can easily find your default IP in just a few steps on your Windows/macOS/Linux/iOS/Android device.
Windows users can find it by using the ipconfig command in the Command Prompt or in the Network and Sharing Center.
macOS users and Linux users can find it through the Terminal. The commands you can use on macOS are netstat -nr or route get default. The commands you can use on Linux are netstat -rn, route -n, and ip route show.
Android and iOS users can find the default IP through the wi-fi settings. It’s easier if you’re using an iOS device – you just have to tap the ”info” icon standing next to the network you’re connected to and scroll down until you find router IP. Android users will have to open advanced options, change the IP settings to static, and look for the gateway address.
How to Use 192.168.1.3 if it’s My Device’s Default IP?
Every default IP address is used in the same way. You type it in your browser (your address bar, not search bar), and you’ll be redirected to the login page of your networking device (router, access point, range extender, etc.).
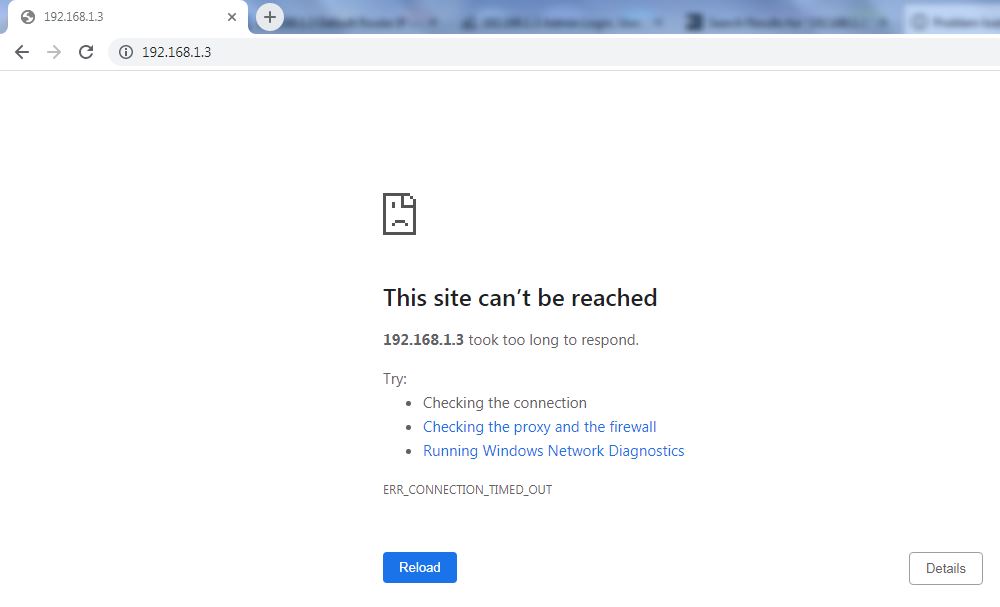
If you enter the address from the title and get a message like in the picture below, then 192.168.1.3 is probably not your default gateway (default IP address).
If 192.168.1.3 is, in fact, your default IP (like in the case of Zyxel PLA5236), you will see a login page like in the picture below.

Zyxel PLA5236 login page
Once the login page opens, you will have to enter the right username and password (or, in this case, just password). When you press Enter, the Configuration page will open. You will first see the status screen.
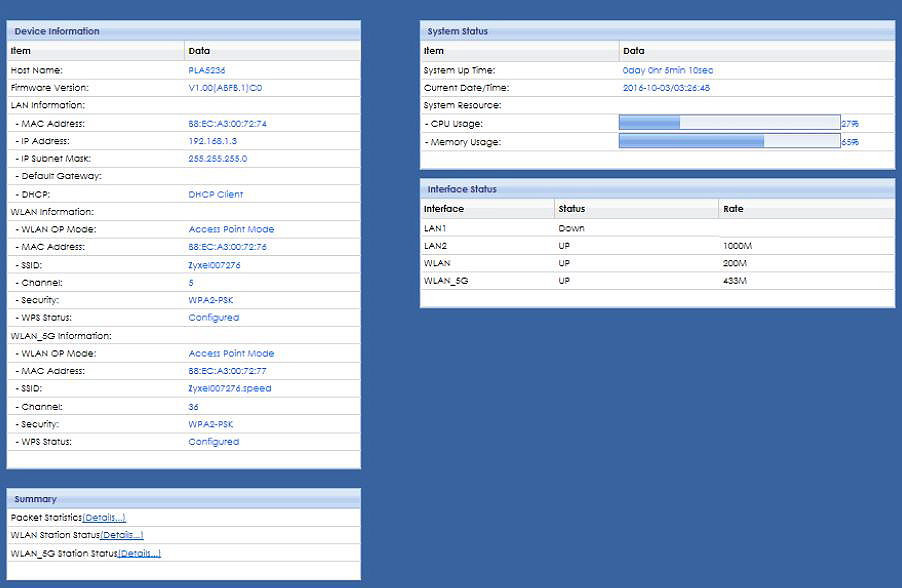
Zyxel PLA5236 status screen
On the left side of the Configuration page, there are a couple of tabs (Monitor, Configuration, Maintenance). Depending on the settings you want to change, you will choose the appropriate tab. Most people will just change the wi-fi network name and protect the network with a password (WPA2-PSK recommended). To do that, you will select the Configuration tab, and go to the first sub-tab (General). To change the network name, enter the desired name in the text box next to SSID. At the bottom of the page, enter the desired password. Finally, click Apply and log out.
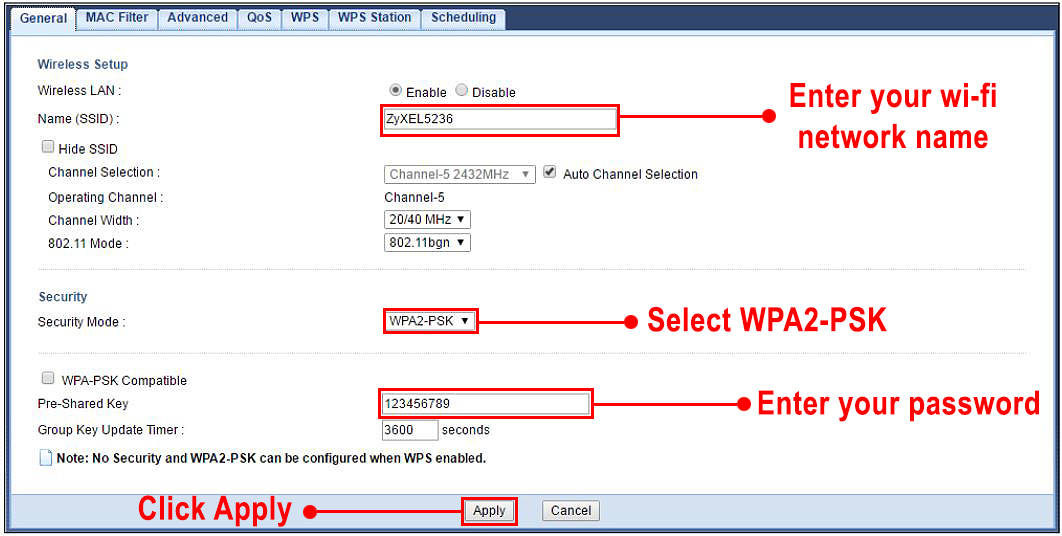
Zyxel PLA5236 – changing SSID and password
Can 192.168.1.3 Be a Host IP?
Yes, it can. In fact, 192.168.1.3 is much more often used as a host/client IP than a default IP. If you remember, 192.168.1.1 is one of the most common default IP addresses and is used by many reputable manufacturers including Actiontec, Linksys, Asus, Belkin, Cisco, D-Link, Huawei, NetComm, Siemens, Synology, TP-Link, Ubiquiti, U.S. Robotics, Zyxel, ZTE, etc.
Routers that use 192.168.1.1 as a default gateway, usually have a DHCP pool that includes all the addresses from the same subnet excluding the network address (192.168.1.0), the default IP address (192.168.1.1), and the broadcast address (192.168.1.255). So, if the router’s default IP is 192.168.1.1, the DHCP pool will span from 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254. One of the addresses in the DHCP pool is the address from the title. If it gets assigned to one of the devices connected to your router, it will become a host/client IP address.
192.168.1.3 as a Dynamic Host IP
The addresses from the DHCP pool will be assigned to every device that connects to the router (the router assigns those addresses automatically). The second available address in the DHCP pool from our example is the address from the title (192.168.1.3). The first device that connects to your wi-fi network will get 192.168.1.2, and the second will get 192.168.1.3. If the address is assigned automatically (not manually), it is considered dynamic.
What makes it dynamic is the fact that it doesn’t stay with one device forever. The address is being leased to a device for a certain period (you can adjust the duration of the lease period). When the lease period expires, the router will try to communicate with your device and check if it’s still online. If it is still connected to your network, your router will renew the lease, and your device will get the same IP address. If it’s not connected, the address will return to the DHCP pool and will be assigned to the next connected device (it can be any device, including the device that previously had this address). If some other device gets 192.168.1.3, when you connect the device that previously used this IP address, it will get the next available address.
192.168.1.3 as a Static Host IP
Like any other private address, 192.168.1.3 can also be a static IP. But, to make it static, you have to assign it manually to your device. When the address is static, it will always be assigned to the same device (until you make it dynamic again) – it won’t be assigned to some other device even if your device is not connected to the network.
The process of turning any private address from the DHCP pool into static is quite straightforward. You can do that in your device’s settings, but it’s safer if you make a DHCP reservation through your router’s configuration page. We’ll show you how to make a DHCP reservation using Linksys EA 8100. The process is very similar for every router – you’ll just have to use a different default IP and different login credentials.
STEP 1 – Enter the default IP in your browser (in this case – 192.168.1.1). Then, enter the right username and password to log in.
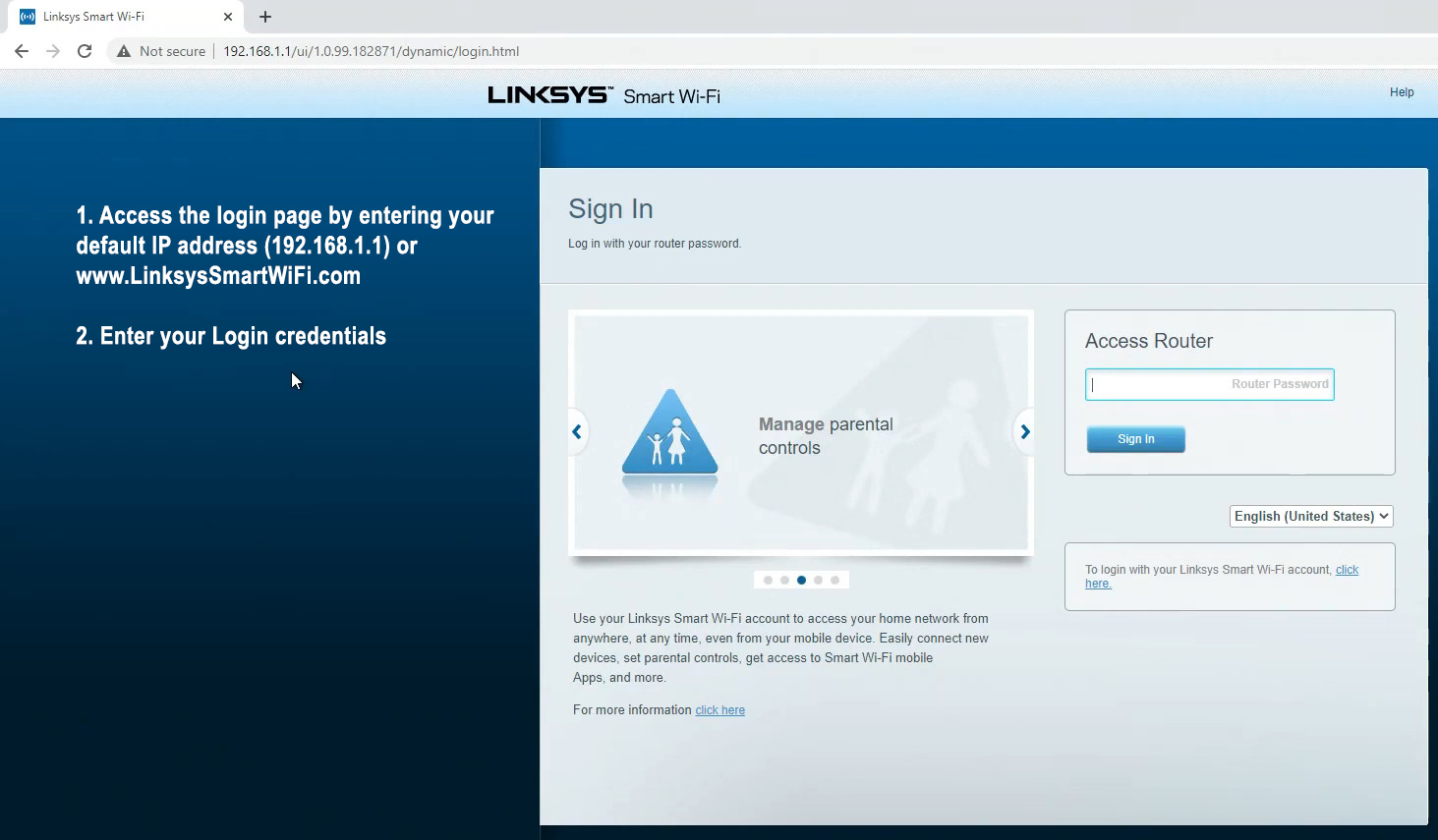
STEP 2 – When the status page appears, go to Router settings > Connectivity.
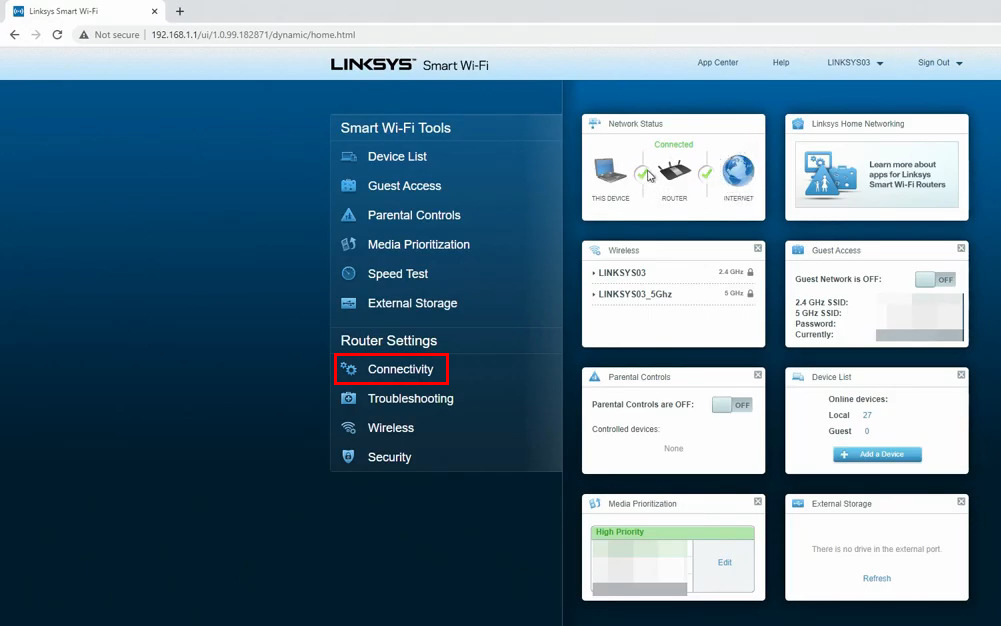
STEP 3 – Select Local Network, and then click on DHCP reservation
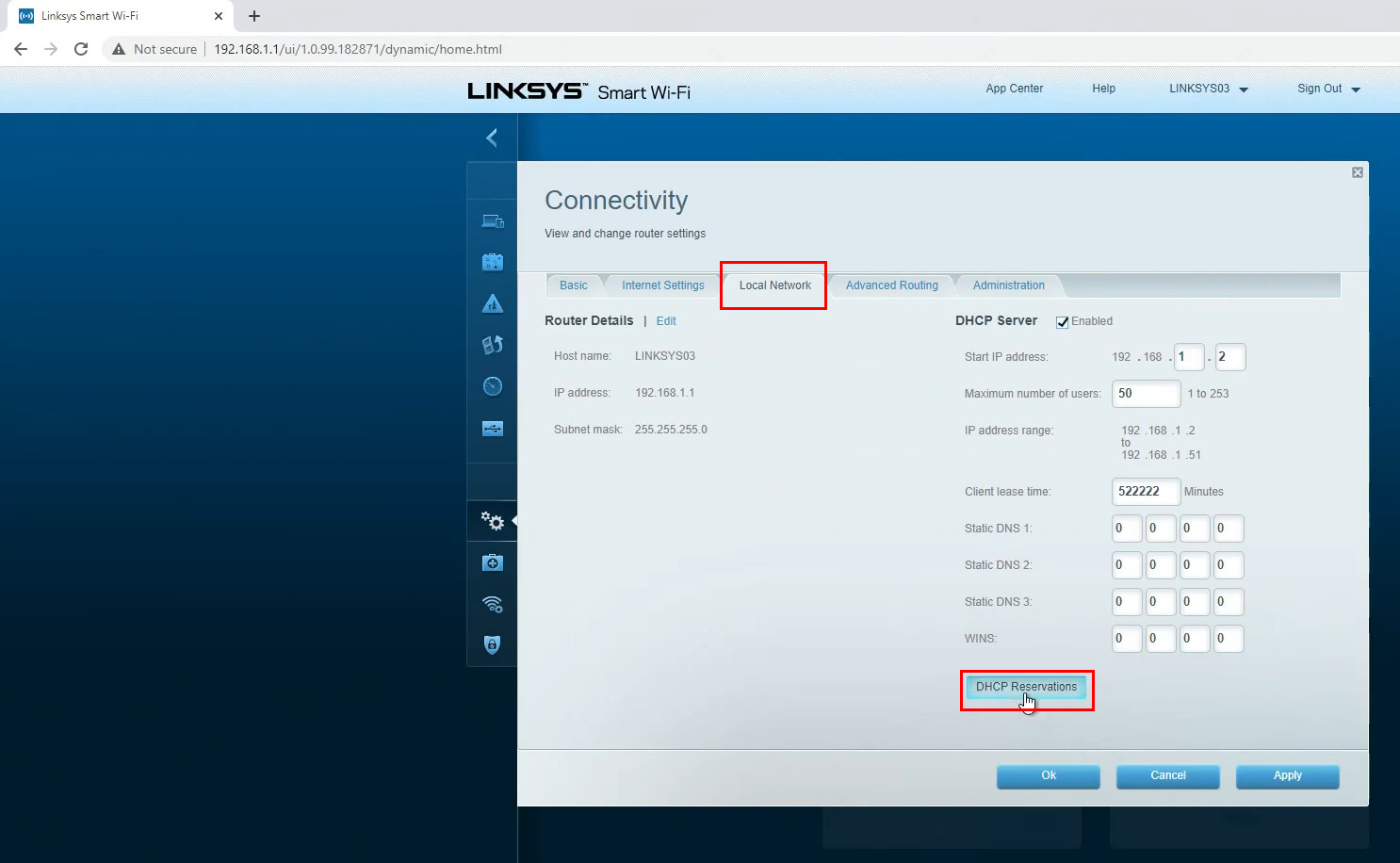
STEP 4 – When the DHCP Reservations window opens, you will see a list of connected devices with their IP addresses and MAC addresses. You can tick the box next to the device you want to assign a static IP to and then click on ”Add DHCP Reservation”.

STEP 5 – If you want to assign a different IP address from the one that is currently in use, you can manually enter the device’s name, its MAC address, and the IP address that you want to use. You can do the same thing if the device is not listed.
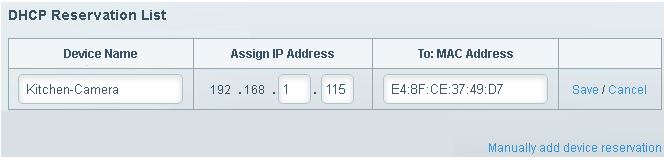
Adding a DHCP reservation manually
STEP 6 – Save changes by clicking OK
Troubleshooting Router Issues
Regardless of your router’s default IP, there are some common issues you may experience when using networking equipment.
Login Issues
If you can’t open the Login page, then you’re probably using the wrong default IP. Read our guide and learn how to find your default IP.
If you can open the Login page but can’t log in, then you’re using the wrong credentials. If you’ve changed the username and/or password and can’t remember them now, the only option is to reset your router to factory settings. Every router has a reset button (or pinhole). You have to press it and hold it until all the LEDs light up. After you reset the router, you can use the default username and password to log in.
IP Conflicts
One private IP address mustn’t be assigned to two devices on the same LAN. If that happens (for any reason), you will experience an IP conflict. When an IP conflict happens, both devices using the same address will have connection issues – they won’t be able to communicate with other devices and won’t be able to go online.
IP conflict could happen if you assign an IP address that is still in use by some other device to your device as a static IP.
To resolve an IP conflict, you will have to disconnect both devices and wait for the lease time to expire. The quicker option is to try to release the IP address manually on one of the devices. Or, you can try to make a change in the DHCP pool and assign a different static IP to your device.

Hey, I’m Jeremy Clifford. I hold a bachelor’s degree in information systems, and I’m a certified network specialist. I worked for several internet providers in LA, San Francisco, Sacramento, and Seattle over the past 21 years.
I worked as a customer service operator, field technician, network engineer, and network specialist. During my career in networking, I’ve come across numerous modems, gateways, routers, and other networking hardware. I’ve installed network equipment, fixed it, designed and administrated networks, etc.
Networking is my passion, and I’m eager to share everything I know with you. On this website, you can read my modem and router reviews, as well as various how-to guides designed to help you solve your network problems. I want to liberate you from the fear that most users feel when they have to deal with modem and router settings.
My favorite free-time activities are gaming, movie-watching, and cooking. I also enjoy fishing, although I’m not good at it. What I’m good at is annoying David when we are fishing together. Apparently, you’re not supposed to talk or laugh while fishing – it scares the fishes.
